Forensic accounting involves the application of specialized investigative skills to detect and prevent fraud, embezzlement, and financial misconduct, often supporting legal proceedings. Financial statement analysis focuses on evaluating a company's financial health through its balance sheets, income statements, and cash flow statements to inform investment or management decisions. Explore more to understand how these distinct accounting disciplines contribute to business integrity and financial transparency.
Why it is important
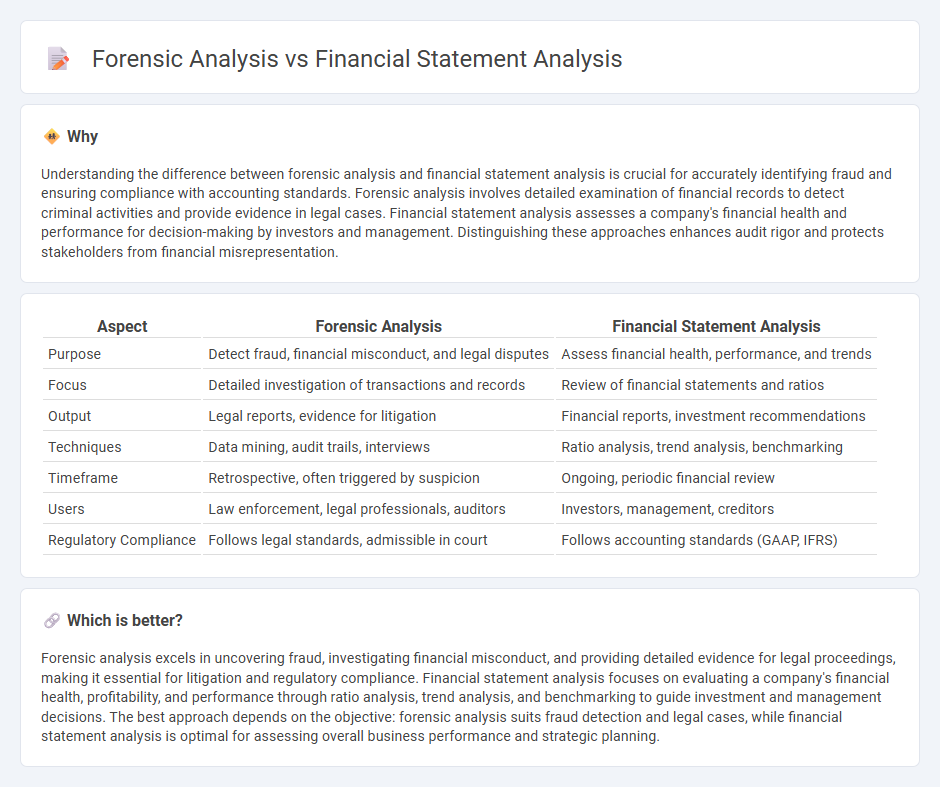
Understanding the difference between forensic analysis and financial statement analysis is crucial for accurately identifying fraud and ensuring compliance with accounting standards. Forensic analysis involves detailed examination of financial records to detect criminal activities and provide evidence in legal cases. Financial statement analysis assesses a company's financial health and performance for decision-making by investors and management. Distinguishing these approaches enhances audit rigor and protects stakeholders from financial misrepresentation.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Forensic Analysis | Financial Statement Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Detect fraud, financial misconduct, and legal disputes | Assess financial health, performance, and trends |
| Focus | Detailed investigation of transactions and records | Review of financial statements and ratios |
| Output | Legal reports, evidence for litigation | Financial reports, investment recommendations |
| Techniques | Data mining, audit trails, interviews | Ratio analysis, trend analysis, benchmarking |
| Timeframe | Retrospective, often triggered by suspicion | Ongoing, periodic financial review |
| Users | Law enforcement, legal professionals, auditors | Investors, management, creditors |
| Regulatory Compliance | Follows legal standards, admissible in court | Follows accounting standards (GAAP, IFRS) |
Which is better?
Forensic analysis excels in uncovering fraud, investigating financial misconduct, and providing detailed evidence for legal proceedings, making it essential for litigation and regulatory compliance. Financial statement analysis focuses on evaluating a company's financial health, profitability, and performance through ratio analysis, trend analysis, and benchmarking to guide investment and management decisions. The best approach depends on the objective: forensic analysis suits fraud detection and legal cases, while financial statement analysis is optimal for assessing overall business performance and strategic planning.
Connection
Forensic analysis and financial statement analysis are connected through their shared goal of detecting financial discrepancies and fraud. Forensic analysis uses detailed financial statement analysis to identify anomalies, inconsistencies, and potential indicators of criminal financial activity. This integration enhances the accuracy of fraud investigations and supports legal proceedings with robust financial evidence.
Key Terms
**Financial Statement Analysis:**
Financial Statement Analysis involves evaluating a company's financial reports, such as income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements, to assess its financial health, profitability, and liquidity. This analysis helps stakeholders make informed decisions by interpreting key ratios and trends in revenue, expenses, assets, and liabilities over time. Explore deeper insights into financial statement analysis techniques and why they matter for business strategy and investment decisions.
Ratio Analysis
Ratio analysis in financial statement analysis utilizes liquidity, profitability, and solvency ratios to evaluate a company's overall financial health and operational efficiency. In forensic analysis, ratio analysis is applied to detect anomalies, fraud indicators, and financial discrepancies by scrutinizing inconsistencies in asset turnover, gross margin, and expense ratios. Explore detailed methodologies and practical applications of ratio analysis in both fields to enhance your financial investigative skills.
Trend Analysis
Trend analysis in financial statement analysis involves examining historical financial data to identify patterns and growth trajectories that aid in predicting future performance and decision-making. Forensic analysis applies trend evaluation to detect anomalies or irregularities signaling potential fraud or financial misconduct within these patterns. Explore the distinctions and applications of trend analysis further to enhance financial insights and fraud detection strategies.
Source and External Links
Analyzing Financial Statements: Key Metrics and Methods - This webpage provides a comprehensive guide to financial statement analysis, covering key metrics and methods for evaluating a company's financial health and performance.
Fundamentals of Financial Statement Analysis - This article outlines a four-step process for analyzing financial statements, including studying historical trends, conducting ratio analysis, and performing cash flow statement analysis.
Financial Statement Analysis: The Basics for Non-Accountants - This blog post offers an introduction to financial statement analysis, focusing on the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement for non-accountants.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com