Carbon accounting quantifies greenhouse gas emissions to help organizations manage environmental impact and comply with climate regulations. International accounting involves standardized financial reporting practices across countries, ensuring transparency and comparability in global business transactions. Discover how integrating carbon accounting with international standards can enhance sustainability reporting and financial accuracy.
Why it is important
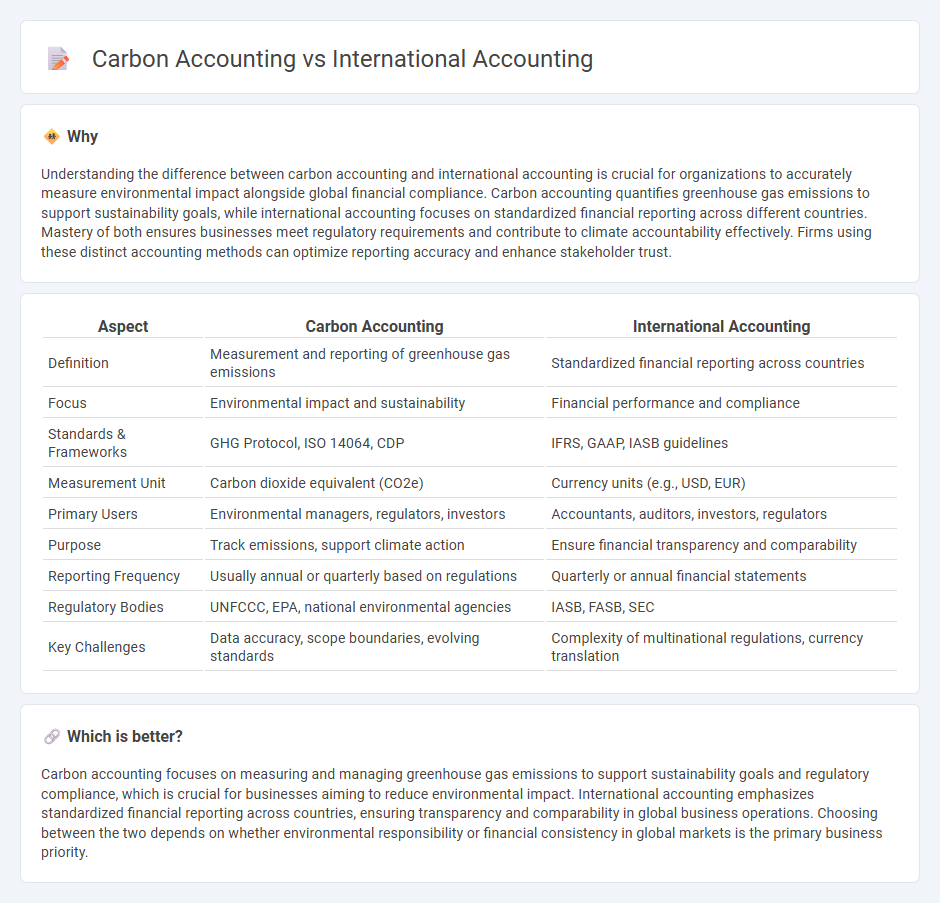
Understanding the difference between carbon accounting and international accounting is crucial for organizations to accurately measure environmental impact alongside global financial compliance. Carbon accounting quantifies greenhouse gas emissions to support sustainability goals, while international accounting focuses on standardized financial reporting across different countries. Mastery of both ensures businesses meet regulatory requirements and contribute to climate accountability effectively. Firms using these distinct accounting methods can optimize reporting accuracy and enhance stakeholder trust.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Carbon Accounting | International Accounting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Measurement and reporting of greenhouse gas emissions | Standardized financial reporting across countries |
| Focus | Environmental impact and sustainability | Financial performance and compliance |
| Standards & Frameworks | GHG Protocol, ISO 14064, CDP | IFRS, GAAP, IASB guidelines |
| Measurement Unit | Carbon dioxide equivalent (CO2e) | Currency units (e.g., USD, EUR) |
| Primary Users | Environmental managers, regulators, investors | Accountants, auditors, investors, regulators |
| Purpose | Track emissions, support climate action | Ensure financial transparency and comparability |
| Reporting Frequency | Usually annual or quarterly based on regulations | Quarterly or annual financial statements |
| Regulatory Bodies | UNFCCC, EPA, national environmental agencies | IASB, FASB, SEC |
| Key Challenges | Data accuracy, scope boundaries, evolving standards | Complexity of multinational regulations, currency translation |
Which is better?
Carbon accounting focuses on measuring and managing greenhouse gas emissions to support sustainability goals and regulatory compliance, which is crucial for businesses aiming to reduce environmental impact. International accounting emphasizes standardized financial reporting across countries, ensuring transparency and comparability in global business operations. Choosing between the two depends on whether environmental responsibility or financial consistency in global markets is the primary business priority.
Connection
Carbon accounting quantifies greenhouse gas emissions to evaluate environmental impact, providing essential data for corporate sustainability reporting and regulatory compliance. International accounting standards incorporate carbon accounting metrics to harmonize financial disclosures related to environmental liabilities and asset valuations. This integration supports global transparency and investor confidence by aligning environmental and financial performance across jurisdictions.
Key Terms
**International Accounting:**
International accounting establishes global standards like IFRS to ensure transparency and consistency in financial reporting across borders. It involves the preparation, analysis, and comparison of financial statements to support multinational business operations and regulatory compliance. Explore more to understand how international accounting frameworks drive global financial integration and corporate accountability.
IFRS (International Financial Reporting Standards)
International accounting governed by IFRS establishes uniform financial reporting standards for global businesses, emphasizing transparency and comparability in financial statements. Carbon accounting measures greenhouse gas emissions, integrating environmental impacts into financial disclosure, which IFRS is increasingly incorporating through sustainability-related standards like the IFRS Sustainability Disclosure Standards (SDS). Explore how IFRS bridges traditional financial reporting with emerging carbon accounting practices to enhance corporate accountability and stakeholder trust.
Consolidation
International accounting consolidation involves integrating financial statements of multiple subsidiaries to present a unified company performance, adhering to standards like IFRS or GAAP. Carbon accounting consolidation aggregates greenhouse gas emissions data across an entire corporate group to provide a comprehensive environmental impact assessment. Explore further to understand how consolidation processes differ and intersect in financial and carbon accounting frameworks.
Source and External Links
Consider a Career in International Accounting - Eastern Washington University offers an online MBA with an Accounting Concentration that includes courses on international accounting issues, preparing students to address global accounting challenges and work in diverse cultural environments.
International Accounting, 6th Edition - McGraw Hill - This textbook provides a comprehensive overview of international accounting topics, including global accounting diversity, IFRS standards, foreign currency transactions, international taxation, and sustainability reporting.
IFRS Foundation - The IFRS Foundation is a global nonprofit organization responsible for developing international accounting and sustainability standards that promote convergence and consistency in financial reporting worldwide.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com