Supply chain finance focuses on optimizing cash flow by allowing buyers and suppliers to extend payment terms while providing early payment options through a financial intermediary. Trade finance involves various financial instruments and products that facilitate international and domestic trade by mitigating risks and enhancing liquidity for exporters and importers. Discover how these distinct financing methods impact global commerce and business operations.
Why it is important
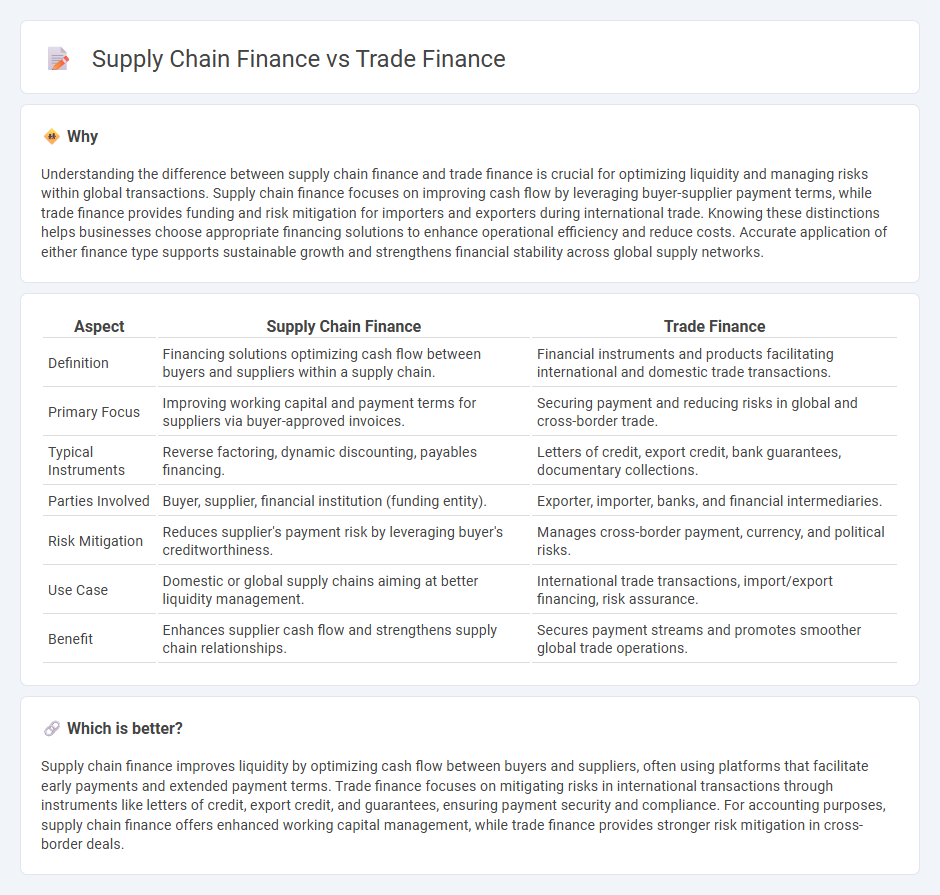
Understanding the difference between supply chain finance and trade finance is crucial for optimizing liquidity and managing risks within global transactions. Supply chain finance focuses on improving cash flow by leveraging buyer-supplier payment terms, while trade finance provides funding and risk mitigation for importers and exporters during international trade. Knowing these distinctions helps businesses choose appropriate financing solutions to enhance operational efficiency and reduce costs. Accurate application of either finance type supports sustainable growth and strengthens financial stability across global supply networks.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Supply Chain Finance | Trade Finance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Financing solutions optimizing cash flow between buyers and suppliers within a supply chain. | Financial instruments and products facilitating international and domestic trade transactions. |
| Primary Focus | Improving working capital and payment terms for suppliers via buyer-approved invoices. | Securing payment and reducing risks in global and cross-border trade. |
| Typical Instruments | Reverse factoring, dynamic discounting, payables financing. | Letters of credit, export credit, bank guarantees, documentary collections. |
| Parties Involved | Buyer, supplier, financial institution (funding entity). | Exporter, importer, banks, and financial intermediaries. |
| Risk Mitigation | Reduces supplier's payment risk by leveraging buyer's creditworthiness. | Manages cross-border payment, currency, and political risks. |
| Use Case | Domestic or global supply chains aiming at better liquidity management. | International trade transactions, import/export financing, risk assurance. |
| Benefit | Enhances supplier cash flow and strengthens supply chain relationships. | Secures payment streams and promotes smoother global trade operations. |
Which is better?
Supply chain finance improves liquidity by optimizing cash flow between buyers and suppliers, often using platforms that facilitate early payments and extended payment terms. Trade finance focuses on mitigating risks in international transactions through instruments like letters of credit, export credit, and guarantees, ensuring payment security and compliance. For accounting purposes, supply chain finance offers enhanced working capital management, while trade finance provides stronger risk mitigation in cross-border deals.
Connection
Supply chain finance optimizes cash flow by bridging payment gaps between buyers and suppliers, while trade finance provides the necessary capital to facilitate international transactions and mitigate risks. Both mechanisms enhance liquidity and reduce financial friction across the supply chain, enabling smoother procurement and delivery processes. Integration of supply chain finance and trade finance contributes to improved working capital management and strengthens global trade relationships.
Key Terms
Letter of Credit
A Letter of Credit (LC) in trade finance serves as a secure payment guarantee between importers and exporters, facilitating international transactions by minimizing payment risks. Supply chain finance, by contrast, leverages LCs to optimize working capital and improve cash flow for suppliers within the supply chain ecosystem. Discover how integrating Letters of Credit enhances financial efficiency and risk management by exploring expert insights.
Receivables Financing
Receivables financing in trade finance involves businesses using their accounts receivable as collateral to secure short-term funding, improving liquidity while managing credit risks. In supply chain finance, receivables financing is structured through collaboration between suppliers and buyers, optimizing working capital by accelerating payments at favorable terms. Explore how receivables financing strategies differ in trade finance and supply chain finance to enhance cash flow management.
Payables Financing
Trade finance and supply chain finance both aim to optimize cash flow for businesses, but payables financing specifically enhances working capital by allowing buyers to extend payment terms while suppliers receive early payments. Trade finance typically involves banks or financial institutions facilitating international trade transactions, whereas supply chain finance leverages technology platforms to streamline payables and receivables within the supply chain. Explore the nuances and benefits of payables financing to improve your business liquidity and supplier relationships.
Source and External Links
What is Trade Finance - Trade finance is the financing of international trade flows, designed to mitigate risks involved in international trade transactions.
Beginners guide to Trade Finance - This guide explains trade finance as a necessary system to facilitate international trade by providing credit, guarantees, and insurance, thereby managing risks and capital requirements.
What Is Trade Finance? A Guide for Beginners - Trade finance provides a set of financial tools to reduce risk, improve cash flow, and enable businesses to confidently engage in international trade transactions.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com