Cryptocurrency taxation involves reporting capital gains and losses from digital asset transactions according to IRS guidelines, while tax loss harvesting strategically sells underperforming investments to offset taxable gains. Understanding the distinct tax implications and IRS regulations for cryptocurrencies is essential for optimizing tax outcomes. Explore detailed strategies to navigate both cryptocurrency taxation and tax loss harvesting effectively.
Why it is important
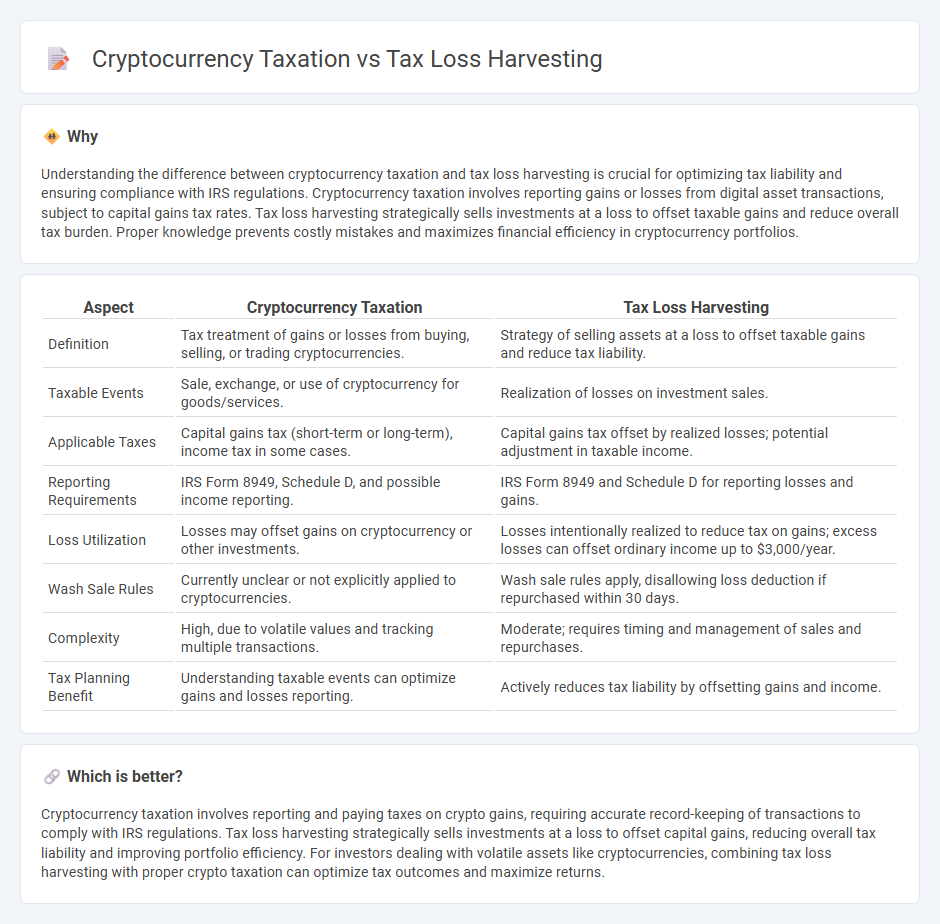
Understanding the difference between cryptocurrency taxation and tax loss harvesting is crucial for optimizing tax liability and ensuring compliance with IRS regulations. Cryptocurrency taxation involves reporting gains or losses from digital asset transactions, subject to capital gains tax rates. Tax loss harvesting strategically sells investments at a loss to offset taxable gains and reduce overall tax burden. Proper knowledge prevents costly mistakes and maximizes financial efficiency in cryptocurrency portfolios.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Cryptocurrency Taxation | Tax Loss Harvesting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Tax treatment of gains or losses from buying, selling, or trading cryptocurrencies. | Strategy of selling assets at a loss to offset taxable gains and reduce tax liability. |
| Taxable Events | Sale, exchange, or use of cryptocurrency for goods/services. | Realization of losses on investment sales. |
| Applicable Taxes | Capital gains tax (short-term or long-term), income tax in some cases. | Capital gains tax offset by realized losses; potential adjustment in taxable income. |
| Reporting Requirements | IRS Form 8949, Schedule D, and possible income reporting. | IRS Form 8949 and Schedule D for reporting losses and gains. |
| Loss Utilization | Losses may offset gains on cryptocurrency or other investments. | Losses intentionally realized to reduce tax on gains; excess losses can offset ordinary income up to $3,000/year. |
| Wash Sale Rules | Currently unclear or not explicitly applied to cryptocurrencies. | Wash sale rules apply, disallowing loss deduction if repurchased within 30 days. |
| Complexity | High, due to volatile values and tracking multiple transactions. | Moderate; requires timing and management of sales and repurchases. |
| Tax Planning Benefit | Understanding taxable events can optimize gains and losses reporting. | Actively reduces tax liability by offsetting gains and income. |
Which is better?
Cryptocurrency taxation involves reporting and paying taxes on crypto gains, requiring accurate record-keeping of transactions to comply with IRS regulations. Tax loss harvesting strategically sells investments at a loss to offset capital gains, reducing overall tax liability and improving portfolio efficiency. For investors dealing with volatile assets like cryptocurrencies, combining tax loss harvesting with proper crypto taxation can optimize tax outcomes and maximize returns.
Connection
Cryptocurrency taxation involves reporting gains and losses from digital asset transactions to comply with IRS regulations, while tax loss harvesting strategically sells losing crypto investments to offset taxable gains. By leveraging tax loss harvesting, investors reduce their overall tax liability on cryptocurrency profits by balancing gains with deductible losses. Effective management of crypto tax records is essential for maximizing tax benefits and ensuring accurate reporting under current tax codes.
Key Terms
Capital Gains
Tax loss harvesting allows investors to offset capital gains by selling cryptocurrencies at a loss, reducing taxable income on crypto investments. Cryptocurrency taxation treats gains from buying and selling digital assets as capital gains, with holding periods influencing short-term or long-term tax rates. Explore how to optimize your tax strategy by understanding the nuances of capital gains and losses in cryptocurrency trading.
Cost Basis
Tax loss harvesting involves selling securities at a loss to offset capital gains and reduce taxable income, specifically considering the cost basis, which is the original value of an asset for tax purposes. Cryptocurrency taxation requires careful tracking of cost basis to accurately report gains or losses, as each purchase and sale impacts taxable events differently compared to traditional assets. Explore more about how strategic cost basis management can optimize tax outcomes in both stock and crypto investments.
Wash Sale Rule
Tax loss harvesting allows investors to offset capital gains by selling securities at a loss, but the IRS's Wash Sale Rule disallows claiming these losses if the same or substantially identical securities are repurchased within 30 days. Cryptocurrency taxation differs as digital assets are not currently subject to the Wash Sale Rule, enabling tax loss harvesting without the 30-day repurchase limitation. Explore further to understand how tax strategies differ between traditional investments and cryptocurrencies under current IRS regulations.
Source and External Links
Tax-Loss Harvesting | Vanguard - Tax-loss harvesting is a strategy involving selling investments at a loss to offset gains in other investments, potentially reducing taxes and increasing after-tax returns.
Tax Loss Harvesting - Tax loss harvesting is an investment strategy that generates capital losses to gain a tax advantage by selling depreciated securities and offsetting gains.
How Does Tax-Loss Harvesting Work? - Tax-loss harvesting is a strategy where you sell investments at a loss to offset current or future capital gains, thereby lowering your tax liability and maintaining your investment exposure.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com