ESG reporting focuses on Environmental, Social, and Governance criteria to evaluate corporate sustainability and social impact, emphasizing measurable outcomes and stakeholder interests. Triple bottom line reporting broadens this scope by integrating financial, social, and environmental performance into a cohesive framework that promotes long-term value creation. Explore the differences and applications of ESG and Triple bottom line reporting to enhance your corporate accountability strategies.
Why it is important
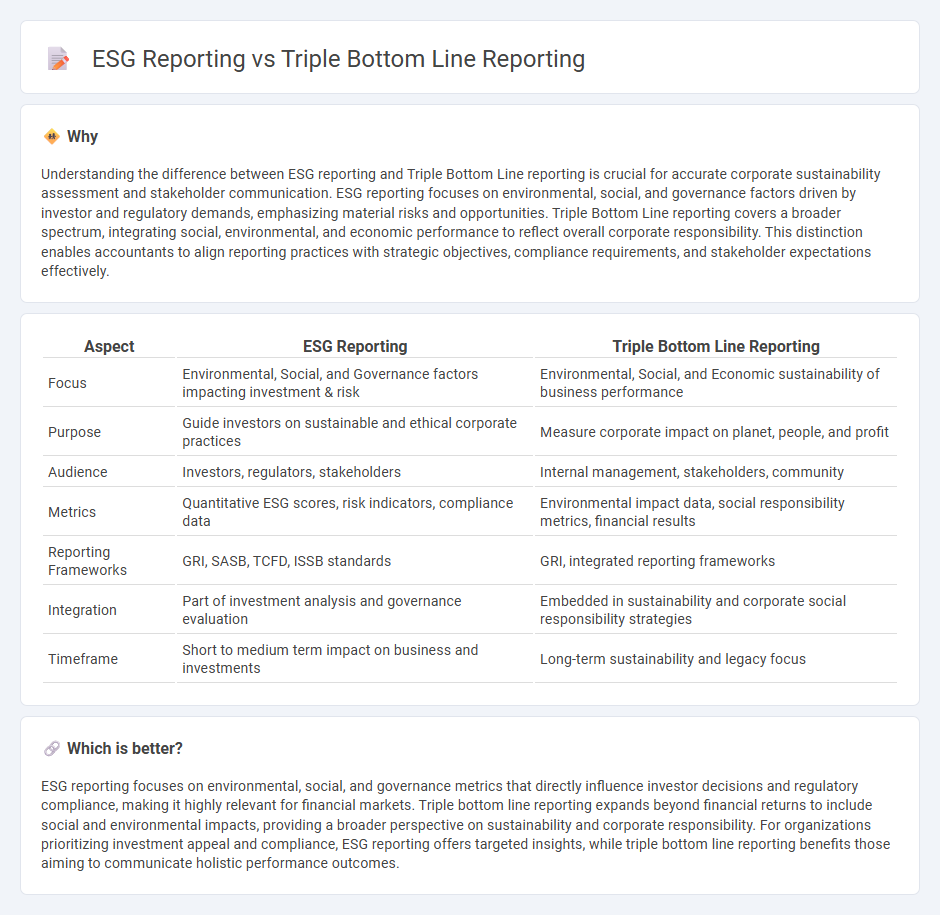
Understanding the difference between ESG reporting and Triple Bottom Line reporting is crucial for accurate corporate sustainability assessment and stakeholder communication. ESG reporting focuses on environmental, social, and governance factors driven by investor and regulatory demands, emphasizing material risks and opportunities. Triple Bottom Line reporting covers a broader spectrum, integrating social, environmental, and economic performance to reflect overall corporate responsibility. This distinction enables accountants to align reporting practices with strategic objectives, compliance requirements, and stakeholder expectations effectively.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | ESG Reporting | Triple Bottom Line Reporting |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Environmental, Social, and Governance factors impacting investment & risk | Environmental, Social, and Economic sustainability of business performance |
| Purpose | Guide investors on sustainable and ethical corporate practices | Measure corporate impact on planet, people, and profit |
| Audience | Investors, regulators, stakeholders | Internal management, stakeholders, community |
| Metrics | Quantitative ESG scores, risk indicators, compliance data | Environmental impact data, social responsibility metrics, financial results |
| Reporting Frameworks | GRI, SASB, TCFD, ISSB standards | GRI, integrated reporting frameworks |
| Integration | Part of investment analysis and governance evaluation | Embedded in sustainability and corporate social responsibility strategies |
| Timeframe | Short to medium term impact on business and investments | Long-term sustainability and legacy focus |
Which is better?
ESG reporting focuses on environmental, social, and governance metrics that directly influence investor decisions and regulatory compliance, making it highly relevant for financial markets. Triple bottom line reporting expands beyond financial returns to include social and environmental impacts, providing a broader perspective on sustainability and corporate responsibility. For organizations prioritizing investment appeal and compliance, ESG reporting offers targeted insights, while triple bottom line reporting benefits those aiming to communicate holistic performance outcomes.
Connection
ESG reporting and Triple Bottom Line reporting are connected through their shared focus on measuring a company's impact beyond financial performance by incorporating environmental, social, and governance factors. Both frameworks emphasize sustainability by assessing environmental stewardship, social responsibility, and economic viability to provide a comprehensive view of corporate accountability. Companies integrating ESG metrics with Triple Bottom Line reporting enhance transparency and stakeholder trust by demonstrating their commitment to sustainable business practices.
Key Terms
Sustainability
Triple bottom line reporting evaluates sustainability through social, environmental, and economic performance to provide a holistic view of corporate responsibility. ESG reporting focuses on Environmental, Social, and Governance criteria, prioritizing metrics relevant to investor risk and compliance. Explore our detailed analysis to understand how these frameworks shape sustainable business practices.
Stakeholders
Triple bottom line reporting evaluates a company's performance based on social, environmental, and economic impacts, emphasizing responsibility to a broad range of stakeholders including communities, employees, and the environment. ESG reporting, centered on Environmental, Social, and Governance criteria, targets investors and regulators by disclosing quantifiable data on sustainability risks and corporate governance practices. Explore the distinct stakeholder-focused objectives and methodologies in both frameworks for a deeper understanding.
Metrics
Triple bottom line reporting emphasizes social, environmental, and economic metrics to measure overall organizational impact, including employee well-being, carbon footprint, and financial performance. ESG reporting targets specific environmental, social, and governance criteria such as greenhouse gas emissions, diversity ratios, and board independence to inform investors. Explore detailed metric comparisons and best practices to optimize your sustainability reporting approach.
Source and External Links
What Is the Triple Bottom Line (TBL)? - IBM - The triple bottom line (TBL) is a sustainability framework focusing on maximizing three P's: people (social impact), planet (environmental stewardship), and profit (financial performance), encouraging organizations to consider social and environmental responsibilities alongside profit.
What is the triple bottom line and why is it important to your ... - Diligent - The triple bottom line concept, also called 3Ps or 3BL, advocates evaluating business success through three interrelated dimensions: profit, people (social well-being), and planet (environmental health), emphasizing that financial goals should not compromise social or ecological outcomes.
Triple bottom line - Wikipedia - The triple bottom line is an accounting framework with three parts: social, environmental (or ecological), and economic, used by some organizations to broaden performance evaluation beyond traditional financial metrics and create greater business value.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com