Sustainable investing integrates environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors into financial decisions to generate long-term value and positive societal impact. The triple bottom line framework evaluates performance based on three dimensions: profit, people, and planet, ensuring businesses measure their social and environmental contributions alongside financial returns. Discover how these approaches redefine the future of banking and responsible finance.
Why it is important
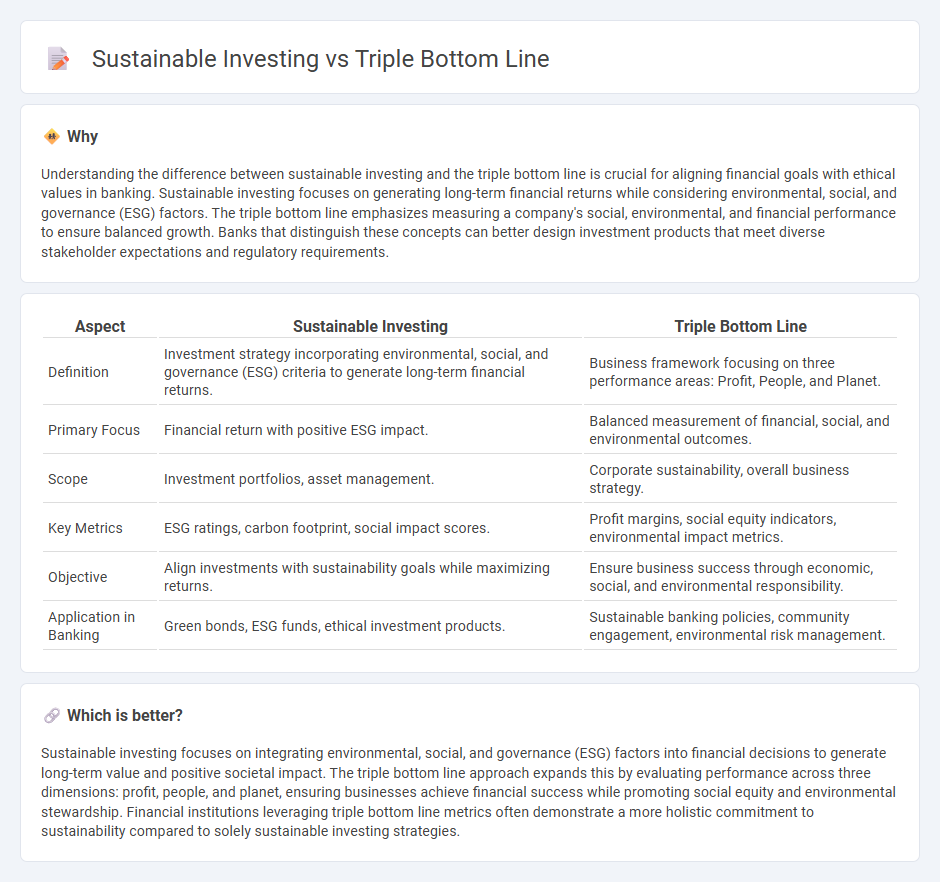
Understanding the difference between sustainable investing and the triple bottom line is crucial for aligning financial goals with ethical values in banking. Sustainable investing focuses on generating long-term financial returns while considering environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors. The triple bottom line emphasizes measuring a company's social, environmental, and financial performance to ensure balanced growth. Banks that distinguish these concepts can better design investment products that meet diverse stakeholder expectations and regulatory requirements.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Sustainable Investing | Triple Bottom Line |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Investment strategy incorporating environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria to generate long-term financial returns. | Business framework focusing on three performance areas: Profit, People, and Planet. |
| Primary Focus | Financial return with positive ESG impact. | Balanced measurement of financial, social, and environmental outcomes. |
| Scope | Investment portfolios, asset management. | Corporate sustainability, overall business strategy. |
| Key Metrics | ESG ratings, carbon footprint, social impact scores. | Profit margins, social equity indicators, environmental impact metrics. |
| Objective | Align investments with sustainability goals while maximizing returns. | Ensure business success through economic, social, and environmental responsibility. |
| Application in Banking | Green bonds, ESG funds, ethical investment products. | Sustainable banking policies, community engagement, environmental risk management. |
Which is better?
Sustainable investing focuses on integrating environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors into financial decisions to generate long-term value and positive societal impact. The triple bottom line approach expands this by evaluating performance across three dimensions: profit, people, and planet, ensuring businesses achieve financial success while promoting social equity and environmental stewardship. Financial institutions leveraging triple bottom line metrics often demonstrate a more holistic commitment to sustainability compared to solely sustainable investing strategies.
Connection
Sustainable investing integrates environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria to generate long-term financial returns while promoting positive societal impact, directly aligning with the triple bottom line framework that balances profit, people, and planet. Banks adopting sustainable investment strategies support renewable energy projects, social equity initiatives, and responsible governance, thereby advancing economic performance alongside environmental stewardship and social responsibility. This alignment fosters resilient financial systems that create value beyond monetary gains, enhancing investor trust and contributing to global sustainability goals.
Key Terms
Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG)
The triple bottom line framework evaluates corporate performance based on environmental, social, and economic factors, emphasizing sustainability in business practices. Sustainable investing integrates Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) criteria to guide investment decisions that promote responsible corporate behavior and long-term value creation. Explore deeper insights into how triple bottom line and ESG investing align to drive sustainable growth and ethical financial strategies.
People, Planet, Profit
The triple bottom line framework emphasizes balanced measurement of a company's social impact (People), environmental stewardship (Planet), and financial performance (Profit), aiming to promote long-term value beyond traditional profit metrics. Sustainable investing integrates Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) criteria into investment decisions, targeting companies that demonstrate strong triple bottom line performance to optimize risk-adjusted returns and positive societal outcomes. Explore in-depth how these approaches redefine responsible business and investment strategies for future resilience.
Impact Measurement
The triple bottom line framework evaluates corporate success based on social, environmental, and financial performance, emphasizing a holistic impact measurement beyond profit alone. Sustainable investing integrates environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria into financial analysis to drive long-term value and measurable positive impact. Explore how impact measurement tools differ between these approaches to enhance responsible decision-making.
Source and External Links
What Is the Triple Bottom Line (TBL)? - IBM - The triple bottom line is a sustainability framework that measures a company's success by its impact on three areas: profit (financial performance), people (social equity and stakeholder well-being), and planet (environmental responsibility), aiming for positive outcomes in all three dimensions.
Why You Should Pay Attention to the Triple Bottom Line - The triple bottom line expands traditional business accounting to include not just financial profit, but also social and environmental performance, encouraging companies to balance financial goals with positive impacts on people and the planet.
Triple bottom line - Wikipedia - Coined by John Elkington in 1994, the triple bottom line is an accounting framework that evaluates organizational success through social (people), environmental (planet), and economic (profit) factors, promoting sustainability and responsible business practices.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com