Digital twin accounting leverages real-time data and simulation models to create dynamic financial representations, enhancing accuracy and predictive capabilities beyond traditional financial accounting methods. Financial accounting primarily focuses on historical data compilation, regulatory compliance, and standardized reporting for stakeholders. Explore how integrating digital twin accounting transforms financial decision-making and business performance insights.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between Digital Twin Accounting and Financial Accounting is crucial for accurate data analysis and decision-making in modern businesses. Digital Twin Accounting focuses on real-time simulation of physical assets and operational processes, enhancing predictive maintenance and performance optimization. Financial Accounting tracks historical financial transactions to ensure compliance, reporting accuracy, and stakeholder transparency. Distinguishing these enables seamless integration of operational insights with financial performance, driving smarter resource allocation and strategic planning.
Comparison Table
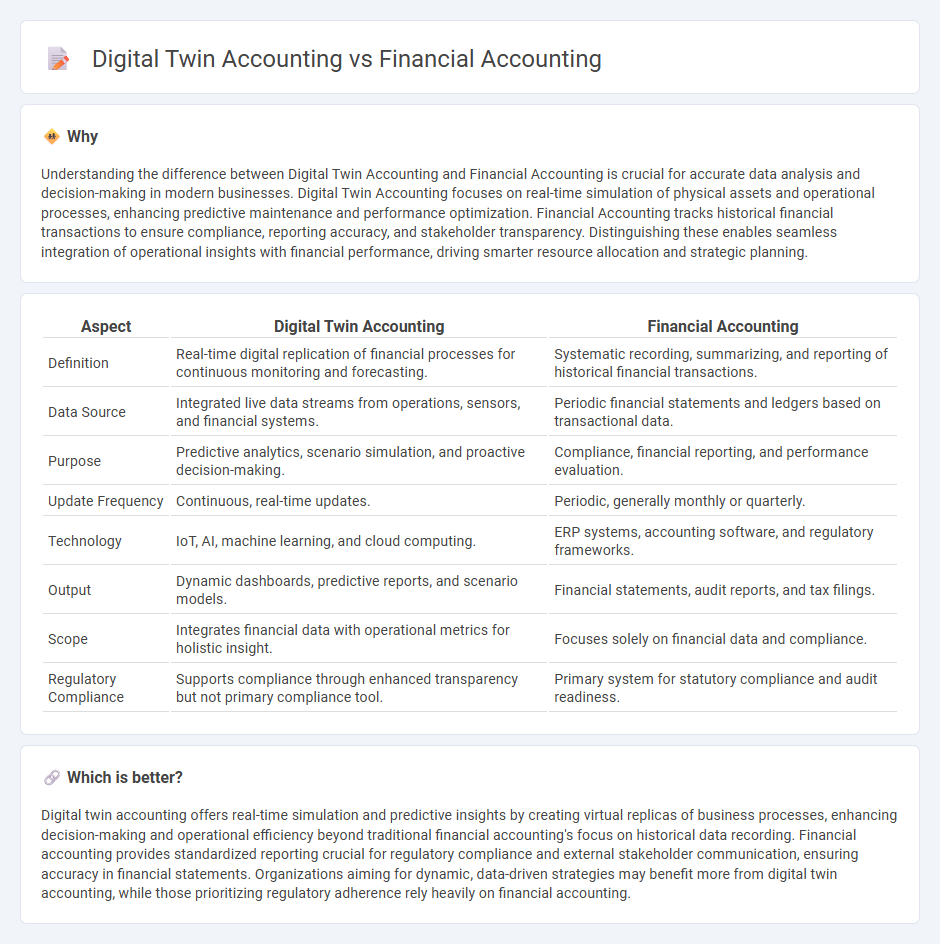
| Aspect | Digital Twin Accounting | Financial Accounting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Real-time digital replication of financial processes for continuous monitoring and forecasting. | Systematic recording, summarizing, and reporting of historical financial transactions. |
| Data Source | Integrated live data streams from operations, sensors, and financial systems. | Periodic financial statements and ledgers based on transactional data. |
| Purpose | Predictive analytics, scenario simulation, and proactive decision-making. | Compliance, financial reporting, and performance evaluation. |
| Update Frequency | Continuous, real-time updates. | Periodic, generally monthly or quarterly. |
| Technology | IoT, AI, machine learning, and cloud computing. | ERP systems, accounting software, and regulatory frameworks. |
| Output | Dynamic dashboards, predictive reports, and scenario models. | Financial statements, audit reports, and tax filings. |
| Scope | Integrates financial data with operational metrics for holistic insight. | Focuses solely on financial data and compliance. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Supports compliance through enhanced transparency but not primary compliance tool. | Primary system for statutory compliance and audit readiness. |
Which is better?
Digital twin accounting offers real-time simulation and predictive insights by creating virtual replicas of business processes, enhancing decision-making and operational efficiency beyond traditional financial accounting's focus on historical data recording. Financial accounting provides standardized reporting crucial for regulatory compliance and external stakeholder communication, ensuring accuracy in financial statements. Organizations aiming for dynamic, data-driven strategies may benefit more from digital twin accounting, while those prioritizing regulatory adherence rely heavily on financial accounting.
Connection
Digital twin accounting leverages real-time data and simulations to enhance financial accounting accuracy by providing dynamic insights into asset performance and operational costs. This integration enables more precise forecasting, risk assessment, and compliance reporting within financial accounting systems. Corporations utilize digital twins to monitor financial health and drive strategic decision-making while ensuring alignment with accounting standards.
Key Terms
Financial Statements
Financial accounting primarily focuses on the accurate preparation and presentation of financial statements such as the balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement, ensuring compliance with accounting standards like GAAP or IFRS. Digital twin accounting integrates real-time data from digital twin technology to enhance financial reporting accuracy, enabling dynamic updates to financial statements and predictive analytics for future financial performance. Explore how digital twin accounting transforms traditional financial statements for more responsive and insightful financial management.
Real-Time Data Integration
Financial accounting traditionally consolidates historical financial data for reporting and compliance, whereas digital twin accounting integrates real-time operational metrics and financial data to enhance accuracy and decision-making. The use of IoT sensors and advanced analytics in digital twin frameworks ensures continuous data flow, improving forecasting, risk management, and performance tracking. Discover how digital twin accounting transforms financial transparency and strategic planning with real-time data integration.
Asset Digital Representation
Financial accounting primarily centers on recording and reporting historical asset transactions using standardized financial statements, while digital twin accounting emphasizes creating dynamic, real-time digital representations of physical assets for continuous monitoring and predictive analysis. Digital twin accounting integrates IoT data, real-time sensors, and AI to enhance asset management by providing up-to-date insights into condition, performance, and lifecycle costs, surpassing traditional static financial reports. Explore further to understand how digital twin accounting revolutionizes asset transparency and decision-making processes.
Source and External Links
What Is Financial Accounting? Key Principles, Careers & More - Financial accounting is the branch of accounting focused on recording and summarizing business transactions to prepare financial statements that provide an accurate view of a company's financial health, following frameworks like GAAP or IFRS to ensure consistency and reliability.
Financial Accounting: Meaning, Principles, and Importance - Financial accounting involves recording, summarizing, and reporting a company's transactions through financial statements such as the income statement and balance sheet, adhering to GAAP to ensure accuracy and comparability for decision-making.
Financial accounting - Wikipedia - Financial accounting systematically records, classifies, and summarizes financial transactions to prepare financial statements that reflect profit/loss, financial position, and solvency, providing stakeholders with reliable information for rational decisions.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com