Blockchain audit trails enhance transparency by recording immutable, time-stamped transaction data that supports robust forensic analysis. Triple-entry accounting introduces a cryptographic verification layer where each transaction is independently validated and linked to a third, secure ledger, reducing fraud and errors. Explore how these innovations revolutionize financial integrity and auditing processes.
Why it is important
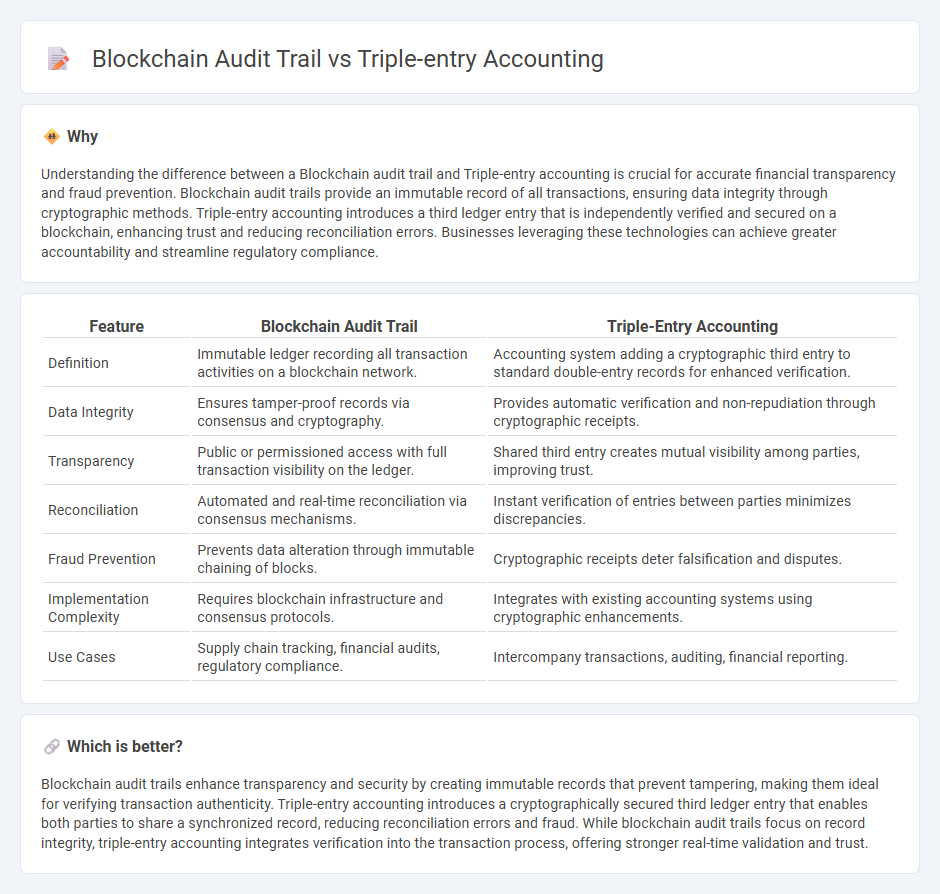
Understanding the difference between a Blockchain audit trail and Triple-entry accounting is crucial for accurate financial transparency and fraud prevention. Blockchain audit trails provide an immutable record of all transactions, ensuring data integrity through cryptographic methods. Triple-entry accounting introduces a third ledger entry that is independently verified and secured on a blockchain, enhancing trust and reducing reconciliation errors. Businesses leveraging these technologies can achieve greater accountability and streamline regulatory compliance.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Blockchain Audit Trail | Triple-Entry Accounting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Immutable ledger recording all transaction activities on a blockchain network. | Accounting system adding a cryptographic third entry to standard double-entry records for enhanced verification. |
| Data Integrity | Ensures tamper-proof records via consensus and cryptography. | Provides automatic verification and non-repudiation through cryptographic receipts. |
| Transparency | Public or permissioned access with full transaction visibility on the ledger. | Shared third entry creates mutual visibility among parties, improving trust. |
| Reconciliation | Automated and real-time reconciliation via consensus mechanisms. | Instant verification of entries between parties minimizes discrepancies. |
| Fraud Prevention | Prevents data alteration through immutable chaining of blocks. | Cryptographic receipts deter falsification and disputes. |
| Implementation Complexity | Requires blockchain infrastructure and consensus protocols. | Integrates with existing accounting systems using cryptographic enhancements. |
| Use Cases | Supply chain tracking, financial audits, regulatory compliance. | Intercompany transactions, auditing, financial reporting. |
Which is better?
Blockchain audit trails enhance transparency and security by creating immutable records that prevent tampering, making them ideal for verifying transaction authenticity. Triple-entry accounting introduces a cryptographically secured third ledger entry that enables both parties to share a synchronized record, reducing reconciliation errors and fraud. While blockchain audit trails focus on record integrity, triple-entry accounting integrates verification into the transaction process, offering stronger real-time validation and trust.
Connection
Blockchain audit trails enhance accounting transparency by providing immutable records of transactions, ensuring data integrity and reducing fraud risks. Triple-entry accounting integrates this technology by adding a cryptographic third entry, creating a decentralized ledger that verifies and synchronizes financial data across all parties. This connection streamlines audits, improves accuracy, and fosters trust between stakeholders through verifiable and tamper-proof accounting records.
Key Terms
Cryptographic Receipts
Triple-entry accounting enhances traditional double-entry bookkeeping by embedding cryptographic receipts that create tamper-proof audit trails, leveraging cryptographic proofs to verify transaction authenticity. Blockchain audit trails use distributed ledgers to maintain immutable records, where each entry is timestamped and linked via cryptographic hashes, ensuring transparency and security. Explore the intricacies of cryptographic receipts to understand how they fortify financial data integrity in modern accounting systems.
Immutable Ledger
Triple-entry accounting enhances traditional double-entry bookkeeping by integrating cryptographic proofs that ensure transaction immutability, creating an immutable ledger resistant to tampering. Blockchain audit trails offer a decentralized, transparent record of transactions secured by consensus mechanisms, providing verifiable and permanent data entries across multiple nodes. Explore how these technologies revolutionize financial transparency and security by maintaining an unalterable audit trail.
Smart Contracts
Triple-entry accounting enhances financial transparency by integrating cryptographic signatures that connect transactions, creating an immutable audit trail. Blockchain audit trails extend this concept by leveraging decentralized ledgers and smart contracts, automating verification and reducing fraud risk in real-time. Explore how smart contracts revolutionize audit accuracy and compliance in decentralized finance environments.
Source and External Links
Triple entry accounting. Example and benefits - Eduyush - Triple-entry accounting adds a third, shared and cryptographically signed ledger entry between two parties in a transaction, enhancing trust, transparency, and immutability by recording the transaction on a blockchain, which reduces fraud and audit costs while enabling automatic validation.
TRIPLE-ENTRY BOOKKEEPING: A critical examination of an ... - rit.edu.croatia - This system uses cryptographically signed receipts linking two companies' accounting records, creating a shared, tamper-proof digital record of transactions to increase trust and reduce discrepancies in books between contracting parties.
Triple entry accounting - CoinGeek - Triple-entry accounting introduces a third Immutable, verifiable, and decentralized record stored on a blockchain as a single source of truth, which advances transparency beyond traditional double-entry bookkeeping by involving an independent distributed system to maintain these records.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com