Blockchain reconciliation leverages decentralized ledger technology to provide transparent, real-time verification of financial transactions, reducing errors and fraud compared to traditional third-party reconciliation. Third-party reconciliation relies on intermediaries to match records between entities, often resulting in delays and increased operational costs. Explore the advantages of blockchain reconciliation to enhance accuracy and efficiency in accounting processes.
Why it is important
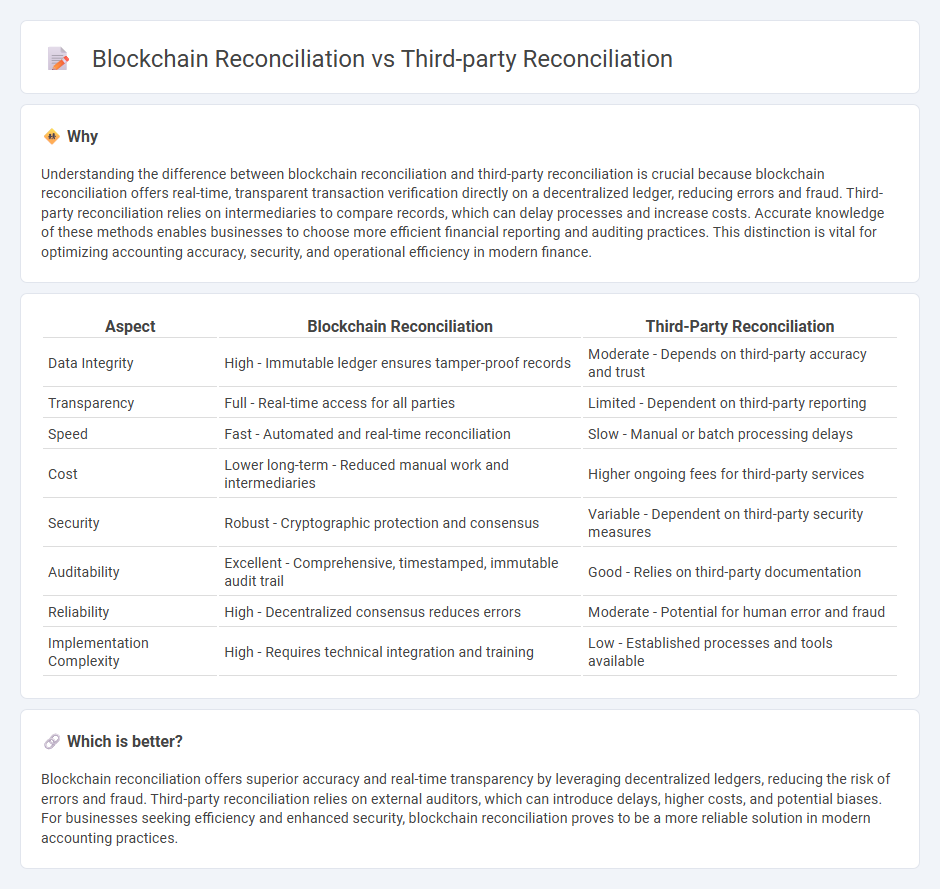
Understanding the difference between blockchain reconciliation and third-party reconciliation is crucial because blockchain reconciliation offers real-time, transparent transaction verification directly on a decentralized ledger, reducing errors and fraud. Third-party reconciliation relies on intermediaries to compare records, which can delay processes and increase costs. Accurate knowledge of these methods enables businesses to choose more efficient financial reporting and auditing practices. This distinction is vital for optimizing accounting accuracy, security, and operational efficiency in modern finance.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Blockchain Reconciliation | Third-Party Reconciliation |
|---|---|---|
| Data Integrity | High - Immutable ledger ensures tamper-proof records | Moderate - Depends on third-party accuracy and trust |
| Transparency | Full - Real-time access for all parties | Limited - Dependent on third-party reporting |
| Speed | Fast - Automated and real-time reconciliation | Slow - Manual or batch processing delays |
| Cost | Lower long-term - Reduced manual work and intermediaries | Higher ongoing fees for third-party services |
| Security | Robust - Cryptographic protection and consensus | Variable - Dependent on third-party security measures |
| Auditability | Excellent - Comprehensive, timestamped, immutable audit trail | Good - Relies on third-party documentation |
| Reliability | High - Decentralized consensus reduces errors | Moderate - Potential for human error and fraud |
| Implementation Complexity | High - Requires technical integration and training | Low - Established processes and tools available |
Which is better?
Blockchain reconciliation offers superior accuracy and real-time transparency by leveraging decentralized ledgers, reducing the risk of errors and fraud. Third-party reconciliation relies on external auditors, which can introduce delays, higher costs, and potential biases. For businesses seeking efficiency and enhanced security, blockchain reconciliation proves to be a more reliable solution in modern accounting practices.
Connection
Blockchain reconciliation enhances transparency and accuracy in accounting by automating the verification of transactions across distributed ledgers, reducing discrepancies commonly resolved through third-party reconciliation. Third-party reconciliation acts as an external verification layer, ensuring that records from different sources align, which complements blockchain's immutable audit trail by addressing exceptions and discrepancies. Together, these processes streamline financial audits and improve trust in financial data integrity by minimizing errors and fraud risks.
Key Terms
Intermediary
Third-party reconciliation relies on intermediaries like banks or clearinghouses to verify and match transaction records, introducing delays and potential errors. Blockchain reconciliation eliminates intermediaries by using a decentralized ledger where all parties have real-time access to immutable transaction data, increasing transparency and reducing reconciliation time. Discover how blockchain technology revolutionizes reconciliation by removing the need for third-party intermediaries.
Immutability
Third-party reconciliation relies heavily on trusted intermediaries to validate and synchronize transaction records, which can introduce delays and risks of data tampering. Blockchain reconciliation leverages decentralized ledger technology to ensure immutability, providing a transparent and tamper-proof record of all transactions without the need for intermediaries. Explore how blockchain's immutable nature transforms reconciliation processes by reducing fraud and enhancing trust.
Transparency
Third-party reconciliation relies on intermediaries to verify transactions, often causing delays and limited transparency due to centralized control. Blockchain reconciliation offers enhanced transparency through an immutable ledger system where every transaction is recorded and can be independently validated in real-time. Discover how leveraging blockchain can revolutionize trust and clarity in your reconciliation processes.
Source and External Links
Third Party Reconciliation - PioneerRx Pharmacy Software - Third-party reconciliation is the process of settling a customer's third-party payment against third-party claims, crucial for managing reimbursements and financial success, especially in independent pharmacies.
Lift Third-Party Delivery Reconciliations - Over Easy Office - Third-party reconciliation involves aggregating and matching transaction data from multiple delivery platforms to ensure accurate financial records, reduce errors, and optimize revenue tracking using automated and real-time tools.
In-house vs. third-party reconciliation - Reiterate Blog - Businesses use third-party reconciliation services to improve efficiency and reduce manual workload in payment reconciliation, though the choice depends on specific cost, scale, and capability needs.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com