Algorithmic compliance leverages automated systems and artificial intelligence to ensure financial transactions and reporting adhere to regulatory standards in real-time, enhancing accuracy and efficiency. Forensic accounting focuses on investigating and analyzing financial records to detect fraud, embezzlement, and other financial discrepancies through detailed examination and expert evaluation. Explore the distinct methodologies and benefits of algorithmic compliance and forensic accounting to optimize your financial oversight strategies.
Why it is important
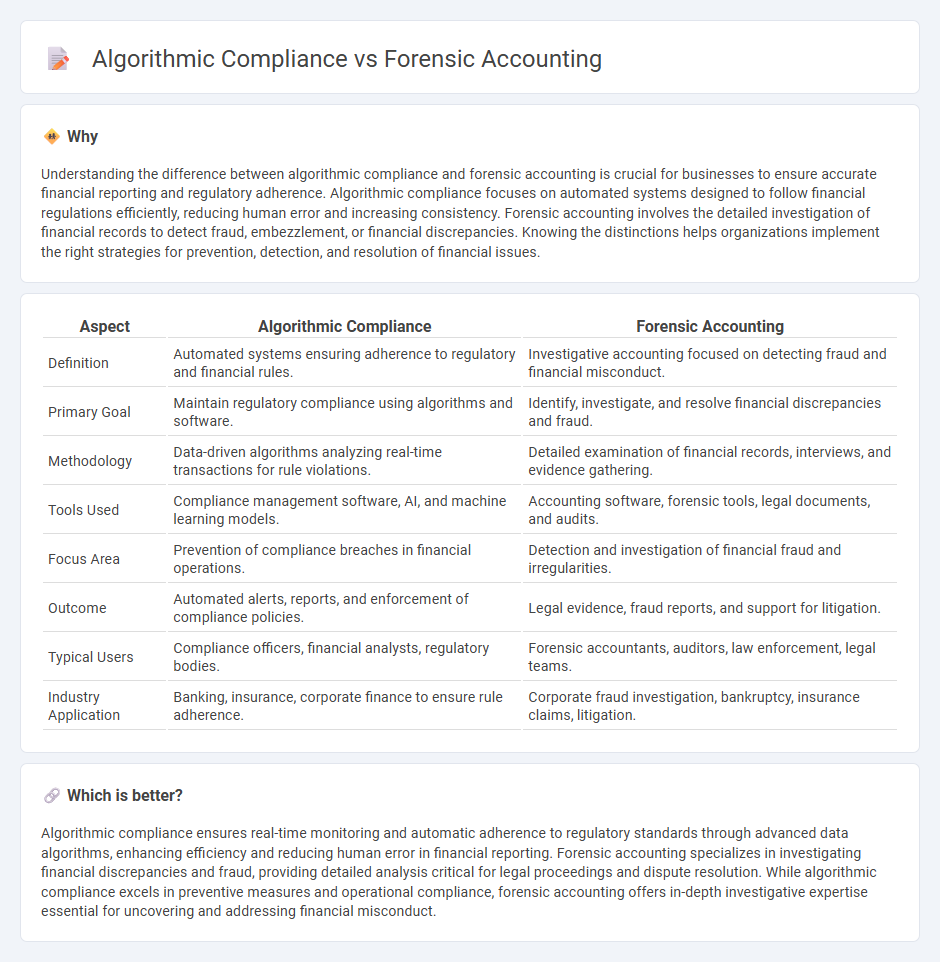
Understanding the difference between algorithmic compliance and forensic accounting is crucial for businesses to ensure accurate financial reporting and regulatory adherence. Algorithmic compliance focuses on automated systems designed to follow financial regulations efficiently, reducing human error and increasing consistency. Forensic accounting involves the detailed investigation of financial records to detect fraud, embezzlement, or financial discrepancies. Knowing the distinctions helps organizations implement the right strategies for prevention, detection, and resolution of financial issues.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Algorithmic Compliance | Forensic Accounting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Automated systems ensuring adherence to regulatory and financial rules. | Investigative accounting focused on detecting fraud and financial misconduct. |
| Primary Goal | Maintain regulatory compliance using algorithms and software. | Identify, investigate, and resolve financial discrepancies and fraud. |
| Methodology | Data-driven algorithms analyzing real-time transactions for rule violations. | Detailed examination of financial records, interviews, and evidence gathering. |
| Tools Used | Compliance management software, AI, and machine learning models. | Accounting software, forensic tools, legal documents, and audits. |
| Focus Area | Prevention of compliance breaches in financial operations. | Detection and investigation of financial fraud and irregularities. |
| Outcome | Automated alerts, reports, and enforcement of compliance policies. | Legal evidence, fraud reports, and support for litigation. |
| Typical Users | Compliance officers, financial analysts, regulatory bodies. | Forensic accountants, auditors, law enforcement, legal teams. |
| Industry Application | Banking, insurance, corporate finance to ensure rule adherence. | Corporate fraud investigation, bankruptcy, insurance claims, litigation. |
Which is better?
Algorithmic compliance ensures real-time monitoring and automatic adherence to regulatory standards through advanced data algorithms, enhancing efficiency and reducing human error in financial reporting. Forensic accounting specializes in investigating financial discrepancies and fraud, providing detailed analysis critical for legal proceedings and dispute resolution. While algorithmic compliance excels in preventive measures and operational compliance, forensic accounting offers in-depth investigative expertise essential for uncovering and addressing financial misconduct.
Connection
Algorithmic compliance leverages automated systems to ensure adherence to accounting regulations by systematically analyzing financial data, while forensic accounting applies investigative techniques to detect fraud and financial discrepancies. Both disciplines rely on data accuracy, pattern recognition, and regulatory frameworks to enhance transparency and accountability within financial reporting. Integrating algorithmic compliance tools with forensic accounting methods improves the identification and prevention of financial misconduct.
Key Terms
Forensic accounting:
Forensic accounting involves the application of accounting principles and investigative techniques to detect and prevent financial fraud, ensuring the integrity of financial statements. It leverages detailed transaction analysis, data mining, and audit trails to uncover discrepancies and support legal proceedings. Explore our comprehensive resources to understand how forensic accounting safeguards organizations against financial misconduct.
Fraud detection
Forensic accounting utilizes detailed financial analysis and investigative techniques to identify discrepancies and fraudulent activities within financial records, emphasizing human judgment and contextual insights. Algorithmic compliance leverages machine learning models and data algorithms to detect patterns indicative of fraud, offering real-time monitoring and scalability across extensive datasets. Explore further to understand how integrating these approaches enhances fraud detection efficacy.
Litigation support
Forensic accounting involves detailed financial analysis and investigation to uncover fraud, misrepresentation, or financial discrepancies, often serving as critical evidence in litigation support. Algorithmic compliance leverages automated systems and artificial intelligence to ensure regulatory adherence, detect anomalies, and generate audit trails that assist in legal disputes. Explore how combining forensic accounting with algorithmic compliance enhances accuracy and efficiency in litigation support processes.
Source and External Links
Forensic Accounting Career Overview - Forensic accountants use accounting and auditing skills to analyze finances for evidence or risk of crime, such as fraud and embezzlement.
What Is Forensic Accounting? - Forensic accountants apply accounting skills to investigate financial crimes, determining the extent and origins of such crimes.
Forensic accounting - Forensic accounting investigates financial crimes by translating complex transactions into understandable terms, often serving as expert witnesses.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com