Sustainable investing focuses on incorporating environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors into investment decisions to generate long-term financial returns alongside positive societal impact. Ethical banking prioritizes transparency, social responsibility, and avoiding investments in industries that harm human rights or the environment. Explore the distinctions between these approaches to understand how your financial choices can contribute to a better future.
Why it is important
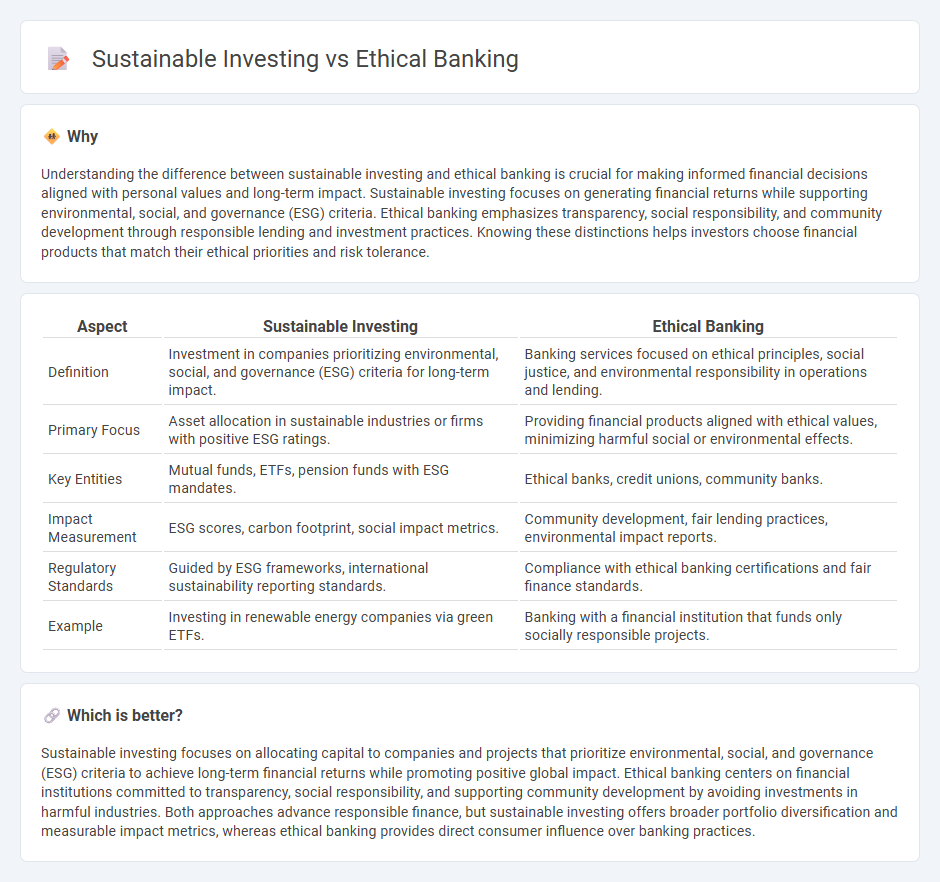
Understanding the difference between sustainable investing and ethical banking is crucial for making informed financial decisions aligned with personal values and long-term impact. Sustainable investing focuses on generating financial returns while supporting environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria. Ethical banking emphasizes transparency, social responsibility, and community development through responsible lending and investment practices. Knowing these distinctions helps investors choose financial products that match their ethical priorities and risk tolerance.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Sustainable Investing | Ethical Banking |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Investment in companies prioritizing environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria for long-term impact. | Banking services focused on ethical principles, social justice, and environmental responsibility in operations and lending. |
| Primary Focus | Asset allocation in sustainable industries or firms with positive ESG ratings. | Providing financial products aligned with ethical values, minimizing harmful social or environmental effects. |
| Key Entities | Mutual funds, ETFs, pension funds with ESG mandates. | Ethical banks, credit unions, community banks. |
| Impact Measurement | ESG scores, carbon footprint, social impact metrics. | Community development, fair lending practices, environmental impact reports. |
| Regulatory Standards | Guided by ESG frameworks, international sustainability reporting standards. | Compliance with ethical banking certifications and fair finance standards. |
| Example | Investing in renewable energy companies via green ETFs. | Banking with a financial institution that funds only socially responsible projects. |
Which is better?
Sustainable investing focuses on allocating capital to companies and projects that prioritize environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria to achieve long-term financial returns while promoting positive global impact. Ethical banking centers on financial institutions committed to transparency, social responsibility, and supporting community development by avoiding investments in harmful industries. Both approaches advance responsible finance, but sustainable investing offers broader portfolio diversification and measurable impact metrics, whereas ethical banking provides direct consumer influence over banking practices.
Connection
Sustainable investing in banking focuses on allocating capital to projects and enterprises that prioritize environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria, directly supporting ethical banking principles that emphasize transparency, social responsibility, and long-term value creation. Ethical banking institutions often integrate sustainable investing strategies into their portfolios to reduce negative environmental impact and promote positive societal outcomes, aligning financial returns with global sustainability goals. This synergy enhances risk management, attracts socially conscious investors, and fosters trust among stakeholders by demonstrating commitment to both fiscal responsibility and ethical standards.
Key Terms
Social Responsibility
Ethical banking prioritizes social responsibility by integrating values such as community welfare, transparency, and fair labor practices into its financial services. Sustainable investing focuses on directing capital towards companies with strong environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria to promote long-term societal impact. Explore further to understand how these approaches drive positive change in financial decision-making.
Environmental Impact
Ethical banking prioritizes responsible financial practices by supporting green projects and reducing carbon footprints within their operations, while sustainable investing allocates capital to companies with strong environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria to promote long-term ecological balance. Environmental impact in ethical banking is often measured through reduced fossil fuel financing and increased renewable energy investments, whereas sustainable investing emphasizes shareholder engagement and ESG scoring to drive corporate environmental responsibility. Explore how these approaches contribute uniquely to environmental preservation and financial growth.
Transparency
Ethical banking emphasizes transparency by openly disclosing investment practices and ensuring clients' funds support socially responsible projects aligned with clear ethical standards. Sustainable investing prioritizes transparency through detailed reporting on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) metrics, enabling investors to assess real impact and risk effectively. Explore comprehensive insights on transparency differences in ethical banking and sustainable investing to make informed financial decisions.
Source and External Links
Ethical Banking - Ethical banks avoid funding harmful industries like fossil fuels and weapons, instead directing money toward businesses and projects with positive social and environmental impacts.
Ethical UK Banks & Current Accounts - Choosing an ethical bank means depositing money where it won't be invested in sectors like fossil fuels, weapons, or gambling, and will instead support positive initiatives such as renewable energy projects.
Ethical banks in the UK: List of 10 providers (2025) - Ethical banks in the UK, such as Triodos and Charity Bank, focus on transparent, positive social and environmental outcomes, including publishing all their investments and lending exclusively to charities and sustainable projects.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com