Greenwashing detection involves identifying misleading claims about a company's environmental practices to prevent deceptive accounting in sustainability reports. Double materiality assessment expands traditional financial analysis by evaluating both the financial impact of sustainability issues on a company and the company's impact on the environment and society. Explore how these methodologies redefine transparency and accountability in corporate reporting.
Why it is important
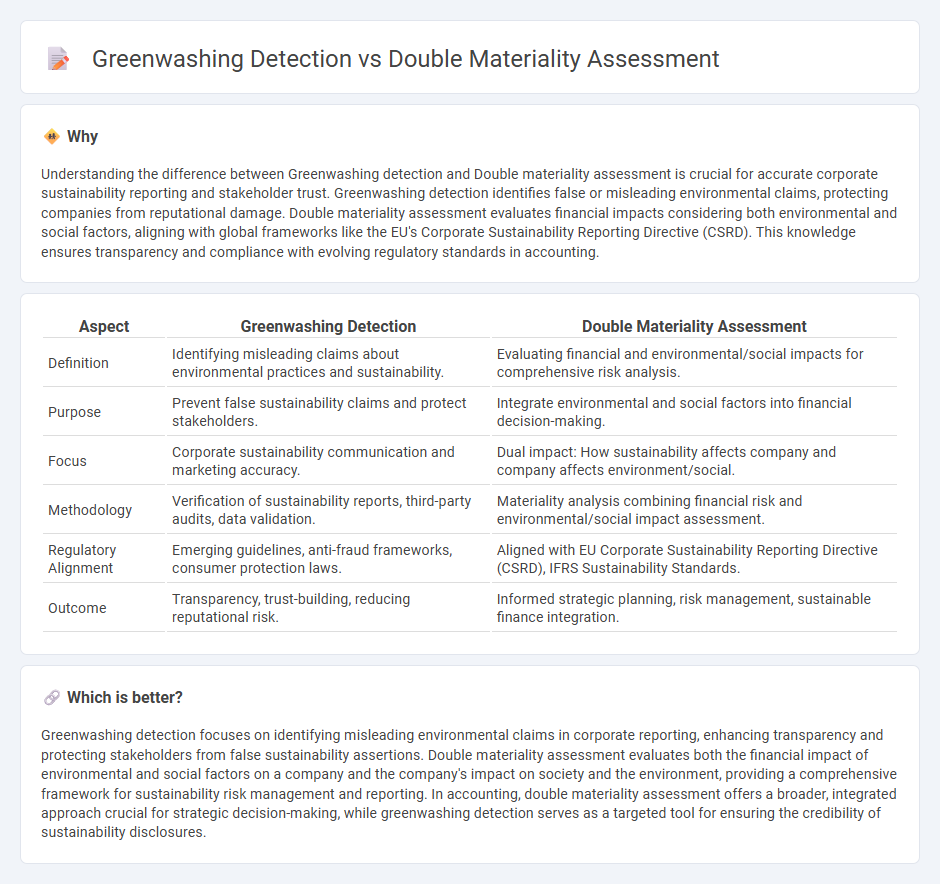
Understanding the difference between Greenwashing detection and Double materiality assessment is crucial for accurate corporate sustainability reporting and stakeholder trust. Greenwashing detection identifies false or misleading environmental claims, protecting companies from reputational damage. Double materiality assessment evaluates financial impacts considering both environmental and social factors, aligning with global frameworks like the EU's Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD). This knowledge ensures transparency and compliance with evolving regulatory standards in accounting.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Greenwashing Detection | Double Materiality Assessment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Identifying misleading claims about environmental practices and sustainability. | Evaluating financial and environmental/social impacts for comprehensive risk analysis. |
| Purpose | Prevent false sustainability claims and protect stakeholders. | Integrate environmental and social factors into financial decision-making. |
| Focus | Corporate sustainability communication and marketing accuracy. | Dual impact: How sustainability affects company and company affects environment/social. |
| Methodology | Verification of sustainability reports, third-party audits, data validation. | Materiality analysis combining financial risk and environmental/social impact assessment. |
| Regulatory Alignment | Emerging guidelines, anti-fraud frameworks, consumer protection laws. | Aligned with EU Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD), IFRS Sustainability Standards. |
| Outcome | Transparency, trust-building, reducing reputational risk. | Informed strategic planning, risk management, sustainable finance integration. |
Which is better?
Greenwashing detection focuses on identifying misleading environmental claims in corporate reporting, enhancing transparency and protecting stakeholders from false sustainability assertions. Double materiality assessment evaluates both the financial impact of environmental and social factors on a company and the company's impact on society and the environment, providing a comprehensive framework for sustainability risk management and reporting. In accounting, double materiality assessment offers a broader, integrated approach crucial for strategic decision-making, while greenwashing detection serves as a targeted tool for ensuring the credibility of sustainability disclosures.
Connection
Greenwashing detection and double materiality assessment are connected through their focus on evaluating corporate sustainability claims by analyzing both financial and environmental impacts. Double materiality assessment provides a framework for identifying significant environmental, social, and governance (ESG) risks and opportunities that affect a company's value and influence stakeholder decisions, which supports identifying misleading green claims in greenwashing detection. Integrating double materiality insights enhances the accuracy and reliability of greenwashing detection by ensuring that reported sustainability practices reflect true financial and environmental performance.
Key Terms
**Double Materiality Assessment:**
Double Materiality Assessment evaluates both the financial impact of environmental and social factors on a company and the company's impact on society and the environment. This approach goes beyond traditional materiality by integrating sustainability risks and opportunities into corporate decision-making and reporting frameworks such as the EU Sustainable Finance Disclosure Regulation (SFDR) and the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD). Discover how Double Materiality Assessment drives transparent, accountable, and sustainable business practices.
Financial Materiality
Double materiality assessment evaluates a company's impact from both financial and environmental-social governance perspectives, emphasizing financial materiality by identifying risks and opportunities that can affect financial performance. Greenwashing detection scrutinizes corporate disclosures to uncover misleading claims, focusing on ensuring transparency and preventing deceptive practices around sustainability reporting. Discover how integrating double materiality assessments enhances accuracy and accountability in financial materiality analysis.
Environmental Impact
Double materiality assessment evaluates both financial impact on companies and environmental impacts of corporate activities, providing a holistic view of sustainability risks and opportunities. Greenwashing detection identifies misleading claims about environmental practices to protect stakeholders from deceptive marketing. Explore how integrating these approaches enhances transparency and accountability in environmental impact reporting.
Source and External Links
Double Materiality Assessment: Definition and Step-by-Step Guide - This resource provides a detailed explanation and guide on performing a double materiality assessment, focusing on both financial and impact materiality.
What is Single and Double Materiality? - This article distinguishes between single and double materiality, highlighting how double materiality considers environmental impacts alongside financial implications.
Unpacking the Double Materiality Assessment Under the E.U. - This publication discusses approaches to performing a double materiality assessment under the EU Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) and its implications.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com