Integrated ESG reporting combines environmental, social, and governance factors into financial reporting to provide a comprehensive view of a company's sustainability performance and risks. Social impact measurement specifically evaluates the social outcomes and changes resulting from an organization's activities, focusing on community well-being and stakeholder value. Explore how integrated ESG reporting and social impact measurement complement each other to enhance transparent and responsible accounting practices.
Why it is important
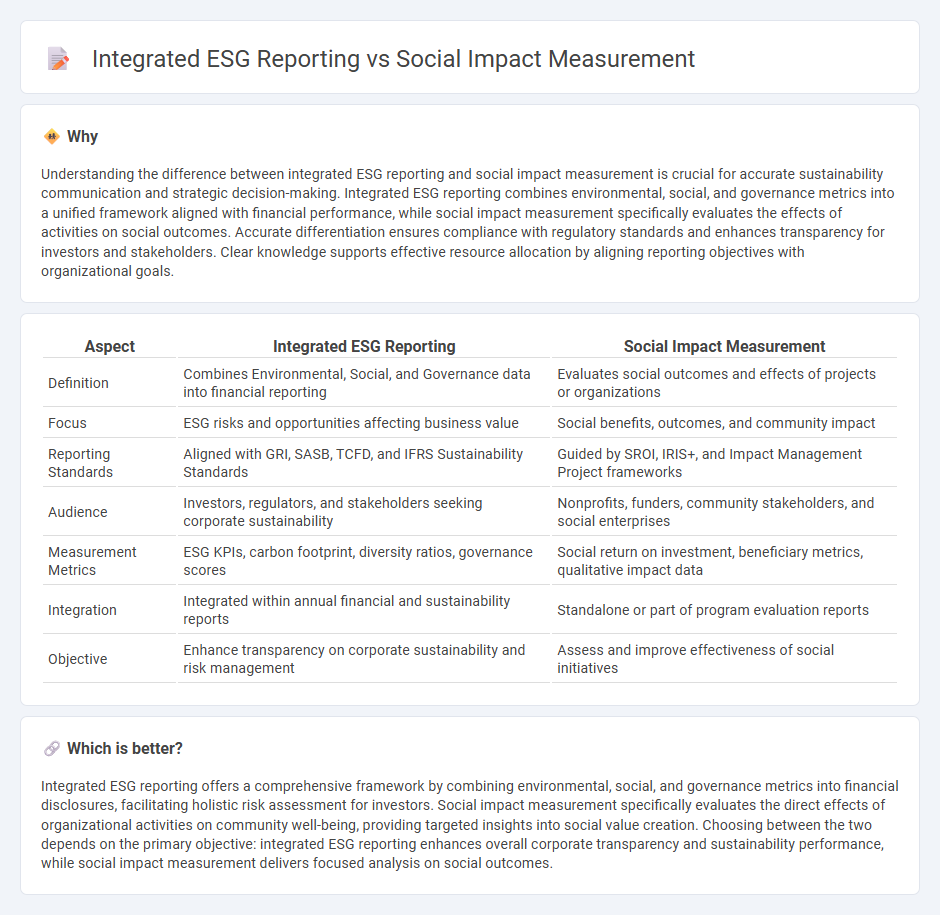
Understanding the difference between integrated ESG reporting and social impact measurement is crucial for accurate sustainability communication and strategic decision-making. Integrated ESG reporting combines environmental, social, and governance metrics into a unified framework aligned with financial performance, while social impact measurement specifically evaluates the effects of activities on social outcomes. Accurate differentiation ensures compliance with regulatory standards and enhances transparency for investors and stakeholders. Clear knowledge supports effective resource allocation by aligning reporting objectives with organizational goals.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Integrated ESG Reporting | Social Impact Measurement |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Combines Environmental, Social, and Governance data into financial reporting | Evaluates social outcomes and effects of projects or organizations |
| Focus | ESG risks and opportunities affecting business value | Social benefits, outcomes, and community impact |
| Reporting Standards | Aligned with GRI, SASB, TCFD, and IFRS Sustainability Standards | Guided by SROI, IRIS+, and Impact Management Project frameworks |
| Audience | Investors, regulators, and stakeholders seeking corporate sustainability | Nonprofits, funders, community stakeholders, and social enterprises |
| Measurement Metrics | ESG KPIs, carbon footprint, diversity ratios, governance scores | Social return on investment, beneficiary metrics, qualitative impact data |
| Integration | Integrated within annual financial and sustainability reports | Standalone or part of program evaluation reports |
| Objective | Enhance transparency on corporate sustainability and risk management | Assess and improve effectiveness of social initiatives |
Which is better?
Integrated ESG reporting offers a comprehensive framework by combining environmental, social, and governance metrics into financial disclosures, facilitating holistic risk assessment for investors. Social impact measurement specifically evaluates the direct effects of organizational activities on community well-being, providing targeted insights into social value creation. Choosing between the two depends on the primary objective: integrated ESG reporting enhances overall corporate transparency and sustainability performance, while social impact measurement delivers focused analysis on social outcomes.
Connection
Integrated ESG reporting and social impact measurement are connected through their shared focus on evaluating a company's non-financial performance, specifically environmental, social, and governance factors alongside social outcomes. Both frameworks utilize comprehensive data collection and analysis to provide stakeholders with transparent insights into corporate responsibility and sustainability practices. This connection enhances strategic decision-making by embedding social value metrics directly into financial reporting processes.
Key Terms
Impact Assessment
Social impact measurement quantifies specific changes in communities or environments directly attributable to an organization's activities, using indicators such as social return on investment (SROI) and outcome mapping. Integrated ESG reporting combines environmental, social, and governance metrics into a comprehensive framework, emphasizing transparency, regulatory compliance, and stakeholder engagement alongside financial performance. Explore how impact assessment methodologies enhance ESG reporting to drive more effective sustainability strategies.
Materiality
Social impact measurement quantifies the tangible effects of projects on communities, emphasizing outcomes related to environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors. Integrated ESG reporting centers on materiality by identifying and disclosing the most significant ESG risks and opportunities that affect long-term business value. Explore how aligning social impact measurement with materiality principles enhances transparent and strategic ESG reporting.
Triple Bottom Line
Social impact measurement quantifies the specific effects of an organization's activities on people and communities, emphasizing social value creation within the Triple Bottom Line framework. Integrated ESG reporting combines environmental, social, and governance data into a comprehensive disclosure, highlighting sustainability performance alongside financial outcomes. Explore how these approaches complement each other to advance holistic corporate responsibility.
Source and External Links
How to Measure Social Impact - Brightest - Social impact measurement is a structured process and framework that links an organization's activities directly to positive social change via specific metrics across inputs, activities, outputs, and outcomes to demonstrate improvements like public health and economic development.
How to Measure Social Impact: 8 Best Practices - Measuring social impact involves selecting an appropriate framework before programming to set performance targets and continuously assessing initiatives to ensure they create systemic, sustainable, and innovative public value.
Social Impact Metrics Guide - Social Impact KPIs are measurable values focused on outcomes rather than activities, used to evaluate how effectively an organization achieves its social goals, capturing the real change produced for communities or environments.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com