Cryptotax regulations govern the taxation of cryptocurrency transactions, ensuring proper reporting of capital gains, income, and losses from digital assets. Withholding tax involves the mandatory deduction of tax at the source on payments such as salaries, dividends, and interest, acting as an advance tax payment mechanism. Explore the key differences and implications of cryptotax and withholding tax to optimize compliance and financial strategy.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between cryptotax and withholding tax is crucial for accurate financial reporting and compliance with tax regulations. Cryptotax refers to the taxation of cryptocurrency transactions, including gains from trading or mining, while withholding tax is a pre-collected tax deducted at the source on income such as dividends or interest. Misclassifying these can lead to penalties or incorrect tax filings, affecting an individual's or business's financial health and legal standing. Proper differentiation ensures optimized tax liability management and adherence to jurisdiction-specific tax laws.
Comparison Table
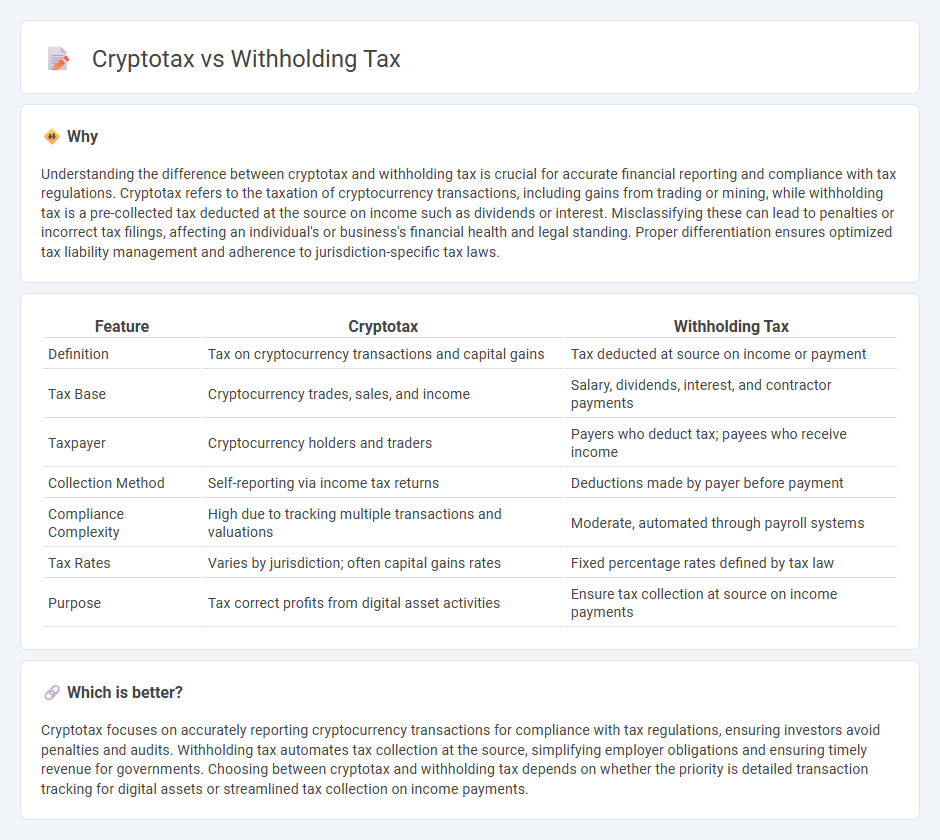
| Feature | Cryptotax | Withholding Tax |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Tax on cryptocurrency transactions and capital gains | Tax deducted at source on income or payment |
| Tax Base | Cryptocurrency trades, sales, and income | Salary, dividends, interest, and contractor payments |
| Taxpayer | Cryptocurrency holders and traders | Payers who deduct tax; payees who receive income |
| Collection Method | Self-reporting via income tax returns | Deductions made by payer before payment |
| Compliance Complexity | High due to tracking multiple transactions and valuations | Moderate, automated through payroll systems |
| Tax Rates | Varies by jurisdiction; often capital gains rates | Fixed percentage rates defined by tax law |
| Purpose | Tax correct profits from digital asset activities | Ensure tax collection at source on income payments |
Which is better?
Cryptotax focuses on accurately reporting cryptocurrency transactions for compliance with tax regulations, ensuring investors avoid penalties and audits. Withholding tax automates tax collection at the source, simplifying employer obligations and ensuring timely revenue for governments. Choosing between cryptotax and withholding tax depends on whether the priority is detailed transaction tracking for digital assets or streamlined tax collection on income payments.
Connection
Cryptotax refers to the taxation of cryptocurrency transactions, which often requires accurate tracking of gains and losses for compliance. Withholding tax may be applied to certain crypto payments, such as income from mining or staking rewards, where a percentage of the payment is withheld by the payer and remitted to tax authorities. Both cryptotax and withholding tax mechanisms are critical for ensuring proper reporting and collection of taxes in digital asset accounting.
Key Terms
Tax Deduction
Withholding tax involves the automatic deduction of taxes from income at the source, ensuring immediate tax compliance and reducing taxpayer liability. Cryptotax, particularly in jurisdictions where cryptocurrency transactions are taxable, requires meticulous tracking of each transaction's capital gains or income, often without automatic deductions. Explore detailed differences and implications to optimize your tax strategy effectively.
Digital Assets
Withholding tax on digital assets refers to the mandatory deduction made at the source of income payments related to cryptocurrencies, ensuring tax compliance during transactions or payouts. Crypto tax encompasses a broader scope, including capital gains, income, and transaction reporting obligations for digital asset holdings and trades. Explore detailed guidelines and compliance strategies for managing withholding tax and crypto tax obligations on digital assets.
Reporting Compliance
Withholding tax requires entities to deduct tax at source on specific payments and report these deductions to tax authorities, ensuring compliance through detailed documentation and timely filings. Cryptotax reporting compliance involves tracking all cryptocurrency transactions, including trades, mining income, and token swaps, with accurate records to meet tax jurisdiction regulations. Explore how to streamline your tax reporting process and ensure full compliance with the latest withholding and crypto tax requirements.
Source and External Links
How to check and change your tax withholding | USAGov - Provides information on how to check and adjust income tax withholding from paychecks using the IRS withholding estimator tool.
Tax withholding - Wikipedia - Explains the concept of tax withholding, its applications, and how it works across different jurisdictions.
Tax withholding | Internal Revenue Service - Discusses income tax withholding, its importance for employees, and the use of the IRS Tax Withholding Estimator to manage withholding amounts.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com