Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) integration in accounting involves systematically incorporating sustainability metrics into financial analysis and reporting, enhancing transparency and accountability. Stakeholder engagement focuses on actively involving diverse groups affected by corporate decisions to align business practices with their values and expectations. Explore how blending ESG integration and stakeholder engagement drives more comprehensive and responsible accounting strategies.
Why it is important
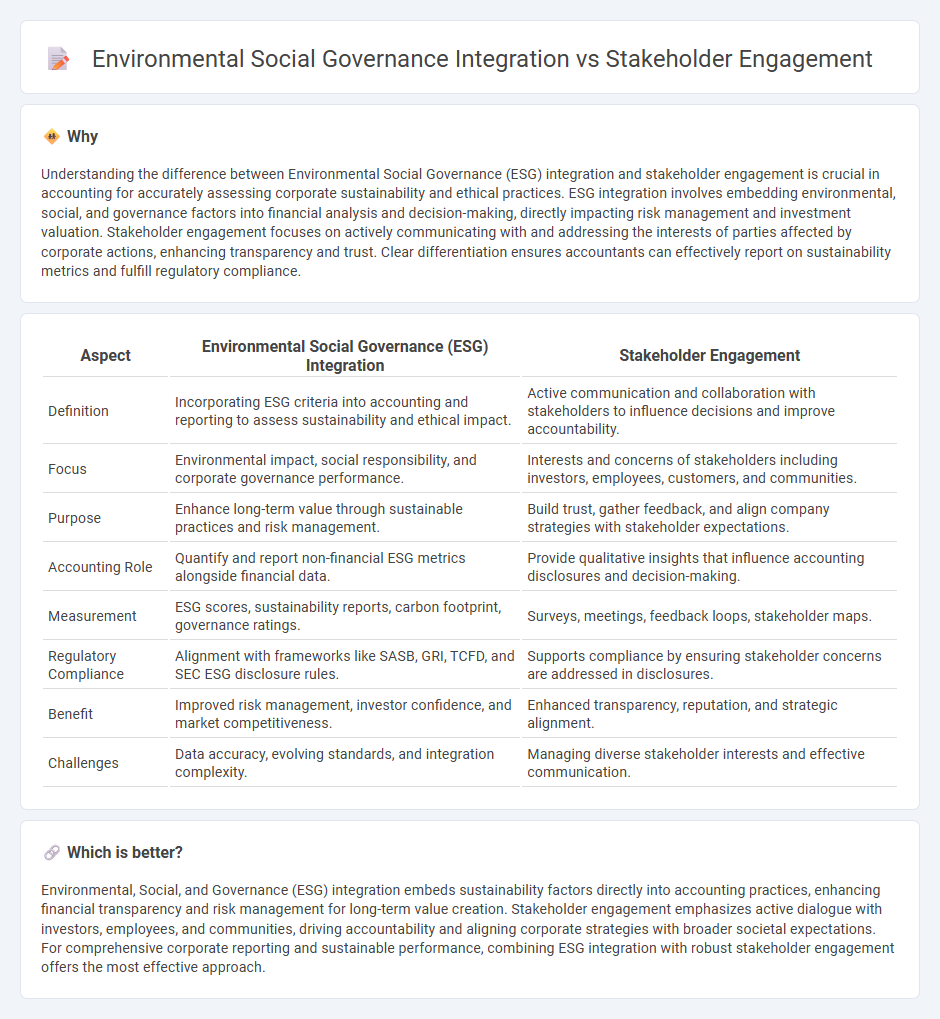
Understanding the difference between Environmental Social Governance (ESG) integration and stakeholder engagement is crucial in accounting for accurately assessing corporate sustainability and ethical practices. ESG integration involves embedding environmental, social, and governance factors into financial analysis and decision-making, directly impacting risk management and investment valuation. Stakeholder engagement focuses on actively communicating with and addressing the interests of parties affected by corporate actions, enhancing transparency and trust. Clear differentiation ensures accountants can effectively report on sustainability metrics and fulfill regulatory compliance.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Environmental Social Governance (ESG) Integration | Stakeholder Engagement |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Incorporating ESG criteria into accounting and reporting to assess sustainability and ethical impact. | Active communication and collaboration with stakeholders to influence decisions and improve accountability. |
| Focus | Environmental impact, social responsibility, and corporate governance performance. | Interests and concerns of stakeholders including investors, employees, customers, and communities. |
| Purpose | Enhance long-term value through sustainable practices and risk management. | Build trust, gather feedback, and align company strategies with stakeholder expectations. |
| Accounting Role | Quantify and report non-financial ESG metrics alongside financial data. | Provide qualitative insights that influence accounting disclosures and decision-making. |
| Measurement | ESG scores, sustainability reports, carbon footprint, governance ratings. | Surveys, meetings, feedback loops, stakeholder maps. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Alignment with frameworks like SASB, GRI, TCFD, and SEC ESG disclosure rules. | Supports compliance by ensuring stakeholder concerns are addressed in disclosures. |
| Benefit | Improved risk management, investor confidence, and market competitiveness. | Enhanced transparency, reputation, and strategic alignment. |
| Challenges | Data accuracy, evolving standards, and integration complexity. | Managing diverse stakeholder interests and effective communication. |
Which is better?
Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) integration embeds sustainability factors directly into accounting practices, enhancing financial transparency and risk management for long-term value creation. Stakeholder engagement emphasizes active dialogue with investors, employees, and communities, driving accountability and aligning corporate strategies with broader societal expectations. For comprehensive corporate reporting and sustainable performance, combining ESG integration with robust stakeholder engagement offers the most effective approach.
