Cryptotax regulations govern the taxation of cryptocurrency transactions, focusing on aspects like capital gains, income reporting, and compliance requirements specific to digital assets. Transfer pricing involves setting prices for transactions between related entities to allocate income and expenses accurately, ensuring tax compliance across jurisdictions. Explore more to understand how these distinct yet crucial financial concepts impact global business and tax strategies.
Why it is important
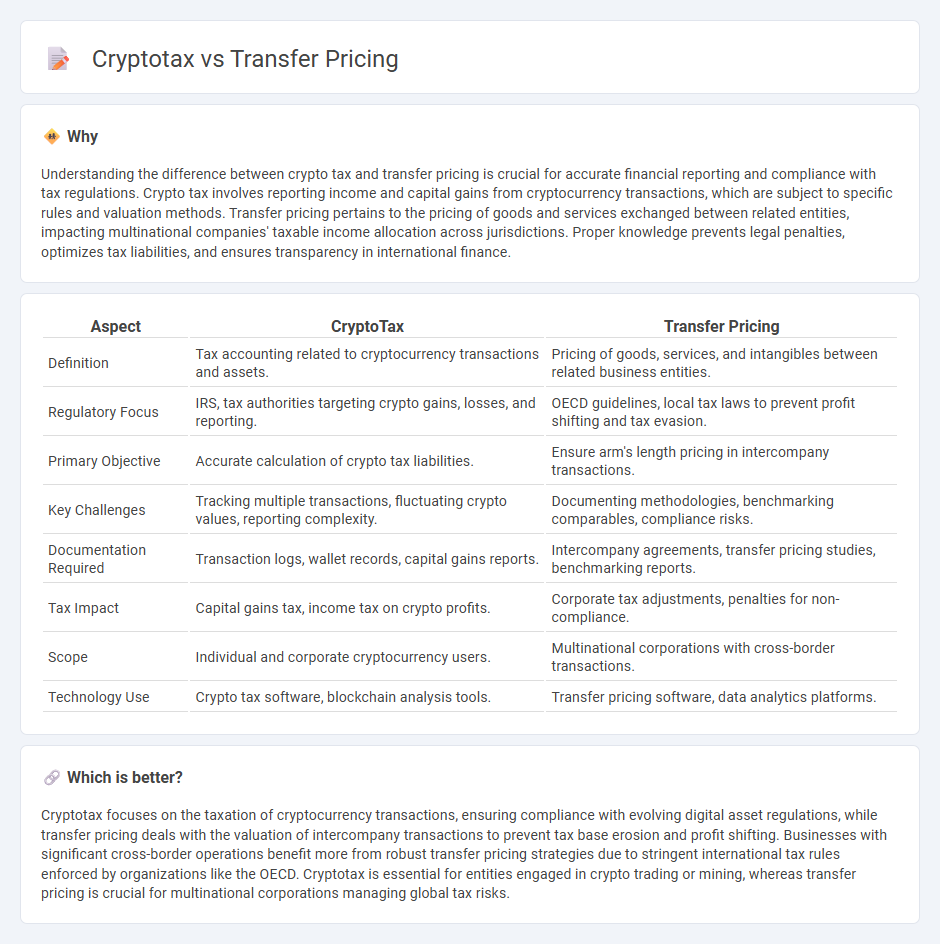
Understanding the difference between crypto tax and transfer pricing is crucial for accurate financial reporting and compliance with tax regulations. Crypto tax involves reporting income and capital gains from cryptocurrency transactions, which are subject to specific rules and valuation methods. Transfer pricing pertains to the pricing of goods and services exchanged between related entities, impacting multinational companies' taxable income allocation across jurisdictions. Proper knowledge prevents legal penalties, optimizes tax liabilities, and ensures transparency in international finance.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | CryptoTax | Transfer Pricing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Tax accounting related to cryptocurrency transactions and assets. | Pricing of goods, services, and intangibles between related business entities. |
| Regulatory Focus | IRS, tax authorities targeting crypto gains, losses, and reporting. | OECD guidelines, local tax laws to prevent profit shifting and tax evasion. |
| Primary Objective | Accurate calculation of crypto tax liabilities. | Ensure arm's length pricing in intercompany transactions. |
| Key Challenges | Tracking multiple transactions, fluctuating crypto values, reporting complexity. | Documenting methodologies, benchmarking comparables, compliance risks. |
| Documentation Required | Transaction logs, wallet records, capital gains reports. | Intercompany agreements, transfer pricing studies, benchmarking reports. |
| Tax Impact | Capital gains tax, income tax on crypto profits. | Corporate tax adjustments, penalties for non-compliance. |
| Scope | Individual and corporate cryptocurrency users. | Multinational corporations with cross-border transactions. |
| Technology Use | Crypto tax software, blockchain analysis tools. | Transfer pricing software, data analytics platforms. |
Which is better?
Cryptotax focuses on the taxation of cryptocurrency transactions, ensuring compliance with evolving digital asset regulations, while transfer pricing deals with the valuation of intercompany transactions to prevent tax base erosion and profit shifting. Businesses with significant cross-border operations benefit more from robust transfer pricing strategies due to stringent international tax rules enforced by organizations like the OECD. Cryptotax is essential for entities engaged in crypto trading or mining, whereas transfer pricing is crucial for multinational corporations managing global tax risks.
Connection
Cryptotax regulations directly impact transfer pricing by requiring multinational companies to accurately report cryptocurrency transactions and valuations across different tax jurisdictions. Transfer pricing rules ensure that intercompany crypto transfers are priced fairly, preventing profit shifting and tax evasion, which is crucial for compliance with tax authorities globally. Effective integration of cryptotax laws with transfer pricing frameworks enhances transparency and reduces risks of audits and penalties in global accounting practices.
Key Terms
**Transfer Pricing:**
Transfer pricing involves setting prices for transactions between related entities, ensuring compliance with tax regulations to prevent profit shifting and tax avoidance across jurisdictions. It requires detailed documentation and adherence to arm's length principles established by organizations like the OECD. Explore more about how transfer pricing strategies impact global tax compliance and multinational corporations.
Arm's Length Principle
The Arm's Length Principle is central to transfer pricing, ensuring transactions between related entities are priced as if between independent parties to prevent tax evasion. In contrast, cryptotax compliance struggles with this principle due to the decentralized and opaque nature of cryptocurrency transactions, complicating valuation and reporting. Explore detailed strategies on applying the Arm's Length Principle in both transfer pricing and cryptotax frameworks for accurate tax compliance.
Intercompany Transactions
Transfer pricing regulations govern the pricing of goods, services, and intangibles exchanged between related entities across borders to ensure compliance with tax laws and prevent profit shifting. Cryptotax issues in intercompany transactions arise from the use of cryptocurrencies, requiring clear valuation methods and reporting standards to address volatility and regulatory uncertainty. Explore how businesses can optimize intercompany transactions by aligning transfer pricing frameworks with evolving cryptotax guidelines.
Source and External Links
Intra-group transactions: the principles of transfer pricing - Transfer pricing is the price charged for goods and services between related companies or divisions within the same group, typically set to reflect arm's length conditions to allocate taxable profits appropriately among multinational enterprise members.
What is transfer pricing? - Transfer pricing is a technique used by multinational corporations to shift profits between subsidiaries by setting prices for goods or services exchanged internally, often resulting in profit shifting to tax havens to reduce tax liabilities.
Transfer Pricing and Cross-Border Transactions - Transfer pricing regulations, including those of the U.S. IRS and OECD guidelines, aim to ensure that income is properly taxed by using arm's length pricing for related-party transactions, preventing profit shifting and double taxation.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com