Green financing focuses on funding projects that promote environmental sustainability, such as renewable energy and pollution control initiatives. Islamic financing operates under Sharia law principles, prohibiting interest and promoting risk-sharing and ethical investments. Explore more to understand how these financing models address economic and social goals differently.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between green financing and Islamic financing is crucial for aligning investments with sustainability goals or religious principles, respectively. Green financing focuses on funding environmentally friendly projects like renewable energy and carbon reduction initiatives. Islamic financing adheres to Sharia law, prohibiting interest and emphasizing ethical investments. Knowing these distinctions helps investors and banks optimize financial strategies to meet diverse regulatory, ethical, and environmental standards.
Comparison Table
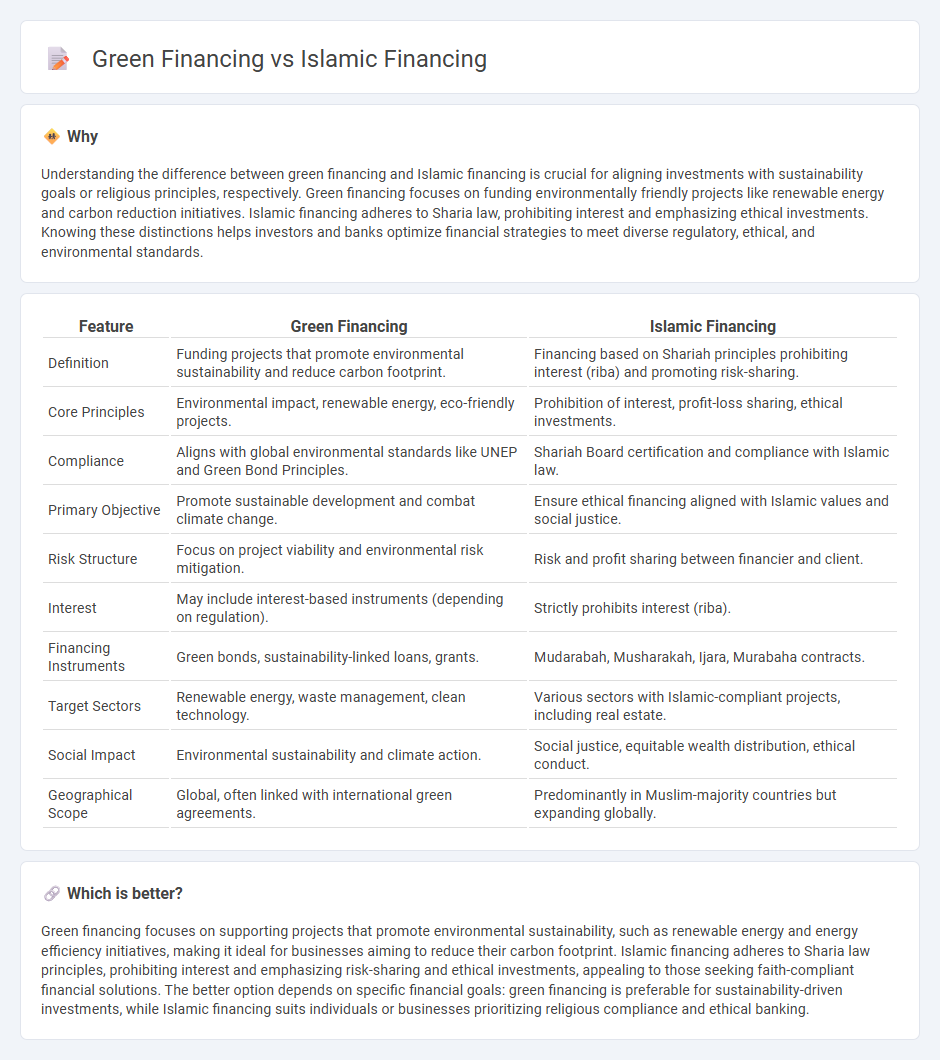
| Feature | Green Financing | Islamic Financing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Funding projects that promote environmental sustainability and reduce carbon footprint. | Financing based on Shariah principles prohibiting interest (riba) and promoting risk-sharing. |
| Core Principles | Environmental impact, renewable energy, eco-friendly projects. | Prohibition of interest, profit-loss sharing, ethical investments. |
| Compliance | Aligns with global environmental standards like UNEP and Green Bond Principles. | Shariah Board certification and compliance with Islamic law. |
| Primary Objective | Promote sustainable development and combat climate change. | Ensure ethical financing aligned with Islamic values and social justice. |
| Risk Structure | Focus on project viability and environmental risk mitigation. | Risk and profit sharing between financier and client. |
| Interest | May include interest-based instruments (depending on regulation). | Strictly prohibits interest (riba). |
| Financing Instruments | Green bonds, sustainability-linked loans, grants. | Mudarabah, Musharakah, Ijara, Murabaha contracts. |
| Target Sectors | Renewable energy, waste management, clean technology. | Various sectors with Islamic-compliant projects, including real estate. |
| Social Impact | Environmental sustainability and climate action. | Social justice, equitable wealth distribution, ethical conduct. |
| Geographical Scope | Global, often linked with international green agreements. | Predominantly in Muslim-majority countries but expanding globally. |
Which is better?
