Real-time auditing enables continuous monitoring of financial transactions, providing immediate insights and enhancing fraud detection capabilities. Automated auditing leverages advanced algorithms and machine learning to efficiently analyze large datasets, increasing accuracy and reducing manual errors. Explore the differences and benefits of these auditing methods to improve your financial oversight.
Why it is important
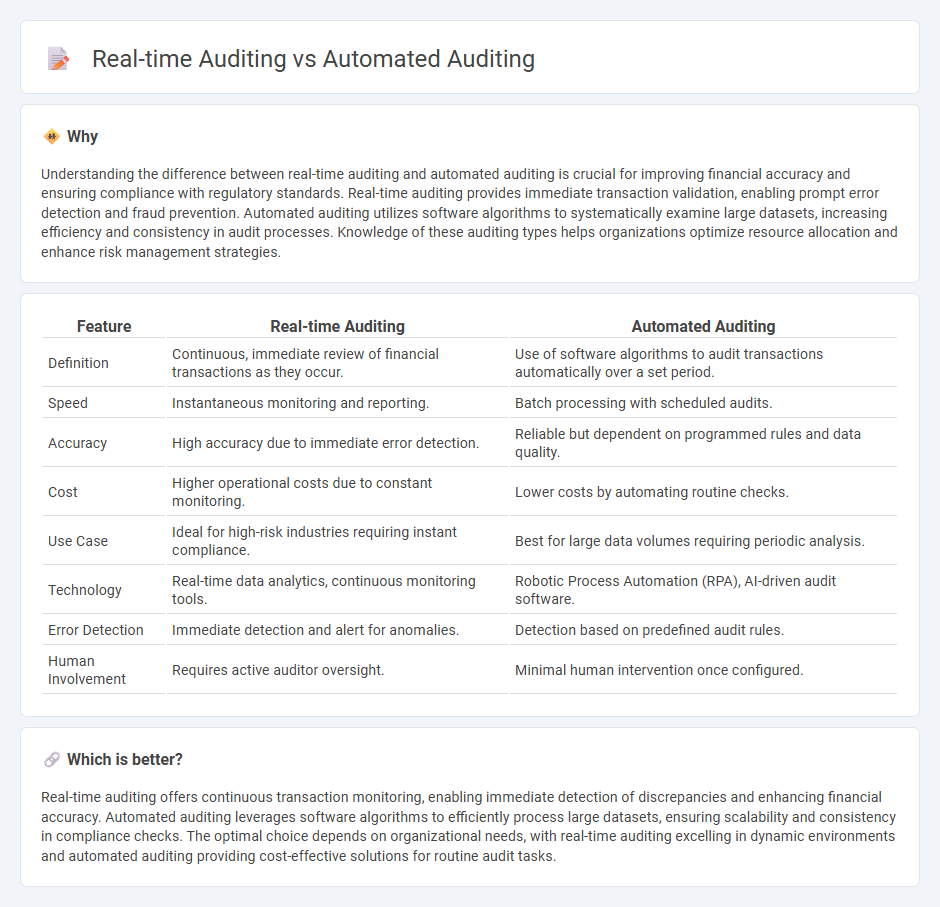
Understanding the difference between real-time auditing and automated auditing is crucial for improving financial accuracy and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards. Real-time auditing provides immediate transaction validation, enabling prompt error detection and fraud prevention. Automated auditing utilizes software algorithms to systematically examine large datasets, increasing efficiency and consistency in audit processes. Knowledge of these auditing types helps organizations optimize resource allocation and enhance risk management strategies.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Real-time Auditing | Automated Auditing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Continuous, immediate review of financial transactions as they occur. | Use of software algorithms to audit transactions automatically over a set period. |
| Speed | Instantaneous monitoring and reporting. | Batch processing with scheduled audits. |
| Accuracy | High accuracy due to immediate error detection. | Reliable but dependent on programmed rules and data quality. |
| Cost | Higher operational costs due to constant monitoring. | Lower costs by automating routine checks. |
| Use Case | Ideal for high-risk industries requiring instant compliance. | Best for large data volumes requiring periodic analysis. |
| Technology | Real-time data analytics, continuous monitoring tools. | Robotic Process Automation (RPA), AI-driven audit software. |
| Error Detection | Immediate detection and alert for anomalies. | Detection based on predefined audit rules. |
| Human Involvement | Requires active auditor oversight. | Minimal human intervention once configured. |
Which is better?
Real-time auditing offers continuous transaction monitoring, enabling immediate detection of discrepancies and enhancing financial accuracy. Automated auditing leverages software algorithms to efficiently process large datasets, ensuring scalability and consistency in compliance checks. The optimal choice depends on organizational needs, with real-time auditing excelling in dynamic environments and automated auditing providing cost-effective solutions for routine audit tasks.
Connection
Real-time auditing leverages continuous data monitoring to identify discrepancies instantly, while automated auditing uses software algorithms to streamline and execute audit tasks without manual intervention. Both approaches integrate advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning to enhance accuracy, efficiency, and risk detection in financial audits. Their connection lies in transforming traditional auditing methods into dynamic, data-driven processes that improve compliance and decision-making for organizations.
Key Terms
Continuous Monitoring
Automated auditing leverages software tools to systematically analyze financial data and compliance metrics, enhancing efficiency and accuracy in identifying discrepancies. Real-time auditing emphasizes continuous monitoring by providing instant access to transaction data and system alerts, enabling proactive risk management and timely decision-making. Explore how continuous monitoring transforms auditing processes for improved transparency and control.
Exception Reporting
Automated auditing leverages advanced algorithms to generate exception reports by continuously analyzing large datasets, enabling quicker identification of anomalies compared to traditional methods. Real-time auditing enhances this process by providing immediate exception reporting, allowing auditors to address discrepancies as they occur and improve compliance monitoring. Explore further to understand how exception reporting transforms auditing efficiency and accuracy.
Data Analytics
Automated auditing leverages data analytics to systematically process large datasets, identifying anomalies and patterns without manual intervention, while real-time auditing employs continuous data monitoring to provide immediate insights and detect irregularities as transactions occur. Both methods enhance audit accuracy and efficiency by integrating advanced analytics tools such as machine learning algorithms and predictive models to assess financial and operational data promptly. Explore the benefits and applications of automated and real-time auditing through data analytics to optimize your audit processes effectively.
Source and External Links
AI-driven audit automation: streamlining processes for scalable success - AI-driven audit automation uses artificial intelligence and machine learning to continuously monitor 100% of financial transactions, detecting anomalies and ensuring compliance in real-time, thus enhancing risk detection, efficiency, and scalability over traditional manual audits.
What Is Audit Automation And How Can It Benefit Firms? - INAA - Audit automation leverages cloud-based technologies to streamline workflows, improve collaboration, enhance data security, and provide deeper insights, enabling auditors to work remotely and efficiently while reducing errors and addressing challenges like data collection and evolving standards.
Audit Automation: Benefits, Implementation Challenges & Use Cases - Audit automation automates repetitive, manual audit tasks such as data entry and risk assessment using tools like robotic process automation and analytics, increasing accuracy, freeing up human resources for higher-value work, and supporting continuous monitoring and improved audit effectiveness.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com