Crypto asset valuation requires specialized models reflecting market volatility and unique asset characteristics, distinct from traditional impairment testing which focuses on assessing asset recoverability based on defined accounting standards like IFRS or GAAP. Accurate valuation hinges on real-time market data, transaction volumes, and asset liquidity, whereas impairment testing depends on estimating future cash flows and discount rates. Explore our comprehensive analysis to understand the nuances between crypto asset valuation and impairment testing methodologies.
Why it is important
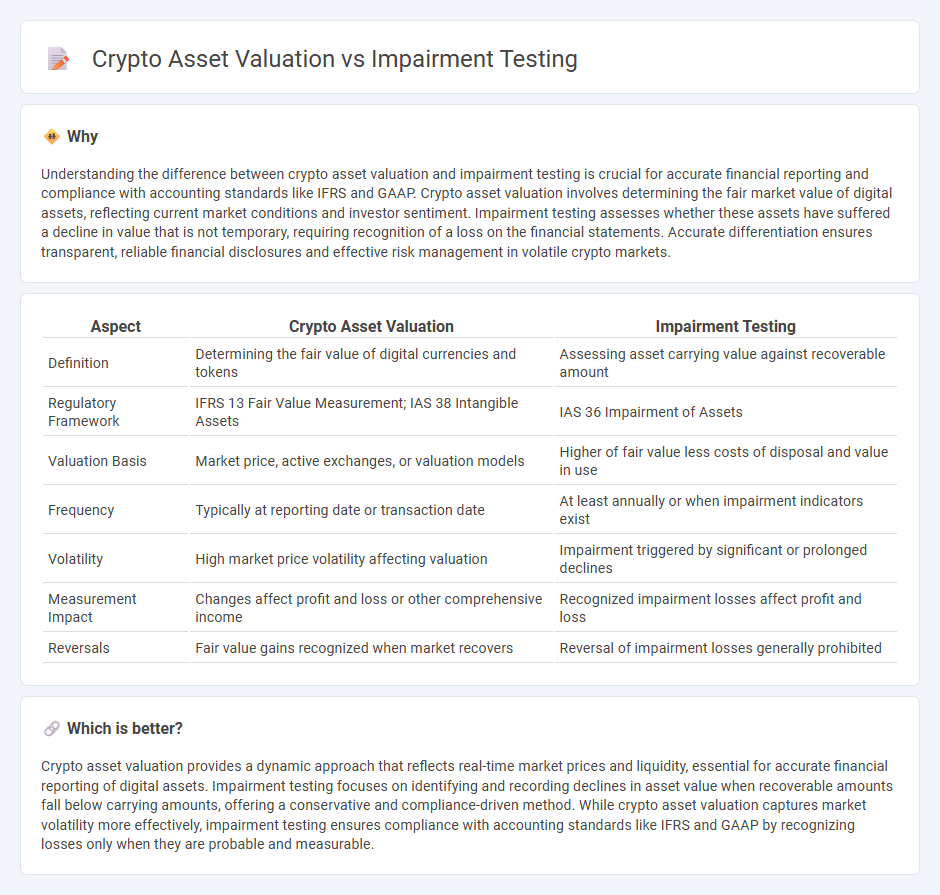
Understanding the difference between crypto asset valuation and impairment testing is crucial for accurate financial reporting and compliance with accounting standards like IFRS and GAAP. Crypto asset valuation involves determining the fair market value of digital assets, reflecting current market conditions and investor sentiment. Impairment testing assesses whether these assets have suffered a decline in value that is not temporary, requiring recognition of a loss on the financial statements. Accurate differentiation ensures transparent, reliable financial disclosures and effective risk management in volatile crypto markets.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Crypto Asset Valuation | Impairment Testing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Determining the fair value of digital currencies and tokens | Assessing asset carrying value against recoverable amount |
| Regulatory Framework | IFRS 13 Fair Value Measurement; IAS 38 Intangible Assets | IAS 36 Impairment of Assets |
| Valuation Basis | Market price, active exchanges, or valuation models | Higher of fair value less costs of disposal and value in use |
| Frequency | Typically at reporting date or transaction date | At least annually or when impairment indicators exist |
| Volatility | High market price volatility affecting valuation | Impairment triggered by significant or prolonged declines |
| Measurement Impact | Changes affect profit and loss or other comprehensive income | Recognized impairment losses affect profit and loss |
| Reversals | Fair value gains recognized when market recovers | Reversal of impairment losses generally prohibited |
Which is better?
Crypto asset valuation provides a dynamic approach that reflects real-time market prices and liquidity, essential for accurate financial reporting of digital assets. Impairment testing focuses on identifying and recording declines in asset value when recoverable amounts fall below carrying amounts, offering a conservative and compliance-driven method. While crypto asset valuation captures market volatility more effectively, impairment testing ensures compliance with accounting standards like IFRS and GAAP by recognizing losses only when they are probable and measurable.
Connection
Crypto asset valuation relies on fair value measurement principles, which require continuous assessment of market conditions and asset performance. Impairment testing is essential in accounting for crypto assets because it identifies when the carrying amount exceeds the recoverable amount, necessitating write-downs to reflect diminished value. Accurate impairment testing ensures financial statements reflect true asset value, complying with IFRS and GAAP standards in volatile crypto markets.
Key Terms
Fair Value
Impairment testing evaluates whether a crypto asset's carrying amount exceeds its recoverable amount, focusing on detecting value declines without considering market fluctuations, while crypto asset valuation at Fair Value reflects current market conditions and investor sentiment, providing a real-time asset price. Fair Value measurement incorporates market data inputs such as quoted prices and trading volumes, offering a more dynamic and transparent representation compared to impairment's historical cost approach. Explore further insights on the nuances and practical applications of Fair Value in crypto asset accounting standards.
Recoverable Amount
Impairment testing determines whether a crypto asset's carrying value exceeds its recoverable amount, which is the higher of fair value less costs to sell or value in use, ensuring accurate financial reporting. Crypto asset valuation involves assessing market volatility, liquidity, and regulatory risks to estimate fair value, impacting the recoverable amount calculation during impairment tests. Explore detailed methodologies and practical applications to enhance your understanding of impairment testing and crypto asset valuation.
Market Volatility
Market volatility significantly influences impairment testing for financial assets and the valuation of crypto assets, as rapid price fluctuations create challenges in determining fair value and potential losses. Impairment testing requires identifying indicators of asset value decline, often complicated by the unpredictable and highly volatile nature of cryptocurrency markets. Explore our detailed analysis to understand how market volatility impacts valuation accuracy and regulatory compliance.
Source and External Links
Impairment Testing - A Critical Process That is Often Underestimated - Impairment testing involves a sequence that starts with assets like inventory, followed by indefinite-lived intangible assets, long-lived assets including Right-of-Use (ROU) lease assets, and lastly goodwill, which is tested on a reporting unit basis.
IMPAIRMENT OF GOODWILL, TANGIBLE AND INTANGIBLE ASSETS (BDO) - Goodwill and indefinite-lived intangible assets require annual qualitative or quantitative impairment tests where fair value is compared with carrying amount, and impairment loss is recognized if carrying amount exceeds fair value.
How and When to Test for Fixed Asset Impairment - Impairment testing should be triggered by indications such as damage, market value decline, or operating losses, and involves comparing net carrying amount to current fair market value to determine impairment amounts.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com