Sustainability ledger tracks a company's overall environmental, social, and governance (ESG) metrics, integrating financial and non-financial data to provide a comprehensive view of sustainable performance. Carbon accounting specifically focuses on measuring and managing greenhouse gas emissions to quantify an organization's carbon footprint and compliance with regulatory standards. Discover how these accounting approaches enhance corporate responsibility and drive informed decision-making.
Why it is important
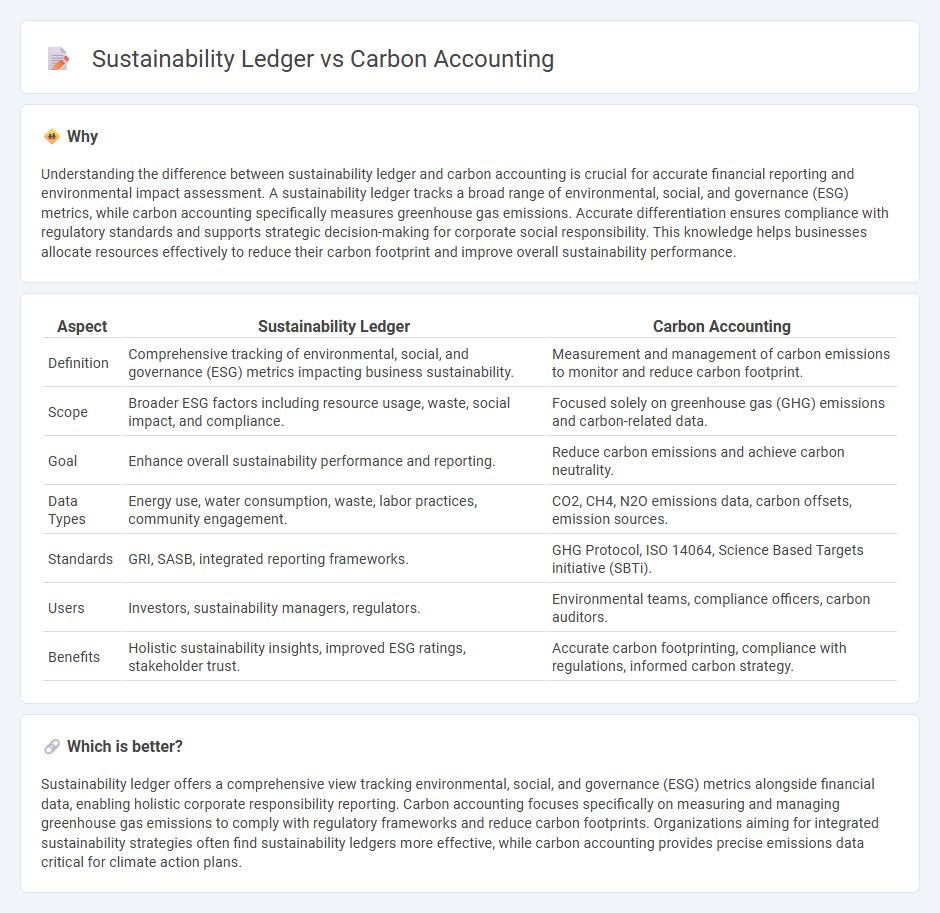
Understanding the difference between sustainability ledger and carbon accounting is crucial for accurate financial reporting and environmental impact assessment. A sustainability ledger tracks a broad range of environmental, social, and governance (ESG) metrics, while carbon accounting specifically measures greenhouse gas emissions. Accurate differentiation ensures compliance with regulatory standards and supports strategic decision-making for corporate social responsibility. This knowledge helps businesses allocate resources effectively to reduce their carbon footprint and improve overall sustainability performance.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Sustainability Ledger | Carbon Accounting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Comprehensive tracking of environmental, social, and governance (ESG) metrics impacting business sustainability. | Measurement and management of carbon emissions to monitor and reduce carbon footprint. |
| Scope | Broader ESG factors including resource usage, waste, social impact, and compliance. | Focused solely on greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions and carbon-related data. |
| Goal | Enhance overall sustainability performance and reporting. | Reduce carbon emissions and achieve carbon neutrality. |
| Data Types | Energy use, water consumption, waste, labor practices, community engagement. | CO2, CH4, N2O emissions data, carbon offsets, emission sources. |
| Standards | GRI, SASB, integrated reporting frameworks. | GHG Protocol, ISO 14064, Science Based Targets initiative (SBTi). |
| Users | Investors, sustainability managers, regulators. | Environmental teams, compliance officers, carbon auditors. |
| Benefits | Holistic sustainability insights, improved ESG ratings, stakeholder trust. | Accurate carbon footprinting, compliance with regulations, informed carbon strategy. |
Which is better?
Sustainability ledger offers a comprehensive view tracking environmental, social, and governance (ESG) metrics alongside financial data, enabling holistic corporate responsibility reporting. Carbon accounting focuses specifically on measuring and managing greenhouse gas emissions to comply with regulatory frameworks and reduce carbon footprints. Organizations aiming for integrated sustainability strategies often find sustainability ledgers more effective, while carbon accounting provides precise emissions data critical for climate action plans.
Connection
Sustainability ledger integrates environmental, social, and governance (ESG) data to provide a comprehensive record of a company's sustainable practices, directly supporting carbon accounting by tracking greenhouse gas emissions and carbon credits. Carbon accounting quantifies emission sources and offsets, enabling businesses to measure their carbon footprint and align with regulatory requirements and sustainability goals. Together, they enhance transparency, facilitate compliance with international standards such as the Greenhouse Gas Protocol, and drive informed decision-making for reducing environmental impact.
Key Terms
**Carbon Accounting:**
Carbon accounting quantifies greenhouse gas emissions across organizational activities, enabling accurate measurement and management of carbon footprints. It provides detailed emissions data crucial for meeting regulatory requirements and setting targeted reduction goals. Explore how carbon accounting drives informed sustainability strategies and enhances environmental accountability.
Greenhouse Gas (GHG) Emissions
Carbon accounting quantifies greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions by systematically tracking carbon footprints across organizational activities to meet regulatory standards and reduce environmental impact. Sustainability ledgers expand this scope by integrating carbon data with broader environmental, social, and governance (ESG) metrics, enabling comprehensive sustainability reporting and strategic decision-making. Explore how these tools transform environmental management and compliance in your sustainability journey.
Carbon Footprint
Carbon accounting quantifies greenhouse gas emissions produced directly or indirectly by organizations, products, or activities, focusing on accurate carbon footprint measurement. Sustainability ledger tracks a broader range of environmental, social, and governance (ESG) metrics, embedding carbon footprint data within comprehensive sustainability performance records. Explore how integrating detailed carbon accounting enhances the effectiveness of sustainability ledgers to drive impactful climate action.
Source and External Links
Carbon accounting, explained - Normative.io - Carbon accounting is the process of calculating how much greenhouse gas an organization emits, enabling businesses to measure their climate impact, comply with regulations, reduce emissions, and report progress to stakeholders.
What Is Carbon Accounting? | IBM - Carbon accounting quantifies greenhouse gas emissions from direct and indirect sources, often expressed in carbon dioxide equivalents (CO2e), helping organizations understand and reduce their climate impact.
Carbon Accounting | CarbonNeutral - Carbon accounting tracks greenhouse gas emissions to help businesses identify emissions hotspots, implement reduction strategies, and comply with increasing legal requirements worldwide.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com