Real-time payments enable instant transfer of funds, offering accelerated transaction settlements compared to traditional batch processing that groups transactions for delayed execution. This immediacy enhances liquidity management and reduces counterparty risk in banking operations, crucial for businesses and consumers. Explore more to understand how these payment methods impact financial efficiency and customer experience.
Why it is important
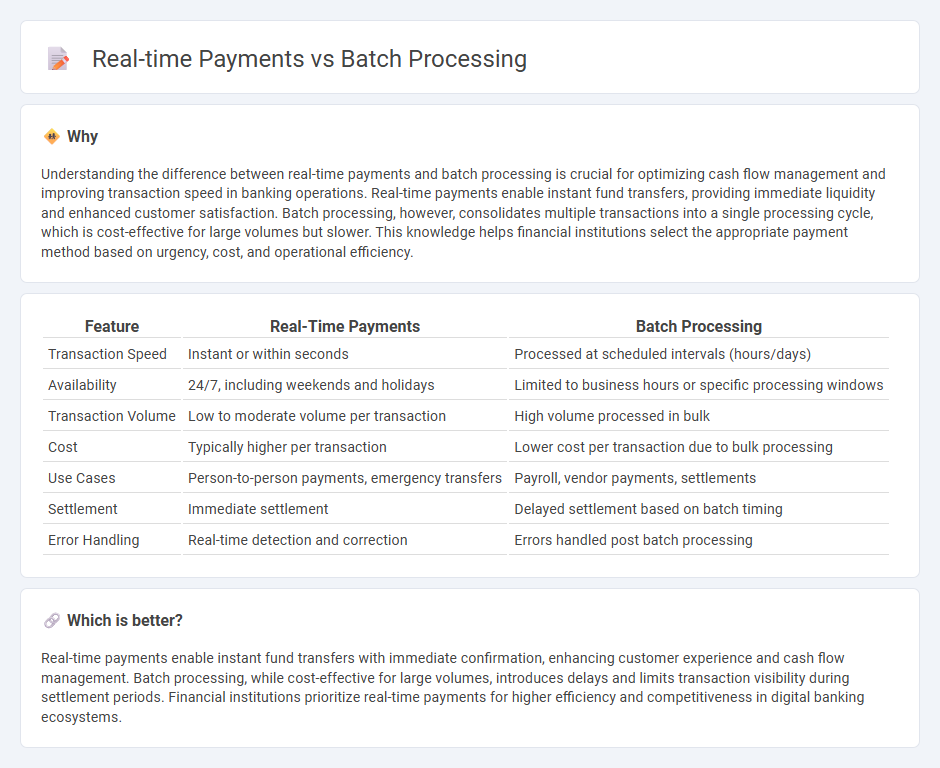
Understanding the difference between real-time payments and batch processing is crucial for optimizing cash flow management and improving transaction speed in banking operations. Real-time payments enable instant fund transfers, providing immediate liquidity and enhanced customer satisfaction. Batch processing, however, consolidates multiple transactions into a single processing cycle, which is cost-effective for large volumes but slower. This knowledge helps financial institutions select the appropriate payment method based on urgency, cost, and operational efficiency.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Real-Time Payments | Batch Processing |
|---|---|---|
| Transaction Speed | Instant or within seconds | Processed at scheduled intervals (hours/days) |
| Availability | 24/7, including weekends and holidays | Limited to business hours or specific processing windows |
| Transaction Volume | Low to moderate volume per transaction | High volume processed in bulk |
| Cost | Typically higher per transaction | Lower cost per transaction due to bulk processing |
| Use Cases | Person-to-person payments, emergency transfers | Payroll, vendor payments, settlements |
| Settlement | Immediate settlement | Delayed settlement based on batch timing |
| Error Handling | Real-time detection and correction | Errors handled post batch processing |
Which is better?
Real-time payments enable instant fund transfers with immediate confirmation, enhancing customer experience and cash flow management. Batch processing, while cost-effective for large volumes, introduces delays and limits transaction visibility during settlement periods. Financial institutions prioritize real-time payments for higher efficiency and competitiveness in digital banking ecosystems.
Connection
Real-time payments rely on continuous, immediate processing, while batch processing handles transactions in groups at scheduled intervals, creating a complementary relationship in banking operations. Financial institutions integrate these systems to balance speed and efficiency, ensuring instant payments for critical transactions and cost-effective management of bulk transfers. This hybrid approach optimizes liquidity management, reduces settlement risks, and enhances overall payment system resilience.
Key Terms
Settlement
Batch processing consolidates multiple transactions for settlement at scheduled intervals, optimizing operational efficiency and reducing processing costs. Real-time payments enable instant settlement, enhancing liquidity and improving cash flow management for businesses and consumers. Explore the advantages and applications of each settlement method to determine the best fit for your financial operations.
Latency
Batch processing payments experience higher latency due to accumulated transactions processed at scheduled intervals, often resulting in delays ranging from hours to days. Real-time payments offer minimal latency by enabling immediate transaction settlement, critical for urgent financial activities and instant fund availability. Explore how latency impacts your payment strategy and enhances operational efficiency.
Transaction Processing
Batch processing groups multiple transactions for collective processing at scheduled intervals, enhancing efficiency for large volumes but potentially causing delays in transaction confirmation. Real-time payments process each transaction individually and instantly, ensuring immediate fund transfer and settlement, critical for time-sensitive financial activities. Explore the advantages and application scenarios to determine which transaction processing method best fits your payment strategy.
Source and External Links
An Introduction to Batch Processing - Splunk - Batch processing is a computational technique where a collection of data is amassed and then processed in a single operation, often automated and scheduled without human intervention, balancing timeliness versus comprehensiveness, and sometimes combined with stream processing for efficiency.
Exploring Batch Processing: Definition, Use Cases, and Benefits - Batch processing automates the handling of large volumes of grouped tasks without human input, ideal for processes that do not require real-time processing, such as monthly credit card billing, making it cost-effective and efficient.
What is Batch Processing? - AWS - Batch processing involves running high-volume, repetitive data jobs by specifying the batch job details like input/output locations and schedule, enabling the system to process large data sets in defined batch windows with dependencies and recurring jobs.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com