Blockchain-based accounting revolutionizes financial record-keeping by leveraging decentralized ledgers to enhance transparency, security, and immutability of transactions. Triple-entry accounting introduces a third ledger entry that cryptographically links transactions between parties, reducing fraud and errors more effectively than traditional double-entry systems. Explore the fundamental differences and benefits to understand how these innovations reshape accounting practices.
Why it is important
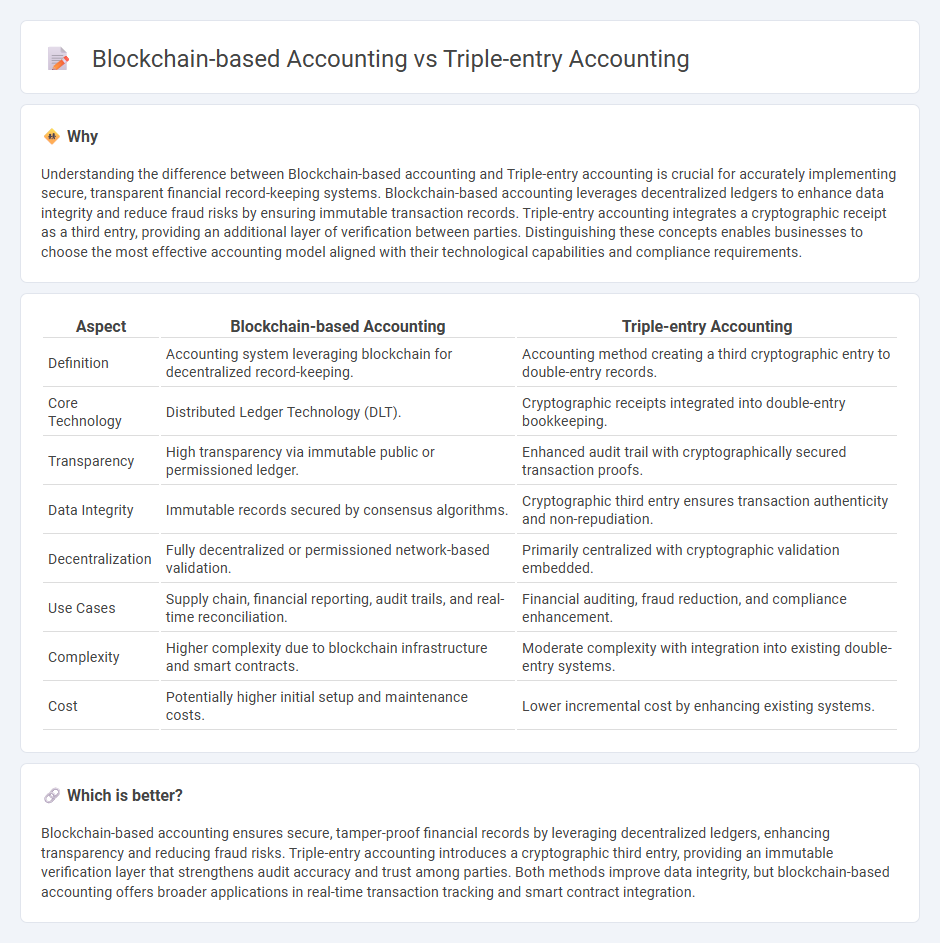
Understanding the difference between Blockchain-based accounting and Triple-entry accounting is crucial for accurately implementing secure, transparent financial record-keeping systems. Blockchain-based accounting leverages decentralized ledgers to enhance data integrity and reduce fraud risks by ensuring immutable transaction records. Triple-entry accounting integrates a cryptographic receipt as a third entry, providing an additional layer of verification between parties. Distinguishing these concepts enables businesses to choose the most effective accounting model aligned with their technological capabilities and compliance requirements.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Blockchain-based Accounting | Triple-entry Accounting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Accounting system leveraging blockchain for decentralized record-keeping. | Accounting method creating a third cryptographic entry to double-entry records. |
| Core Technology | Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT). | Cryptographic receipts integrated into double-entry bookkeeping. |
| Transparency | High transparency via immutable public or permissioned ledger. | Enhanced audit trail with cryptographically secured transaction proofs. |
| Data Integrity | Immutable records secured by consensus algorithms. | Cryptographic third entry ensures transaction authenticity and non-repudiation. |
| Decentralization | Fully decentralized or permissioned network-based validation. | Primarily centralized with cryptographic validation embedded. |
| Use Cases | Supply chain, financial reporting, audit trails, and real-time reconciliation. | Financial auditing, fraud reduction, and compliance enhancement. |
| Complexity | Higher complexity due to blockchain infrastructure and smart contracts. | Moderate complexity with integration into existing double-entry systems. |
| Cost | Potentially higher initial setup and maintenance costs. | Lower incremental cost by enhancing existing systems. |
Which is better?
