Data lake auditing involves continuous monitoring and analysis of vast datasets within an organization's data repository, ensuring data integrity, compliance, and real-time risk management. External audit focuses on independent assessment of financial statements and regulatory adherence, providing assurance on accuracy and transparency for stakeholders. Explore the key differences and benefits of each auditing method for comprehensive accounting oversight.
Why it is important
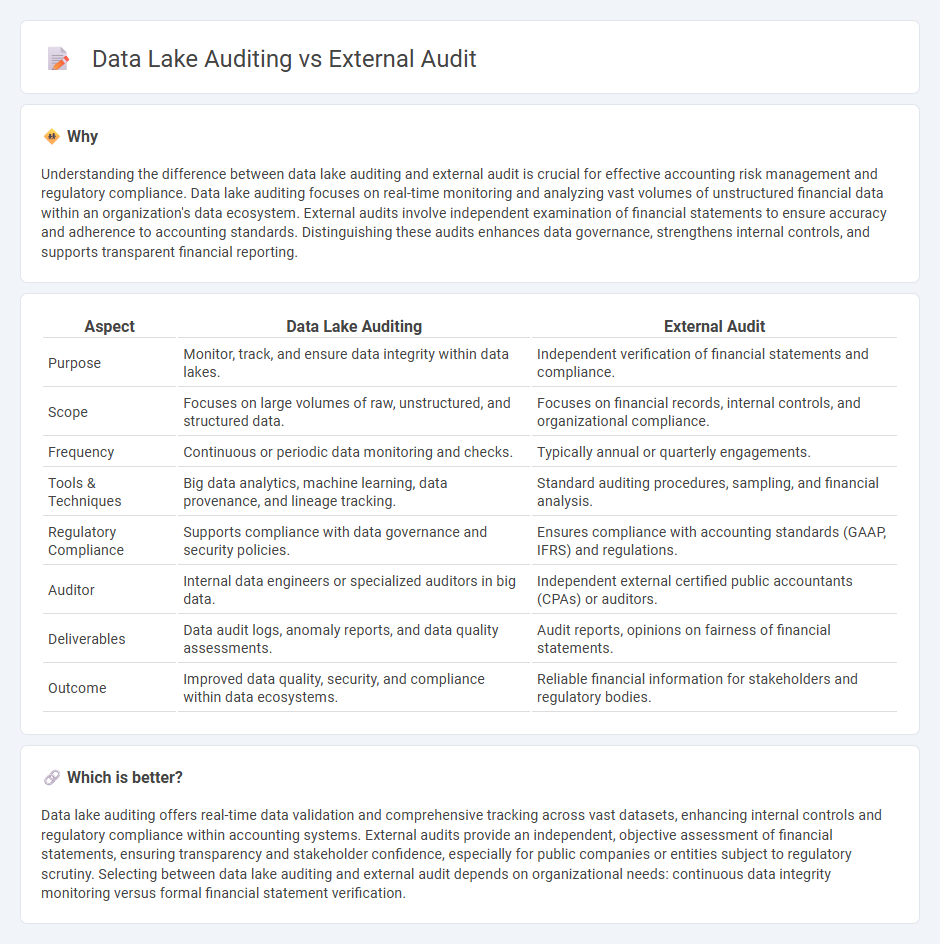
Understanding the difference between data lake auditing and external audit is crucial for effective accounting risk management and regulatory compliance. Data lake auditing focuses on real-time monitoring and analyzing vast volumes of unstructured financial data within an organization's data ecosystem. External audits involve independent examination of financial statements to ensure accuracy and adherence to accounting standards. Distinguishing these audits enhances data governance, strengthens internal controls, and supports transparent financial reporting.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Data Lake Auditing | External Audit |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Monitor, track, and ensure data integrity within data lakes. | Independent verification of financial statements and compliance. |
| Scope | Focuses on large volumes of raw, unstructured, and structured data. | Focuses on financial records, internal controls, and organizational compliance. |
| Frequency | Continuous or periodic data monitoring and checks. | Typically annual or quarterly engagements. |
| Tools & Techniques | Big data analytics, machine learning, data provenance, and lineage tracking. | Standard auditing procedures, sampling, and financial analysis. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Supports compliance with data governance and security policies. | Ensures compliance with accounting standards (GAAP, IFRS) and regulations. |
| Auditor | Internal data engineers or specialized auditors in big data. | Independent external certified public accountants (CPAs) or auditors. |
| Deliverables | Data audit logs, anomaly reports, and data quality assessments. | Audit reports, opinions on fairness of financial statements. |
| Outcome | Improved data quality, security, and compliance within data ecosystems. | Reliable financial information for stakeholders and regulatory bodies. |
Which is better?
Data lake auditing offers real-time data validation and comprehensive tracking across vast datasets, enhancing internal controls and regulatory compliance within accounting systems. External audits provide an independent, objective assessment of financial statements, ensuring transparency and stakeholder confidence, especially for public companies or entities subject to regulatory scrutiny. Selecting between data lake auditing and external audit depends on organizational needs: continuous data integrity monitoring versus formal financial statement verification.
Connection
Data lake auditing collects comprehensive, raw data from financial systems, enabling detailed traceability and real-time monitoring essential for accurate accounting records. External audits rely on this audited data lake information to validate financial statements, ensuring regulatory compliance and reducing risks of material misstatements. Integration of data lake auditing streamlines evidence gathering, enhances transparency, and supports more efficient external audit processes in accounting.
Key Terms
Independence
External audit emphasizes independence by involving unbiased third-party auditors to ensure objective financial assessments and regulatory compliance. Data lake auditing, while maintaining integrity through automated logs and access controls, primarily focuses on data governance within the organization rather than independence from stakeholders. Discover how the distinct roles of independence shape both external audits and data lake auditing processes.
Data integrity
External audit ensures data integrity by independently verifying financial statements and compliance with regulations through systematic examination and validation of source records. Data lake auditing focuses on continuous monitoring of data lineage, access controls, and transformation processes to maintain accuracy and reliability of large volumes of unstructured and structured data within the lake. Explore the detailed differences and best practices in data integrity management between external audits and data lake auditing.
Audit trail
External audit relies on independent verification of financial records, emphasizing transparency and regulatory compliance through comprehensive audit trails. Data lake auditing focuses on tracking data ingestion, transformation, and access within vast repositories, ensuring data integrity and security. Discover how effective audit trails enhance accountability across both financial and data environments.
Source and External Links
Understanding the Purpose and Benefits of External Audits - Concur - An external audit is an independent review of financial statements and internal controls conducted by an outside auditor to provide accurate financial reporting, identify weaknesses, and improve organizational decision making through a structured multi-step process.
External Audit vs. Internal Audit: What's the Difference? - Hilbert College - External audits are performed by independent certified public accountants to verify the accuracy and fairness of financial statements for stakeholders, providing an impartial opinion and highlighting issues or weaknesses under generally accepted auditing standards.
Definition of External Audit - Gartner Finance Glossary - An external audit is a financial review conducted by an independent party according to regulatory frameworks like SOX, producing impartial reports used by investors and regulators to assess a company's financial integrity.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com