Blockchain audit trails create tamper-proof records by distributing transaction data across a decentralized ledger, ensuring transparency and security in accounting processes. Immutable audit logs maintain a fixed, unalterable record of accounting entries within a system, safeguarding data integrity and compliance with regulatory standards. Explore how these technologies transform auditing accuracy and trust in financial reporting.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between Blockchain audit trails and Immutable audit logs is crucial for accurate financial reporting and fraud prevention in accounting. Blockchain audit trails provide a decentralized and transparent record of transactions, ensuring data integrity through cryptographic proof. Immutable audit logs guarantee that once data is recorded, it cannot be altered or deleted, enhancing compliance with regulatory standards such as SOX and GDPR. This knowledge helps accountants implement robust internal controls and maintain trustworthy financial records.
Comparison Table
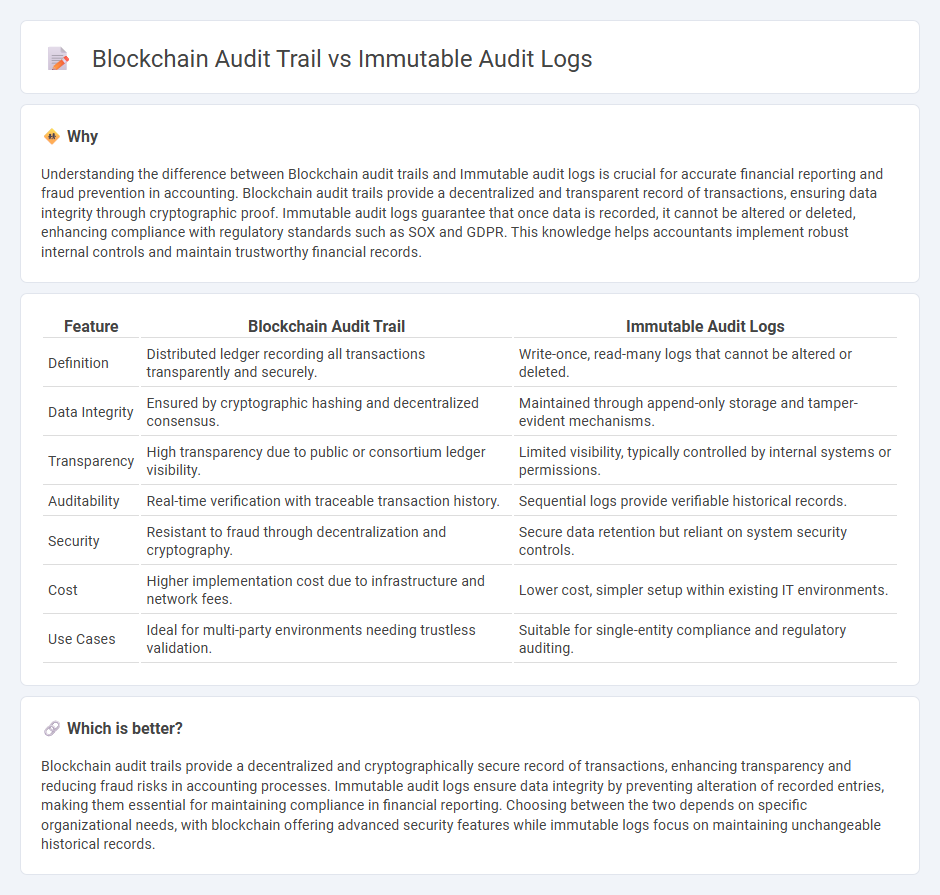
| Feature | Blockchain Audit Trail | Immutable Audit Logs |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Distributed ledger recording all transactions transparently and securely. | Write-once, read-many logs that cannot be altered or deleted. |
| Data Integrity | Ensured by cryptographic hashing and decentralized consensus. | Maintained through append-only storage and tamper-evident mechanisms. |
| Transparency | High transparency due to public or consortium ledger visibility. | Limited visibility, typically controlled by internal systems or permissions. |
| Auditability | Real-time verification with traceable transaction history. | Sequential logs provide verifiable historical records. |
| Security | Resistant to fraud through decentralization and cryptography. | Secure data retention but reliant on system security controls. |
| Cost | Higher implementation cost due to infrastructure and network fees. | Lower cost, simpler setup within existing IT environments. |
| Use Cases | Ideal for multi-party environments needing trustless validation. | Suitable for single-entity compliance and regulatory auditing. |
Which is better?
Blockchain audit trails provide a decentralized and cryptographically secure record of transactions, enhancing transparency and reducing fraud risks in accounting processes. Immutable audit logs ensure data integrity by preventing alteration of recorded entries, making them essential for maintaining compliance in financial reporting. Choosing between the two depends on specific organizational needs, with blockchain offering advanced security features while immutable logs focus on maintaining unchangeable historical records.
Connection
Blockchain audit trails create a transparent and tamper-proof record of financial transactions, ensuring data integrity in accounting processes. Immutable audit logs, inherent to blockchain technology, guarantee that once a transaction is recorded, it cannot be altered or deleted, enhancing trust and compliance. This connection strengthens the accuracy and reliability of audit records, reducing fraud and errors in financial reporting.
Key Terms
Immutability
Immutable audit logs ensure data integrity by preventing any alterations after entry, using cryptographic hashing and secure storage methods. Blockchain audit trails achieve immutability through distributed ledger technology, where each block is cryptographically linked and consensus mechanisms safeguard against tampering. Explore more to understand the technical distinctions and application scenarios between these two approaches.
Transparency
Immutable audit logs provide a secure and tamper-proof record of transactions within centralized systems, ensuring data integrity and transparency by preventing unauthorized modifications. Blockchain audit trails leverage decentralized ledger technology to create public, verifiable, and transparent records across participants, enhancing trust through consensus mechanisms and cryptographic proofs. Explore how these technologies redefine transparency and accountability in auditing by diving deeper into their comparative benefits.
Decentralization
Immutable audit logs provide tamper-proof records maintained by a central authority, limiting transparency and increasing trust dependency. Blockchain audit trails leverage decentralized consensus mechanisms across distributed nodes, enhancing security and transparency while eliminating single points of failure. Explore the detailed implications of decentralization on audit practices to understand which solution fits your organizational needs.
Source and External Links
Defining Immutable Audit Trail Basics and Their Importance - Astrella - Immutable audit logs maintain a tamper-proof cumulative history of all transactions, enhancing security, privacy, auditability, and efficiency by preventing overwriting or deletion of records through cryptographic linking.
Audit Logging: What It Is & How It Works | Datadog - Audit logs provide an immutable and detailed historical record of user and system activities to satisfy compliance and security requirements, distinctly different from regular logs meant for troubleshooting.
What Is an Audit Log for Compliance? [Includes Solutions] - Kiteworks - Secure immutable audit logs through encryption, strict access controls, detection of tampering, and exporting to external systems or archives to prevent unauthorized alteration and ensure long-term integrity.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com