Connection
Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) integration in accounting ensures that financial reports reflect a company's sustainability and ethical practices, aligning with stakeholders' values and expectations. Stakeholder engagement provides critical insights and feedback that enhance the accuracy and relevance of ESG disclosures, fostering transparency and accountability. This connection drives better risk management and long-term value creation by incorporating diverse stakeholder perspectives into corporate strategy and reporting.
Key Terms
Materiality
Stakeholder engagement plays a crucial role in identifying and prioritizing material ESG issues that directly impact business value and societal outcomes. Materiality assessments integrate environmental, social, and governance factors to align corporate strategies with stakeholder expectations and regulatory requirements. Discover more about leveraging materiality for enhanced ESG integration and effective stakeholder collaboration.
Impact assessment
Stakeholder engagement is a critical process in impact assessment, ensuring diverse perspectives shape environmental and social outcomes, while Environmental Social Governance (ESG) integration embeds these considerations into corporate strategy and risk management. Effective impact assessment requires harmonizing stakeholder input with ESG metrics to measure and enhance sustainability performance accurately. Explore how integrating these approaches can drive more transparent and accountable impact evaluations.
Sustainability reporting
Stakeholder engagement enhances sustainability reporting by directly incorporating diverse perspectives, ensuring transparency, and fostering accountability across environmental, social, and governance (ESG) dimensions. ESG integration systematically embeds sustainability criteria into corporate strategy and operations, driving measurable improvements in environmental impact, social responsibility, and governance practices. Explore comprehensive strategies to optimize sustainability reporting through effective stakeholder engagement and ESG integration.
Source and External Links
Stakeholder engagement - Wikipedia - Stakeholder engagement is the process by which an organization involves people who may be affected by its decisions or can influence their implementation, emphasizing meaningful participation where stakeholders can influence outcomes and is a key aspect of corporate social responsibility.
What is Stakeholder Engagement, and Why is it Important for Strategic Planning? - Stakeholder engagement involves identifying, understanding, and collaborating with individuals or groups invested in an organization's outcomes to build trust, reduce risks, and ensure alignment with strategic goals and initiatives.
Stakeholder Engagement | FAQ | Sustainable Business Network and ... - Meaningful stakeholder engagement must be focused, timely, representative, inclusive, respectful, and candid, ensuring diverse and potentially vulnerable groups are heard and that engagement informs business decisions transparently and fairly.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com