Data lake reconciliation involves comparing and verifying large-scale, unstructured financial data stored in a data lake to ensure accuracy before further processing. Subledger to general ledger reconciliation focuses on matching detailed transaction records within subledgers to the summarized entries in the general ledger for accurate financial reporting. Explore the differences and best practices for each reconciliation method to enhance accounting accuracy and efficiency.
Why it is important
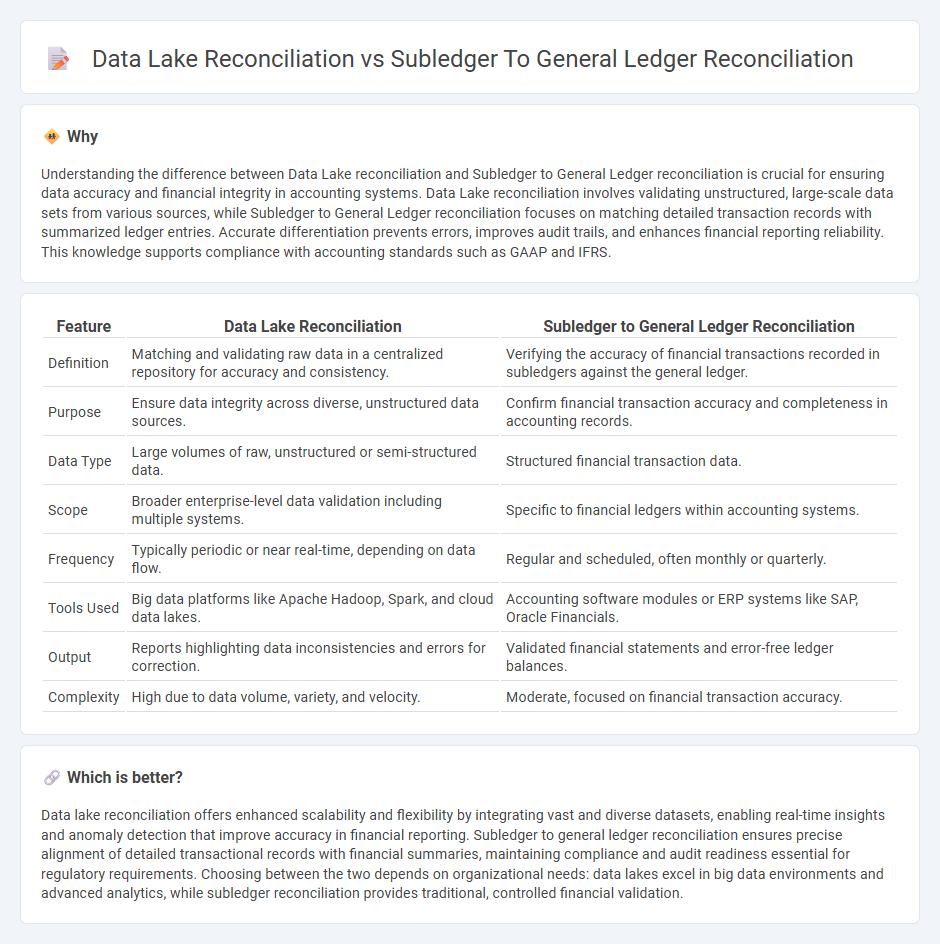
Understanding the difference between Data Lake reconciliation and Subledger to General Ledger reconciliation is crucial for ensuring data accuracy and financial integrity in accounting systems. Data Lake reconciliation involves validating unstructured, large-scale data sets from various sources, while Subledger to General Ledger reconciliation focuses on matching detailed transaction records with summarized ledger entries. Accurate differentiation prevents errors, improves audit trails, and enhances financial reporting reliability. This knowledge supports compliance with accounting standards such as GAAP and IFRS.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Data Lake Reconciliation | Subledger to General Ledger Reconciliation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Matching and validating raw data in a centralized repository for accuracy and consistency. | Verifying the accuracy of financial transactions recorded in subledgers against the general ledger. |
| Purpose | Ensure data integrity across diverse, unstructured data sources. | Confirm financial transaction accuracy and completeness in accounting records. |
| Data Type | Large volumes of raw, unstructured or semi-structured data. | Structured financial transaction data. |
| Scope | Broader enterprise-level data validation including multiple systems. | Specific to financial ledgers within accounting systems. |
| Frequency | Typically periodic or near real-time, depending on data flow. | Regular and scheduled, often monthly or quarterly. |
| Tools Used | Big data platforms like Apache Hadoop, Spark, and cloud data lakes. | Accounting software modules or ERP systems like SAP, Oracle Financials. |
| Output | Reports highlighting data inconsistencies and errors for correction. | Validated financial statements and error-free ledger balances. |
| Complexity | High due to data volume, variety, and velocity. | Moderate, focused on financial transaction accuracy. |
Which is better?
Data lake reconciliation offers enhanced scalability and flexibility by integrating vast and diverse datasets, enabling real-time insights and anomaly detection that improve accuracy in financial reporting. Subledger to general ledger reconciliation ensures precise alignment of detailed transactional records with financial summaries, maintaining compliance and audit readiness essential for regulatory requirements. Choosing between the two depends on organizational needs: data lakes excel in big data environments and advanced analytics, while subledger reconciliation provides traditional, controlled financial validation.
Connection
Data lake reconciliation aggregates large volumes of transaction data, enabling comprehensive cross-checks with subledger records to identify discrepancies early. Subledger to general ledger reconciliation ensures that detailed financial transactions recorded in subledgers accurately reflect in the general ledger, maintaining financial integrity. Integrating data lakes with reconciliation processes enhances real-time data validation and improves accuracy in financial reporting.
Key Terms
Subledger to general ledger reconciliation:
Subledger to general ledger reconciliation involves matching detailed transactional data from subledgers, such as accounts payable or receivable, with the summarized balances in the general ledger to ensure accuracy and completeness in financial reporting. This process helps identify discrepancies, errors, or unrecorded transactions that could impact financial statements and compliance with accounting standards. Explore more about effective reconciliation techniques and tools to enhance financial integrity and accuracy.
Journal Entries
Subledger to general ledger reconciliation involves verifying journal entries to ensure all transaction details align between subsidiary records and the consolidated financial ledger, maintaining accuracy in financial reporting. Data lake reconciliation focuses on validating journal entry data integrity across vast, unstructured datasets to support analytics and compliance. Explore how each method enhances journal entry accuracy and financial transparency.
Trial Balance
Subledger to general ledger reconciliation ensures that detailed transaction data in subledgers accurately matches summary balances in the general ledger, directly impacting the trial balance accuracy. Data lake reconciliation involves validating financial data stored in large, unstructured repositories against the general ledger to support comprehensive audit trails and advanced analytics. Explore how these reconciliation methods enhance trial balance integrity and streamline financial reporting accuracy.
Source and External Links
A Guide for General Ledger to Subledger Reconciliation - Leapfin - Subledger to general ledger reconciliation involves comparing balances, investigating differences, making adjustments, and confirming accuracy through an 8-step process including trial balance reports, data mapping, aggregation, and iterative checks.
General Ledger Reconciliations: How to Conduct GL Recs - Numeric - The reconciliation process includes comparing balances, investigating discrepancies, adjusting entries in both ledgers, and verifying matched balances, with automation recommended to improve efficiency and accuracy in this traditionally time-consuming task.
Account Reconciliation and Subledgers - Oracle Help Center - Reconciliation is performed by comparing subledger balances (e.g., payables and receivables) against the general ledger, with automated identification of exceptions such as unmatched transactions or incomplete accounting entries.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com