Synthetic identity fraud involves creating fake identities using a combination of real and fabricated information to exploit banking systems, while application fraud occurs when criminals use stolen or falsified personal data directly during the account or loan application process. Both types of fraud lead to significant financial losses and increased risk for banks due to unauthorized access and credit issuance. Discover how financial institutions combat these complex fraud schemes to protect customer assets and maintain trust.
Why it is important
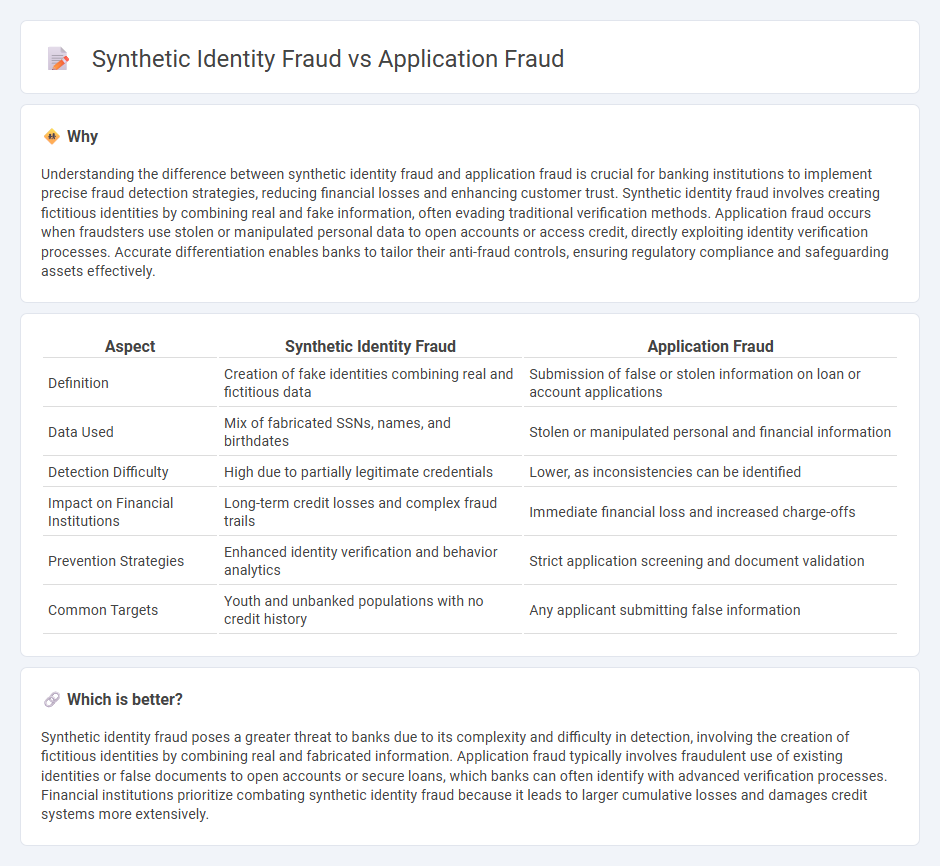
Understanding the difference between synthetic identity fraud and application fraud is crucial for banking institutions to implement precise fraud detection strategies, reducing financial losses and enhancing customer trust. Synthetic identity fraud involves creating fictitious identities by combining real and fake information, often evading traditional verification methods. Application fraud occurs when fraudsters use stolen or manipulated personal data to open accounts or access credit, directly exploiting identity verification processes. Accurate differentiation enables banks to tailor their anti-fraud controls, ensuring regulatory compliance and safeguarding assets effectively.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Synthetic Identity Fraud | Application Fraud |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Creation of fake identities combining real and fictitious data | Submission of false or stolen information on loan or account applications |
| Data Used | Mix of fabricated SSNs, names, and birthdates | Stolen or manipulated personal and financial information |
| Detection Difficulty | High due to partially legitimate credentials | Lower, as inconsistencies can be identified |
| Impact on Financial Institutions | Long-term credit losses and complex fraud trails | Immediate financial loss and increased charge-offs |
| Prevention Strategies | Enhanced identity verification and behavior analytics | Strict application screening and document validation |
| Common Targets | Youth and unbanked populations with no credit history | Any applicant submitting false information |
Which is better?
Synthetic identity fraud poses a greater threat to banks due to its complexity and difficulty in detection, involving the creation of fictitious identities by combining real and fabricated information. Application fraud typically involves fraudulent use of existing identities or false documents to open accounts or secure loans, which banks can often identify with advanced verification processes. Financial institutions prioritize combating synthetic identity fraud because it leads to larger cumulative losses and damages credit systems more extensively.
Connection
Synthetic identity fraud involves creating fictitious identities by combining real and fake information, which criminals then use to open bank accounts or apply for credit. Application fraud often leverages these synthetic identities to submit falsified loan or credit card applications, bypassing traditional verification methods. This connection enables fraudsters to exploit banking systems, leading to significant financial losses and increased risk for financial institutions.
Key Terms
Identity Verification
Application fraud involves the use of stolen or fake personal information to obtain products or services, often bypassing identity verification processes. Synthetic identity fraud combines real and fabricated data to create new identities, posing significant challenges for traditional verification systems due to its complexity. Explore advanced identity verification techniques to effectively detect and prevent both types of fraud.
Credit Bureau Data
Application fraud manipulates legitimate personal information during credit applications to obtain unauthorized credit access, directly impacting credit bureau data accuracy. Synthetic identity fraud fabricates new identities by combining real and fake information, causing complex distortions in credit bureau databases that complicate fraud detection. Explore in-depth how credit bureaus combat these distinct threats to safeguard financial integrity.
Fraudulent Documentation
Application fraud involves submitting false or altered documentation like fake IDs or income statements to secure loans or credit, often using real personal information. Synthetic identity fraud combines fabricated and real data to create entirely new identities, with fraudulent documentation like fake Social Security numbers or counterfeit utility bills used to establish credit profiles. Explore the differences in documentation tactics and prevention strategies to strengthen fraud detection efforts.
Source and External Links
What is application fraud? - GBG - Application fraud occurs when individuals or entities submit false or misleading information to financial institutions, either for personal gain, financial advantage, or to facilitate crimes like money laundering.
What Is Application Fraud? And How Do You Detect It? - FICO - Application fraud involves the deception of misrepresenting personal details or using stolen identities to obtain financial benefits, such as opening accounts or securing credit, often leveraging digital tools to evade detection.
Application Fraud - DataVisor Digital Fraud Wiki - Fraudsters exploit digital lending channels by using stolen or synthetic identities to apply for loans or credit with no intention of repayment, sometimes building fake credit histories to access larger sums before disappearing.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com