Blockchain audit trails provide an immutable record of transactions, ensuring transparency and enhancing fraud prevention in accounting practices. Distributed ledger technology (DLT) enables decentralized data sharing across multiple nodes, improving data integrity and reducing reconciliation errors in financial systems. Explore how these technologies revolutionize accounting accuracy and security by learning more.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between Blockchain audit trail and Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) is crucial for accounting professionals to ensure accurate transaction verification and compliance. Blockchain audit trail provides an immutable chronological record of transactions ideal for forensic analysis, while DLT encompasses a broader range of technologies enabling decentralized data management. Accurate distinction aids in selecting the appropriate system for secure financial reporting and fraud prevention. This knowledge enhances transparency and trust in auditing processes within digital accounting environments.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Blockchain Audit Trail | Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) |
|---|---|---|
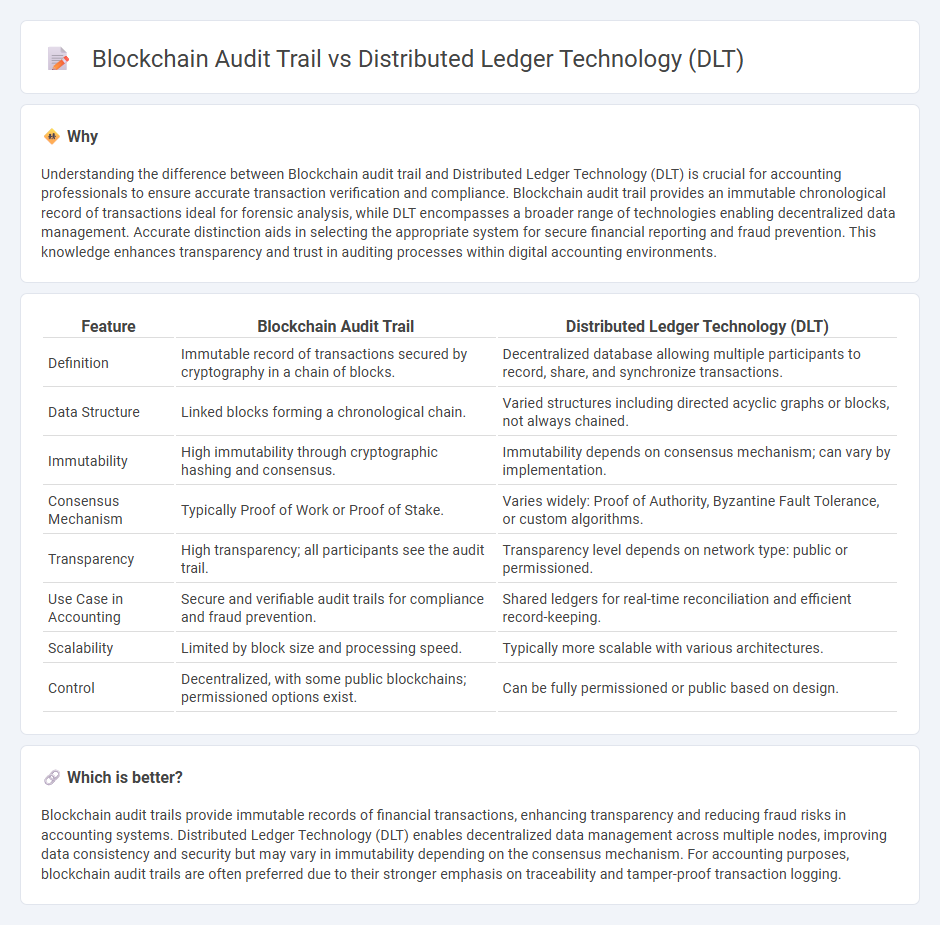
| Definition | Immutable record of transactions secured by cryptography in a chain of blocks. | Decentralized database allowing multiple participants to record, share, and synchronize transactions. |
| Data Structure | Linked blocks forming a chronological chain. | Varied structures including directed acyclic graphs or blocks, not always chained. |
| Immutability | High immutability through cryptographic hashing and consensus. | Immutability depends on consensus mechanism; can vary by implementation. |
| Consensus Mechanism | Typically Proof of Work or Proof of Stake. | Varies widely: Proof of Authority, Byzantine Fault Tolerance, or custom algorithms. |
| Transparency | High transparency; all participants see the audit trail. | Transparency level depends on network type: public or permissioned. |
| Use Case in Accounting | Secure and verifiable audit trails for compliance and fraud prevention. | Shared ledgers for real-time reconciliation and efficient record-keeping. |
| Scalability | Limited by block size and processing speed. | Typically more scalable with various architectures. |
| Control | Decentralized, with some public blockchains; permissioned options exist. | Can be fully permissioned or public based on design. |
Which is better?
Blockchain audit trails provide immutable records of financial transactions, enhancing transparency and reducing fraud risks in accounting systems. Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) enables decentralized data management across multiple nodes, improving data consistency and security but may vary in immutability depending on the consensus mechanism. For accounting purposes, blockchain audit trails are often preferred due to their stronger emphasis on traceability and tamper-proof transaction logging.
Connection
Blockchain audit trails and Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) are interconnected through their shared foundation of decentralized and immutable record-keeping systems, which enhance transparency and security in accounting processes. Blockchain provides a chronological and tamper-proof audit trail by leveraging cryptographic hashing and consensus mechanisms inherent in DLT, ensuring data integrity and real-time verification. This integration enables auditors and accountants to trace transactions with greater accuracy, reduce fraud, and streamline compliance with financial regulations.
Key Terms
Immutability
Distributed ledger technology (DLT) ensures data consistency across multiple locations, while blockchain audit trails specifically emphasize immutability through cryptographic hashing and consensus mechanisms. Immutability in blockchain prevents any alteration once data is recorded, enhancing transparency and security in audit processes compared to generic DLTs. Explore deeper to understand how immutability impacts audit integrity and compliance standards.
Transparency
Distributed ledger technology (DLT) provides a decentralized database where every participant maintains an identical copy of the ledger, enhancing transparency through shared data access. Blockchain audit trails, a subset of DLT, ensure an immutable and chronological record of transactions, which increases accountability and traceability in operations. Explore how both technologies revolutionize transparency in financial and operational systems.
Real-time reconciliation
Distributed ledger technology (DLT) enables real-time reconciliation by providing a synchronized and immutable record of transactions across multiple nodes, ensuring data consistency without a central authority. Blockchain audit trails enhance transparency and security through timestamped, cryptographically linked blocks, enabling efficient verification and reducing reconciliation errors. Explore how these technologies transform financial auditing processes with real-time accuracy and reliability.
Source and External Links
What is distributed ledger technology (DLT)? - Distributed ledger technology (DLT) is a digital system for recording transactions of assets, where transaction details are recorded simultaneously in multiple locations or nodes, with no central data store or administration, enabling consensus on data veracity across a network.
Distributed ledger - A distributed ledger is a peer-to-peer network-based system where replicated digital data is synchronized across multiple geographically distributed nodes without a central administrator, using consensus algorithms to securely update the ledger.
What is a DLT? | Law Glossary - DLT is a decentralized, shared database duplicated across computers in different locations, allowing participants to update and audit the record without a central authority, with blockchain being one type of distributed ledger.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com