Green financing focuses on supporting projects that promote environmental sustainability, such as renewable energy and energy efficiency initiatives, making it ideal for businesses aiming to reduce their carbon footprint. Islamic financing adheres to Sharia law principles, prohibiting interest and emphasizing risk-sharing and ethical investments, appealing to those seeking faith-compliant financial solutions. The better option depends on specific financial goals: green financing is preferable for sustainability-driven investments, while Islamic financing suits individuals or businesses prioritizing religious compliance and ethical banking.
Connection
Green financing and Islamic financing intersect through their shared principles of ethical and socially responsible investment, emphasizing sustainability and avoiding harm to society or the environment. Both frameworks prioritize projects that support renewable energy, environmental conservation, and social welfare, aligning with Islamic finance's prohibition of investments in harmful industries and the promotion of equitable economic development. This synergy enhances funding avenues for sustainable development projects within compliance-based financial models.
Key Terms
Shariah-compliance
Islamic financing adheres strictly to Shariah principles, prohibiting interest (riba) and emphasizing profit-and-loss sharing, ethical investments, and asset-backed financing, ensuring financial activities align with Islamic law. Green financing prioritizes funding projects that promote environmental sustainability, such as renewable energy, waste reduction, and climate resilience, with increasing interest in Shariah-compliant green bonds and sukuk to integrate both ethical and ecological values. Explore how the convergence of Shariah compliance and green financing is shaping sustainable investment opportunities worldwide.
Environmental sustainability
Islamic financing promotes environmental sustainability through principles like the prohibition of harmful activities, ethical investing, and profit-and-loss sharing, which encourage responsible resource use and social justice. Green financing directly targets environmental goals by funding renewable energy projects, pollution control, and conservation efforts to mitigate climate change. Explore more to understand how both financing models drive sustainable development and environmental stewardship.
Profit-and-loss sharing
Islamic financing emphasizes profit-and-loss sharing (PLS) as a core principle, aligning investor and entrepreneur interests through equity-based contracts like Mudarabah and Musharakah, which promote risk-sharing and ethical investment. Green financing, while primarily targeting environmentally sustainable projects, may incorporate PLS models to enhance financial transparency and encourage responsible risk allocation in green ventures. Explore detailed comparisons and practical applications of PLS in both Islamic and green financing to understand their unique benefits and synergies.
Source and External Links
Principles and Types of Islamic Finance - Islamic finance is financing that complies strictly with Sharia law, prohibiting interest (riba) and investments in haram activities like alcohol or pork, with a global sector managing over $2 trillion and growing 15%-25% annually.
Islamic banking and finance - Wikipedia - Islamic finance prohibits earning money from money alone and demands risk sharing based on tangible assets, with Sharia boards supervising compliance, and varying interpretations across countries regarding financial transactions and risk return.
What Is An Islamic Mortgage? How Does It Work? | Guidance - Islamic financing, including home mortgages, avoids interest and is structured on profit-and-loss sharing or co-ownership models such as Musharakah, offering an ethical alternative suitable for both Muslims and non-Muslims.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com