Regulatory sandboxes enable financial institutions to test innovative products under regulator supervision, ensuring compliance with legal frameworks while minimizing customer risk. Beta testing focuses on releasing a product to a limited user base to identify usability issues and gather feedback before full market launch. Explore the differences and benefits of regulatory sandboxes versus beta testing to optimize your banking innovation strategy.
Why it is important
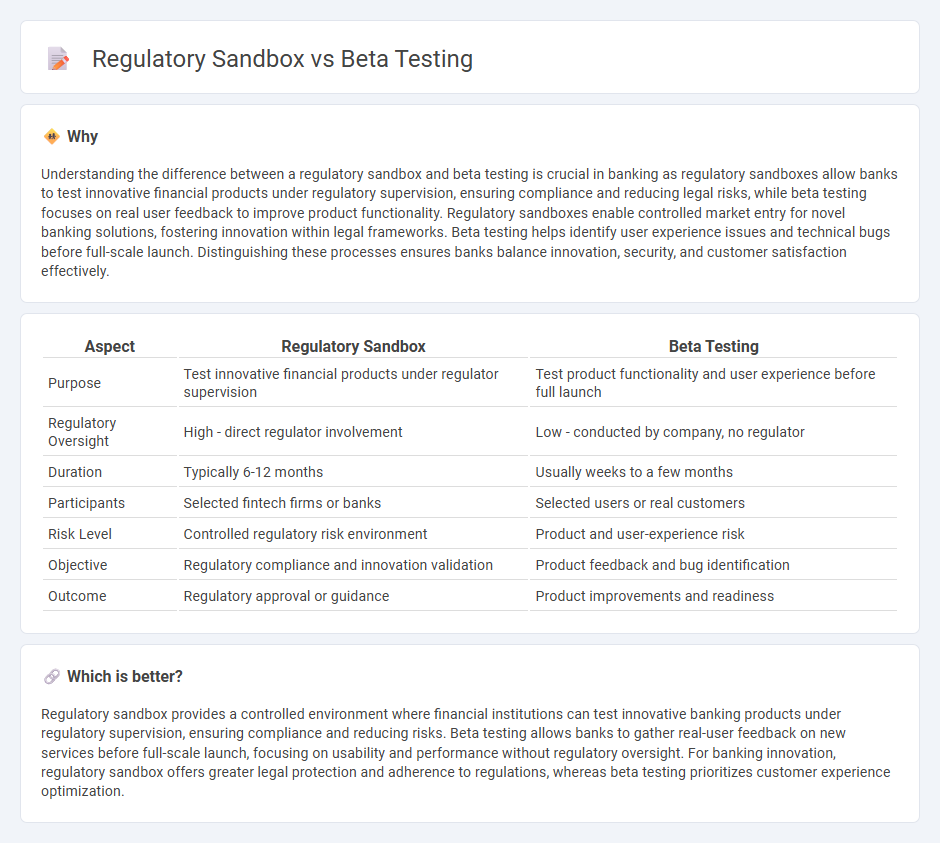
Understanding the difference between a regulatory sandbox and beta testing is crucial in banking as regulatory sandboxes allow banks to test innovative financial products under regulatory supervision, ensuring compliance and reducing legal risks, while beta testing focuses on real user feedback to improve product functionality. Regulatory sandboxes enable controlled market entry for novel banking solutions, fostering innovation within legal frameworks. Beta testing helps identify user experience issues and technical bugs before full-scale launch. Distinguishing these processes ensures banks balance innovation, security, and customer satisfaction effectively.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Regulatory Sandbox | Beta Testing |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Test innovative financial products under regulator supervision | Test product functionality and user experience before full launch |
| Regulatory Oversight | High - direct regulator involvement | Low - conducted by company, no regulator |
| Duration | Typically 6-12 months | Usually weeks to a few months |
| Participants | Selected fintech firms or banks | Selected users or real customers |
| Risk Level | Controlled regulatory risk environment | Product and user-experience risk |
| Objective | Regulatory compliance and innovation validation | Product feedback and bug identification |
| Outcome | Regulatory approval or guidance | Product improvements and readiness |
Which is better?
Regulatory sandbox provides a controlled environment where financial institutions can test innovative banking products under regulatory supervision, ensuring compliance and reducing risks. Beta testing allows banks to gather real-user feedback on new services before full-scale launch, focusing on usability and performance without regulatory oversight. For banking innovation, regulatory sandbox offers greater legal protection and adherence to regulations, whereas beta testing prioritizes customer experience optimization.
Connection
Regulatory sandboxes allow banks and fintech firms to test innovative financial products and services in a controlled environment with relaxed regulatory requirements. Beta testing within these sandboxes provides real-world user feedback and performance data, helping to identify risks and compliance issues before broader market launch. This connection accelerates innovation while ensuring adherence to regulatory standards in the banking sector.
Key Terms
User Feedback
Beta testing gathers real user feedback to identify issues and improve product functionality before official launch, maximizing user satisfaction. Regulatory sandbox allows companies to trial innovations under regulatory supervision, ensuring compliance while collecting feedback on usability and risk. Explore how combining user feedback in both can accelerate innovation in your sector.
Compliance
Beta testing involves releasing a product to a limited audience to identify bugs and gather user feedback before full launch, primarily focusing on functionality and user experience. Regulatory sandboxes allow innovative financial products to operate under regulatory oversight in a controlled environment, emphasizing compliance with legal and regulatory requirements. Explore more to understand how these approaches impact compliance strategies in product development.
Risk Management
Beta testing evaluates software performance under real-world conditions to identify bugs and usability issues before full release, minimizing technical risks. Regulatory sandbox offers a controlled environment for fintech firms to test innovative products with regulatory oversight, mitigating compliance and legal risks. Explore deeper insights on balancing innovation and risk management strategies in both frameworks.
Source and External Links
Beta Testing - Complete Guide to Validate Products | GAT - Beta testing is a critical phase where external end users test a product in real-world environments before official release to gather feedback on performance, usability, and scalability, distinguishing it from internal alpha testing done by company employees.
Beta Test: Definition, Examples, and Importance - Roadmunk - Beta testing occurs late in development with external users testing the product to identify remaining bugs and usability issues, and comes in types such as closed, open, and post-release beta testing for ongoing feedback and improvement.
What is a Beta Test? | Definition | Product Management Glossary - Beta testing allows real users to use the product in a production setting to find bugs and usability issues before wide release, and can be open or closed with the main goal of validating performance and user experience under real-world conditions.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com