Dynamic allocation tracing continuously monitors and allocates costs in real-time, providing immediate insights into financial resource utilization. Periodic reconciliation, on the other hand, involves reviewing and adjusting accounts at regular intervals to ensure accuracy over time. Explore these contrasting accounting methods to optimize your financial management strategy.
Why it is important
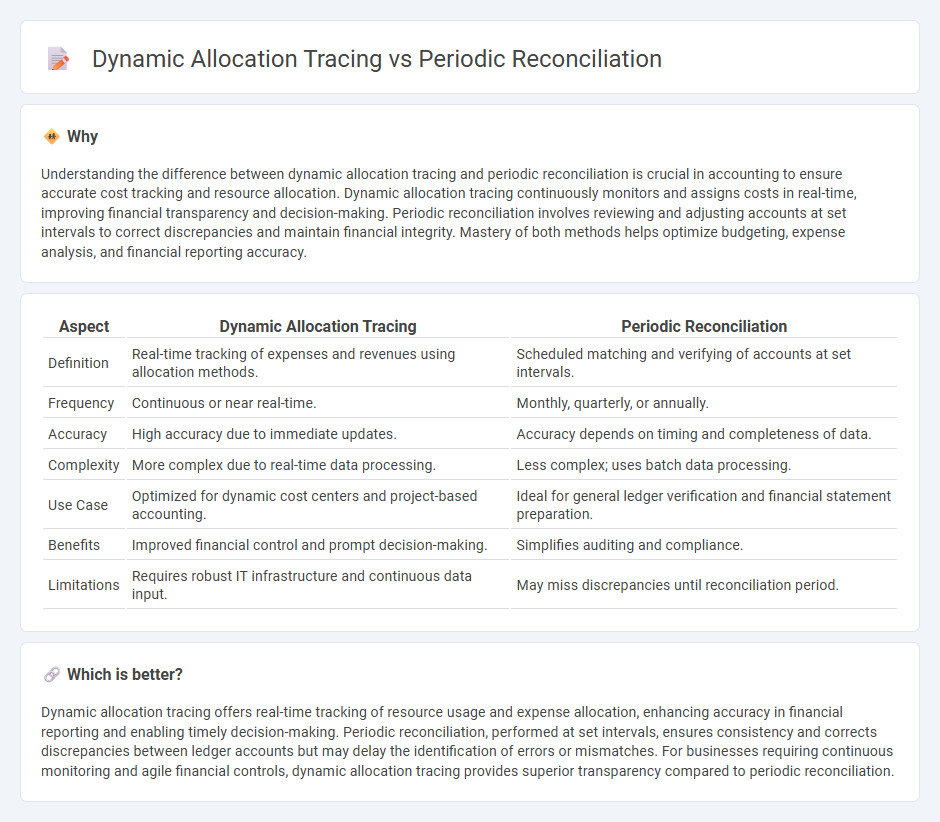
Understanding the difference between dynamic allocation tracing and periodic reconciliation is crucial in accounting to ensure accurate cost tracking and resource allocation. Dynamic allocation tracing continuously monitors and assigns costs in real-time, improving financial transparency and decision-making. Periodic reconciliation involves reviewing and adjusting accounts at set intervals to correct discrepancies and maintain financial integrity. Mastery of both methods helps optimize budgeting, expense analysis, and financial reporting accuracy.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Dynamic Allocation Tracing | Periodic Reconciliation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Real-time tracking of expenses and revenues using allocation methods. | Scheduled matching and verifying of accounts at set intervals. |
| Frequency | Continuous or near real-time. | Monthly, quarterly, or annually. |
| Accuracy | High accuracy due to immediate updates. | Accuracy depends on timing and completeness of data. |
| Complexity | More complex due to real-time data processing. | Less complex; uses batch data processing. |
| Use Case | Optimized for dynamic cost centers and project-based accounting. | Ideal for general ledger verification and financial statement preparation. |
| Benefits | Improved financial control and prompt decision-making. | Simplifies auditing and compliance. |
| Limitations | Requires robust IT infrastructure and continuous data input. | May miss discrepancies until reconciliation period. |
Which is better?
Dynamic allocation tracing offers real-time tracking of resource usage and expense allocation, enhancing accuracy in financial reporting and enabling timely decision-making. Periodic reconciliation, performed at set intervals, ensures consistency and corrects discrepancies between ledger accounts but may delay the identification of errors or mismatches. For businesses requiring continuous monitoring and agile financial controls, dynamic allocation tracing provides superior transparency compared to periodic reconciliation.
Connection
Dynamic allocation tracing tracks resource usage in real time, providing detailed insights into financial transactions and cost centers. Periodic reconciliation uses this data to match internal records with external statements, ensuring accuracy and consistency in accounting. Their integration enhances the precision of financial reporting and improves budget management.
Key Terms
Inventory Valuation
Periodic reconciliation in inventory valuation involves updating stock values at fixed intervals, often leading to discrepancies due to timing differences. Dynamic allocation tracing continuously monitors inventory movements, providing real-time, precise valuation reflective of actual stock levels and costs. Explore detailed insights on how these methods impact accuracy and financial reporting in inventory management.
Real-time Tracking
Periodic reconciliation involves batch processing at set intervals to update resource allocation data, providing snapshots of usage without continuous monitoring. Dynamic allocation tracing offers real-time tracking by continuously capturing allocation and deallocation events, enabling immediate detection of memory leaks and performance bottlenecks. Explore in-depth comparisons and best practices for optimizing resource management through real-time tracking techniques.
Adjustment Entries
Periodic reconciliation involves manually reviewing and correcting discrepancies in financial records at regular intervals, generating adjustment entries to align accounts. Dynamic allocation tracing tracks resource usage or costs continuously, automatically updating adjustment entries to reflect real-time data changes. Explore detailed insights on how adjustment entries optimize accuracy in both reconciliation methods.
Source and External Links
What is Bank Reconciliation? - Periodic bank reconciliation involves regularly comparing bank statements to internal records, typically monthly or quarterly, to ensure accuracy and identify discrepancies.
Handbook for Conducting Periodic Reconciliation - This handbook outlines the process for conducting periodic reconciliations, such as budgeted to actual costs, with options for semi-annual or quarterly reconciliation.
Reconciliation Procedures - Periodic reconciliations, such as monthly bank reconciliations, are required to ensure that financial records accurately reflect account balances and statements from financial institutions.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com