Collaborative audit trails enhance transparency and accuracy by allowing multiple parties to record and verify transactions in real time within a shared ledger, reducing discrepancies and fraud risks. Blockchain accounting leverages decentralized, immutable ledgers secured by cryptographic protocols to ensure data integrity and streamline auditing processes. Explore the unique benefits and applications of collaborative audit trails versus blockchain accounting to optimize financial management.
Why it is important
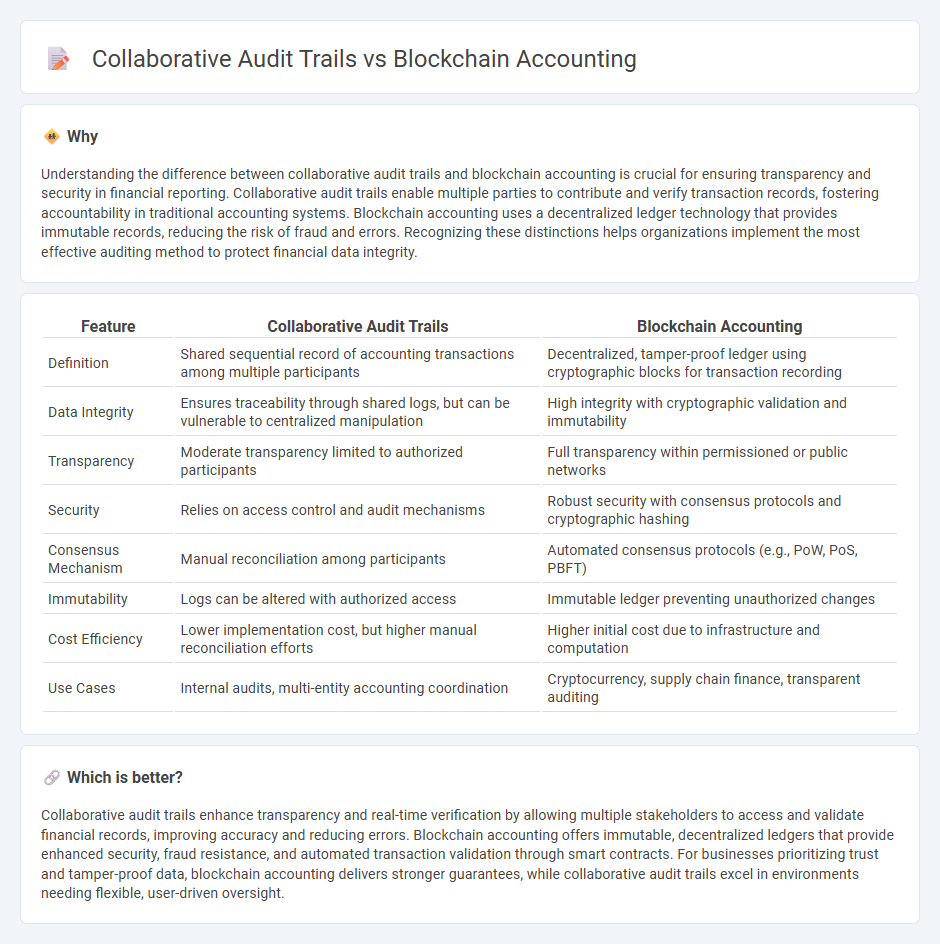
Understanding the difference between collaborative audit trails and blockchain accounting is crucial for ensuring transparency and security in financial reporting. Collaborative audit trails enable multiple parties to contribute and verify transaction records, fostering accountability in traditional accounting systems. Blockchain accounting uses a decentralized ledger technology that provides immutable records, reducing the risk of fraud and errors. Recognizing these distinctions helps organizations implement the most effective auditing method to protect financial data integrity.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Collaborative Audit Trails | Blockchain Accounting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Shared sequential record of accounting transactions among multiple participants | Decentralized, tamper-proof ledger using cryptographic blocks for transaction recording |
| Data Integrity | Ensures traceability through shared logs, but can be vulnerable to centralized manipulation | High integrity with cryptographic validation and immutability |
| Transparency | Moderate transparency limited to authorized participants | Full transparency within permissioned or public networks |
| Security | Relies on access control and audit mechanisms | Robust security with consensus protocols and cryptographic hashing |
| Consensus Mechanism | Manual reconciliation among participants | Automated consensus protocols (e.g., PoW, PoS, PBFT) |
| Immutability | Logs can be altered with authorized access | Immutable ledger preventing unauthorized changes |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower implementation cost, but higher manual reconciliation efforts | Higher initial cost due to infrastructure and computation |
| Use Cases | Internal audits, multi-entity accounting coordination | Cryptocurrency, supply chain finance, transparent auditing |
Which is better?
Collaborative audit trails enhance transparency and real-time verification by allowing multiple stakeholders to access and validate financial records, improving accuracy and reducing errors. Blockchain accounting offers immutable, decentralized ledgers that provide enhanced security, fraud resistance, and automated transaction validation through smart contracts. For businesses prioritizing trust and tamper-proof data, blockchain accounting delivers stronger guarantees, while collaborative audit trails excel in environments needing flexible, user-driven oversight.
Connection
Collaborative audit trails leverage blockchain accounting by utilizing its decentralized ledger technology to ensure transparent, tamper-proof record-keeping. Blockchain's immutable data structure enhances audit trail reliability, enabling multiple stakeholders to verify financial transactions in real-time. This integration reduces fraud risk and streamlines compliance processes in accounting systems.
Key Terms
Distributed Ledger
Blockchain accounting leverages distributed ledger technology to provide a decentralized, immutable record of financial transactions, ensuring enhanced transparency and security. Collaborative audit trails utilize similar distributed ledgers to enable multiple stakeholders to verify and validate transaction histories in real time, reducing the risk of errors and fraud. Explore how distributed ledger innovations are transforming financial accountability and audit processes.
Real-Time Verification
Blockchain accounting enables real-time verification through an immutable ledger that records every transaction transparently and securely, reducing the risk of data tampering. Collaborative audit trails enhance this process by allowing multiple stakeholders to simultaneously verify and validate financial data, increasing accuracy and trustworthiness across the audit lifecycle. Discover how integrating these technologies can revolutionize financial transparency and efficiency.
Immutable Records
Blockchain accounting provides immutable records by recording transactions in a decentralized ledger that cannot be altered or deleted, ensuring transparency and data integrity. Collaborative audit trails enhance transparency by combining multiple audit inputs to create a comprehensive record of financial activities, though these records may not be inherently immutable. Explore the distinct advantages of blockchain's tamper-proof nature versus the collective validation approach in collaborative audit trails.
Source and External Links
How Blockchain is Changing Accounting Practices - Paystand - Blockchain transforms accounting by providing an immutable, transparent ledger that improves transaction verification, automates reconciliations with smart contracts, enhances fraud detection, streamlines audits, and secures financial data through decentralization and cryptography.
Blockchain Accounting - Guide & Use Cases - Blockchain accounting enables real-time transaction recording on a shared, immutable ledger, facilitating automated processes and triple entry accounting that reduces fraud, lowers reconciliation and audit costs, and enhances data security via consensus mechanisms and cryptography.
What is Blockchain Accounting? - FreshBooks - Blockchain supports accounting by providing a secure, digitally signed ledger for transactions that improves audit efficiency and trustworthiness while complementing rather than replacing traditional accounting tasks.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com