Blockchain-based accounting ensures secure, tamper-proof financial records by leveraging decentralized ledgers, enhancing transparency and reducing fraud risks. Triple-entry accounting introduces a cryptographic third entry, providing an immutable verification layer that strengthens audit accuracy and trust among parties. Both methods improve data integrity, but blockchain-based accounting offers broader applications in real-time transaction tracking and smart contract integration.
Connection
Blockchain-based accounting leverages decentralized ledger technology to ensure transparent, immutable financial records, directly supporting the principles of triple-entry accounting where a cryptographic verification acts as a third entry. This integration enhances auditability and reduces fraud by enabling real-time, tamper-proof confirmation of transactions between multiple parties. Enterprises adopting blockchain-based triple-entry accounting benefit from increased trust and efficiency in financial reporting processes.
Key Terms
Immutable Ledger
Triple-entry accounting enhances traditional double-entry bookkeeping by integrating a cryptographic verification layer that records transactions in a shared, immutable ledger. Blockchain-based accounting builds upon this principle by decentralizing the ledger across multiple nodes, ensuring tamper-proof transaction records and real-time consensus. Explore the advantages and implementation strategies of immutable ledgers in modern accounting systems to improve transparency and auditability.
Cryptographic Verification
Triple-entry accounting integrates cryptographic verification to create a secure and tamper-proof financial record by including a cryptographic receipt shared between parties, enhancing transparency and trust beyond traditional double-entry systems. Blockchain-based accounting extends this concept by leveraging decentralized ledger technology, providing immutable, time-stamped transaction records validated through consensus algorithms, thereby reducing fraud and errors. Explore the advancements and practical applications of cryptographic verification in accounting to optimize financial integrity and security.
Smart Contracts
Triple-entry accounting enhances financial transparency by recording transactions in a cryptographically secured ledger shared among participants, enabling automatic verification of entries. Blockchain-based accounting leverages decentralized ledgers and smart contracts to automate transaction validation, enforce contractual terms, and reduce reconciliation errors. Discover how smart contracts revolutionize accounting accuracy and compliance in modern financial systems.
Source and External Links
Triple entry accounting. Example and benefits - Eduyush - Triple-entry accounting, especially when combined with blockchain, creates a third shared, immutable, and digitally signed transaction record--in addition to the traditional debit and credit entries--which enhances transparency, reduces fraud, and streamlines audits by making each transaction independently verifiable across all involved parties.
Triple Entry Accounting - iang.org - Triple-entry bookkeeping connects standard double-entry records between separate entities with a digitally signed receipt that links and validates the transaction across all parties, proposing an evolution rather than a revolution in accounting to increase reliability and reduce disputes.
Triple entry accounting - CoinGeek - Triple-entry accounting stores transaction records in a decentralized, time-stamped, and immutable system (such as a blockchain) that serves as a single, independently verifiable source of truth for all participants, further increasing trust through enhanced transparency and shared access to data.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com