Cryptocurrency taxation involves reporting digital asset transactions and capital gains to comply with IRS regulations, while self-employment tax applies to income earned from independent business activities subject to Social Security and Medicare contributions. Understanding the distinctions between these tax obligations is crucial for accurate financial reporting and legal compliance. Explore detailed guidelines to navigate the complexities of cryptocurrency taxation and self-employment tax effectively.
Why it is important
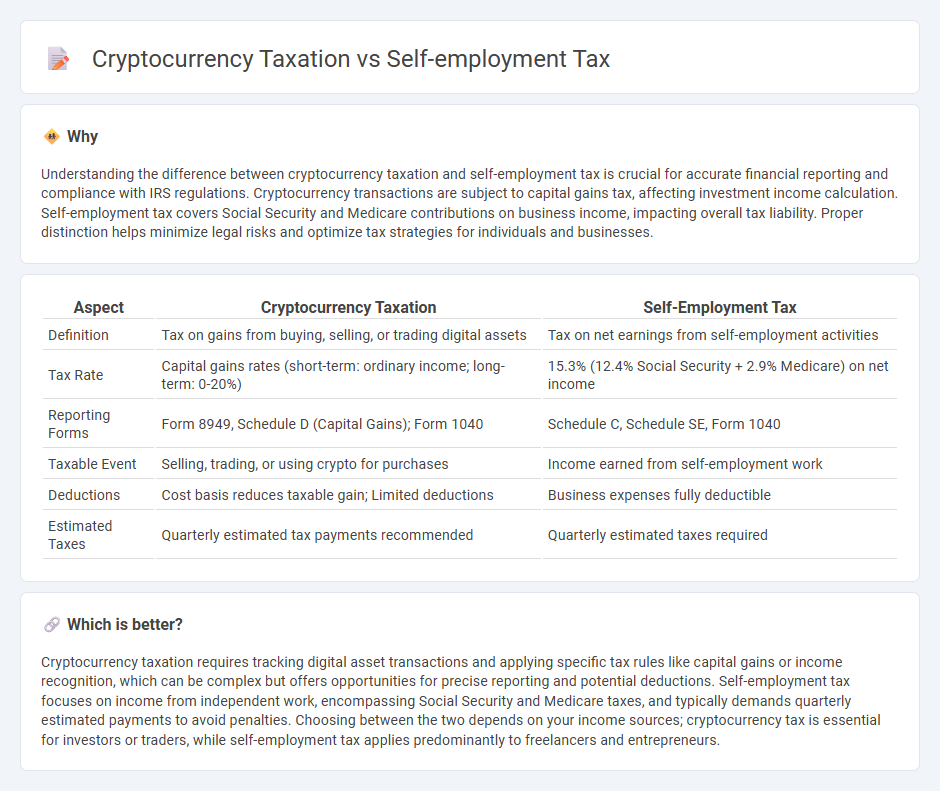
Understanding the difference between cryptocurrency taxation and self-employment tax is crucial for accurate financial reporting and compliance with IRS regulations. Cryptocurrency transactions are subject to capital gains tax, affecting investment income calculation. Self-employment tax covers Social Security and Medicare contributions on business income, impacting overall tax liability. Proper distinction helps minimize legal risks and optimize tax strategies for individuals and businesses.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Cryptocurrency Taxation | Self-Employment Tax |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Tax on gains from buying, selling, or trading digital assets | Tax on net earnings from self-employment activities |
| Tax Rate | Capital gains rates (short-term: ordinary income; long-term: 0-20%) | 15.3% (12.4% Social Security + 2.9% Medicare) on net income |
| Reporting Forms | Form 8949, Schedule D (Capital Gains); Form 1040 | Schedule C, Schedule SE, Form 1040 |
| Taxable Event | Selling, trading, or using crypto for purchases | Income earned from self-employment work |
| Deductions | Cost basis reduces taxable gain; Limited deductions | Business expenses fully deductible |
| Estimated Taxes | Quarterly estimated tax payments recommended | Quarterly estimated taxes required |
Which is better?
Cryptocurrency taxation requires tracking digital asset transactions and applying specific tax rules like capital gains or income recognition, which can be complex but offers opportunities for precise reporting and potential deductions. Self-employment tax focuses on income from independent work, encompassing Social Security and Medicare taxes, and typically demands quarterly estimated payments to avoid penalties. Choosing between the two depends on your income sources; cryptocurrency tax is essential for investors or traders, while self-employment tax applies predominantly to freelancers and entrepreneurs.
Connection
Cryptocurrency taxation intersects with self-employment tax when individuals receive digital assets as payment for freelance services or business activities, classifying this income as self-employment earnings. The IRS requires reporting of fair market value of cryptocurrency received, which is subject to income tax and self-employment tax rates of approximately 15.3%. Proper accounting for these transactions ensures compliance and accurate calculation of both income and self-employment tax liabilities.
Key Terms
**Self-Employment Income**
Self-employment income is subject to self-employment tax, which covers Social Security and Medicare contributions, calculated at 15.3% on net earnings. Cryptocurrency taxation for self-employed individuals requires reporting income at fair market value when received, with gains or losses subject to capital gains tax rules upon disposal. Learn more about managing self-employment income taxation in the evolving cryptocurrency landscape.
**Capital Gains**
Capital gains tax on cryptocurrency is calculated based on the difference between the purchase price and the sale price of the digital asset, with rates varying depending on the holding period and overall income. Self-employment tax applies to net earnings from business activities, including crypto-related income such as mining or trading profits, and is separate from capital gains tax obligations. Learn more about how capital gains impact cryptocurrency taxation and the interplay with self-employment tax requirements.
**Estimated Tax Payments**
Estimated tax payments are crucial for self-employed individuals who must pay both income tax and self-employment tax quarterly to avoid penalties. Cryptocurrency taxation also requires estimated payments when gains from trading or mining significantly increase taxable income, with the IRS treating digital assets as property subject to capital gains rules. Learn more about managing your estimated tax payments to stay compliant with both self-employment and cryptocurrency tax obligations.
Source and External Links
Self-Employment Tax: Everything You Need to Know - Provides detailed explanations of self-employment tax rates, calculations, and how they apply to net earnings from self-employment.
Self-Employment Tax: Calculator, Rates - Offers a comprehensive overview of self-employment tax rates, including the 15.3% total rate and how it breaks down into Social Security and Medicare components.
Self-employment tax: Definition, rates, and how to calculate - Explains the steps to calculate self-employment tax, including determining net earnings and applying the tax rate to a portion of those earnings.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com