Forensic data analytics leverages advanced data analysis techniques to detect fraud, uncover financial anomalies, and support legal investigations, focusing on accuracy and evidential value. Information systems audit evaluates the controls, security, and efficiency of information technology systems to ensure integrity, confidentiality, and compliance with regulatory standards. Explore the distinctions between forensic data analytics and information systems audit to enhance your accounting and auditing strategies.
Why it is important
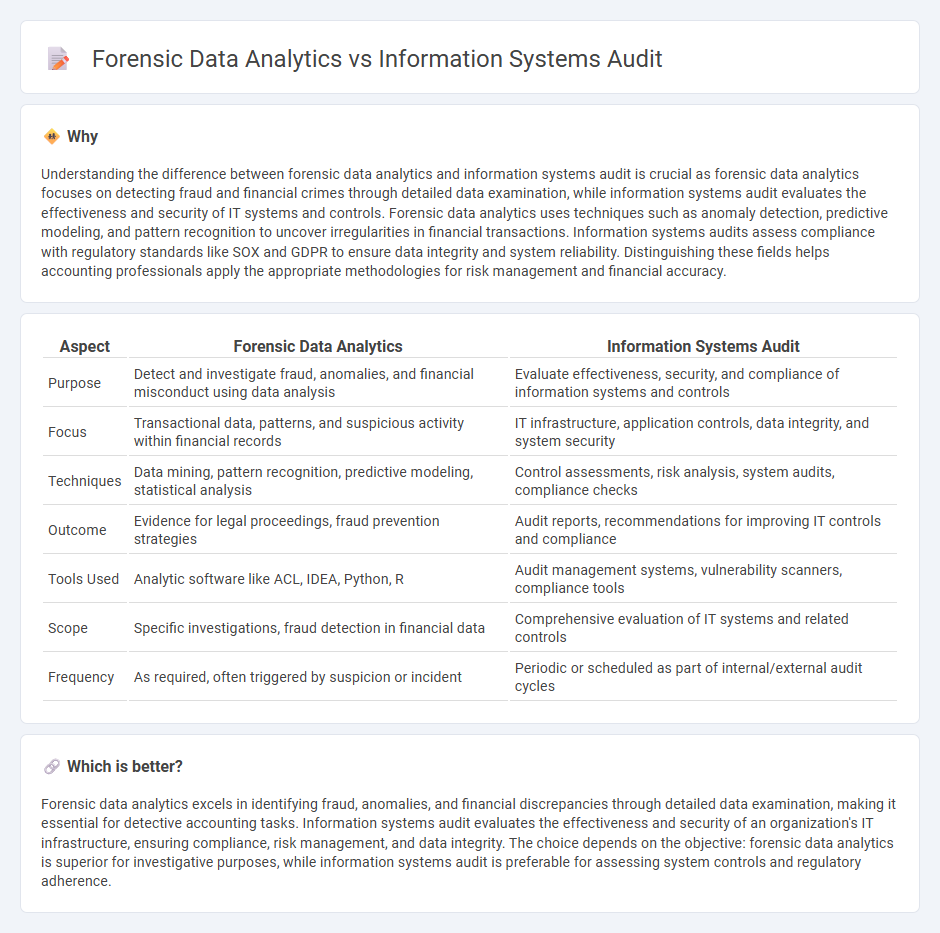
Understanding the difference between forensic data analytics and information systems audit is crucial as forensic data analytics focuses on detecting fraud and financial crimes through detailed data examination, while information systems audit evaluates the effectiveness and security of IT systems and controls. Forensic data analytics uses techniques such as anomaly detection, predictive modeling, and pattern recognition to uncover irregularities in financial transactions. Information systems audits assess compliance with regulatory standards like SOX and GDPR to ensure data integrity and system reliability. Distinguishing these fields helps accounting professionals apply the appropriate methodologies for risk management and financial accuracy.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Forensic Data Analytics | Information Systems Audit |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Detect and investigate fraud, anomalies, and financial misconduct using data analysis | Evaluate effectiveness, security, and compliance of information systems and controls |
| Focus | Transactional data, patterns, and suspicious activity within financial records | IT infrastructure, application controls, data integrity, and system security |
| Techniques | Data mining, pattern recognition, predictive modeling, statistical analysis | Control assessments, risk analysis, system audits, compliance checks |
| Outcome | Evidence for legal proceedings, fraud prevention strategies | Audit reports, recommendations for improving IT controls and compliance |
| Tools Used | Analytic software like ACL, IDEA, Python, R | Audit management systems, vulnerability scanners, compliance tools |
| Scope | Specific investigations, fraud detection in financial data | Comprehensive evaluation of IT systems and related controls |
| Frequency | As required, often triggered by suspicion or incident | Periodic or scheduled as part of internal/external audit cycles |
Which is better?
Forensic data analytics excels in identifying fraud, anomalies, and financial discrepancies through detailed data examination, making it essential for detective accounting tasks. Information systems audit evaluates the effectiveness and security of an organization's IT infrastructure, ensuring compliance, risk management, and data integrity. The choice depends on the objective: forensic data analytics is superior for investigative purposes, while information systems audit is preferable for assessing system controls and regulatory adherence.
Connection
Forensic data analytics and information systems audit are interconnected through their shared focus on detecting and preventing fraud within accounting processes. Forensic data analytics leverages advanced data analysis techniques to uncover anomalies and suspicious transactions, while information systems audit evaluates the integrity and security of the accounting information systems hosting that data. Together, they enhance financial transparency and ensure compliance with regulatory standards by combining technical system assessments with detailed transactional investigations.
Key Terms
**Information systems audit:**
Information systems audit systematically evaluates an organization's IT infrastructure, applications, and policies to ensure data integrity, security, and compliance with regulatory standards such as ISO 27001 and GDPR. It identifies vulnerabilities, assesses risk management effectiveness, and verifies the reliability of financial reporting systems to prevent fraud and operational disruptions. Discover how these audits safeguard your enterprise and enhance IT governance by exploring further details.
IT General Controls (ITGC)
Information systems audit emphasizes evaluating IT General Controls (ITGC) to ensure the reliability, integrity, and security of financial and operational data within an organization. Forensic data analytics, on the other hand, leverages ITGC assessments to detect, investigate, and prevent fraud or cybercrimes by analyzing patterns and anomalies in data. Explore how these approaches intersect to strengthen organizational IT governance and risk management.
Access Controls
Information systems audit evaluates access controls to ensure proper authentication, authorization, and compliance with organizational policies, identifying potential vulnerabilities in system permissions. Forensic data analytics investigates access control anomalies and breaches by analyzing log data and user activities to detect unauthorized access or fraudulent behavior. Explore further to understand how each approach safeguards digital assets and enhances security frameworks.
Source and External Links
Information Systems Auditing - This webpage provides an overview of information systems auditing, including its critical role in ensuring security, integrity, and effective use of information systems within organizations.
Information Technology Audit - This page describes information technology audits as examinations of management controls within IT infrastructures to safeguard assets, maintain data integrity, and operate effectively.
An Introduction to Information Systems (IS) Auditing - This chapter introduces IS auditing as a specialized branch of auditing that assesses IT system controls and processes to ensure they support business objectives securely and efficiently.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com