Digital identity verification in banking ensures secure customer authentication using biometrics, document scanning, and AI-driven checks, enhancing fraud prevention and regulatory compliance. Mobile SIM-based verification relies on validating a customer's phone number through their SIM card, offering convenience but limited security compared to multifactor digital methods. Explore more about how these verification techniques impact banking security and customer experience.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between digital identity verification and mobile SIM-based verification is crucial in banking to ensure secure and compliant customer authentication. Digital identity verification uses biometric data, government-issued IDs, and AI-driven checks, offering higher accuracy and fraud prevention. Mobile SIM-based verification relies on phone number validation, which can be vulnerable to SIM swapping and port-out scams. Banks leveraging robust digital identity methods reduce fraud risk, enhance regulatory compliance, and improve customer trust.
Comparison Table
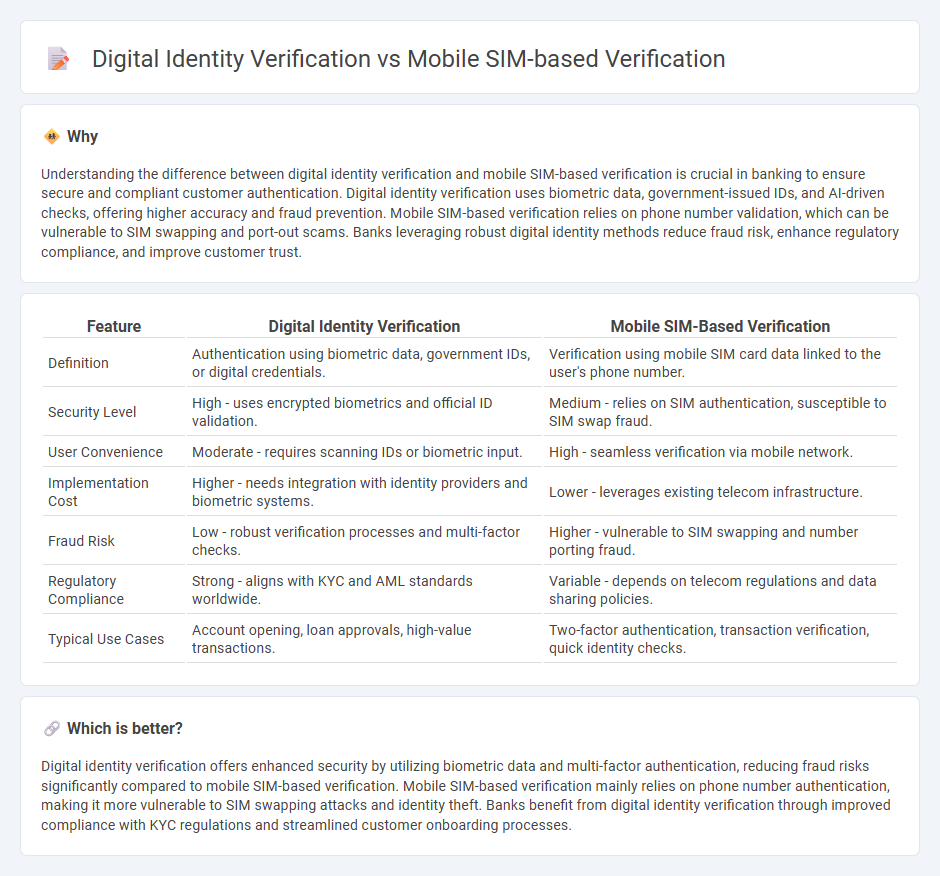
| Feature | Digital Identity Verification | Mobile SIM-Based Verification |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Authentication using biometric data, government IDs, or digital credentials. | Verification using mobile SIM card data linked to the user's phone number. |
| Security Level | High - uses encrypted biometrics and official ID validation. | Medium - relies on SIM authentication, susceptible to SIM swap fraud. |
| User Convenience | Moderate - requires scanning IDs or biometric input. | High - seamless verification via mobile network. |
| Implementation Cost | Higher - needs integration with identity providers and biometric systems. | Lower - leverages existing telecom infrastructure. |
| Fraud Risk | Low - robust verification processes and multi-factor checks. | Higher - vulnerable to SIM swapping and number porting fraud. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Strong - aligns with KYC and AML standards worldwide. | Variable - depends on telecom regulations and data sharing policies. |
| Typical Use Cases | Account opening, loan approvals, high-value transactions. | Two-factor authentication, transaction verification, quick identity checks. |
Which is better?
Digital identity verification offers enhanced security by utilizing biometric data and multi-factor authentication, reducing fraud risks significantly compared to mobile SIM-based verification. Mobile SIM-based verification mainly relies on phone number authentication, making it more vulnerable to SIM swapping attacks and identity theft. Banks benefit from digital identity verification through improved compliance with KYC regulations and streamlined customer onboarding processes.
Connection
Digital identity verification in banking integrates mobile SIM-based verification to enhance security and streamline customer authentication processes. By linking a user's mobile SIM data with their identity credentials, banks reduce fraud risks and ensure real-time validation during transactions. This connection supports compliance with regulatory standards like KYC (Know Your Customer) and AML (Anti-Money Laundering) protocols.
Key Terms
SIM Swap Fraud
SIM Swap Fraud exploits vulnerabilities in mobile SIM-based verification by hijacking users' phone numbers to intercept authentication codes. Digital identity verification enhances security through multi-factor authentication and biometrics, significantly reducing the risk of unauthorized access caused by SIM swapping. Explore how advanced digital identity solutions protect against SIM Swap Fraud and ensure robust user authentication.
Biometric Authentication
Mobile SIM-based verification relies on the authentication of user identity through the SIM card linked to a mobile number, offering a layer of security grounded in mobile network operator data. Biometric authentication in digital identity verification enhances security by utilizing unique physiological traits such as fingerprints, facial recognition, or iris scans, making it harder for unauthorized access compared to SIM-based methods. Explore the latest advancements in biometric technologies to understand how they revolutionize identity verification.
KYC (Know Your Customer)
Mobile SIM-based verification leverages the unique subscriber identity module to authenticate users by linking mobile numbers with personal information, providing fast and accessible KYC compliance particularly in telecom and financial sectors. Digital identity verification encompasses broader methods including biometric authentication, document scanning, and database cross-verification to establish user identity with higher security and fraud prevention. Explore the latest advancements and comparative effectiveness of these verification techniques for robust KYC processes.
Source and External Links
SIM-Based Verification: Reduce the Risk of Cyber Attacks - Discusses SIM-based verification methods like SMS, voice, and data to onboard and authenticate users securely across all countries.
SIM-Based Authentication, eSIM, and iSIM - Explains how SIM-based authentication works using physical, eSIM, and iSIM to ensure secure connectivity and device authentication.
Secure Identity Verification to Prevent SIM Swapping - Describes how identity verification can prevent SIM swapping attacks by providing secure onboarding and account recovery processes.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com