Transfer pricing analytics involves evaluating and optimizing intercompany transactions to ensure compliance with tax regulations and maximize profit allocation across jurisdictions. Segment reporting focuses on disclosing financial performance and operational results of distinct business units to provide transparency for investors and regulators. Explore these accounting practices to understand their impact on financial strategy and regulatory compliance.
Why it is important
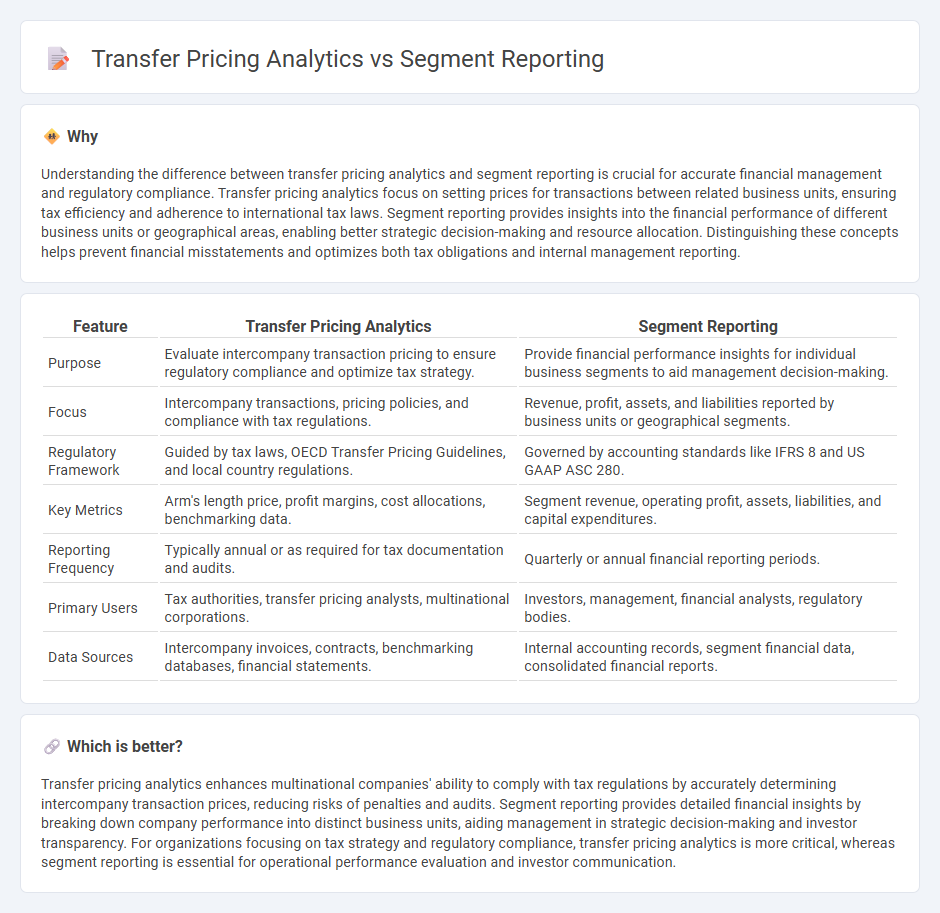
Understanding the difference between transfer pricing analytics and segment reporting is crucial for accurate financial management and regulatory compliance. Transfer pricing analytics focus on setting prices for transactions between related business units, ensuring tax efficiency and adherence to international tax laws. Segment reporting provides insights into the financial performance of different business units or geographical areas, enabling better strategic decision-making and resource allocation. Distinguishing these concepts helps prevent financial misstatements and optimizes both tax obligations and internal management reporting.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Transfer Pricing Analytics | Segment Reporting |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Evaluate intercompany transaction pricing to ensure regulatory compliance and optimize tax strategy. | Provide financial performance insights for individual business segments to aid management decision-making. |
| Focus | Intercompany transactions, pricing policies, and compliance with tax regulations. | Revenue, profit, assets, and liabilities reported by business units or geographical segments. |
| Regulatory Framework | Guided by tax laws, OECD Transfer Pricing Guidelines, and local country regulations. | Governed by accounting standards like IFRS 8 and US GAAP ASC 280. |
| Key Metrics | Arm's length price, profit margins, cost allocations, benchmarking data. | Segment revenue, operating profit, assets, liabilities, and capital expenditures. |
| Reporting Frequency | Typically annual or as required for tax documentation and audits. | Quarterly or annual financial reporting periods. |
| Primary Users | Tax authorities, transfer pricing analysts, multinational corporations. | Investors, management, financial analysts, regulatory bodies. |
| Data Sources | Intercompany invoices, contracts, benchmarking databases, financial statements. | Internal accounting records, segment financial data, consolidated financial reports. |
Which is better?
Transfer pricing analytics enhances multinational companies' ability to comply with tax regulations by accurately determining intercompany transaction prices, reducing risks of penalties and audits. Segment reporting provides detailed financial insights by breaking down company performance into distinct business units, aiding management in strategic decision-making and investor transparency. For organizations focusing on tax strategy and regulatory compliance, transfer pricing analytics is more critical, whereas segment reporting is essential for operational performance evaluation and investor communication.
Connection
Transfer pricing analytics and segment reporting are interconnected through their shared goal of enhancing financial transparency and compliance. Transfer pricing analytics involves evaluating intercompany transactions to ensure prices reflect market conditions, which directly impacts the accuracy of segment reporting by allocating revenues and expenses correctly to distinct business units. Accurate segment reporting relies on precise transfer pricing data to provide stakeholders with detailed financial insights, facilitating better decision-making and regulatory adherence.
Key Terms
**Segment Reporting:**
Segment reporting provides detailed insights into a company's financial performance by breaking down revenue, expenses, assets, and liabilities across different business units or geographical areas. It enables stakeholders to assess the profitability and risk of each segment independently, aiding in strategic decision-making and regulatory compliance. Explore in-depth how segment reporting enhances transparency and drives better financial analysis.
Operating Segments
Segment reporting provides financial insights by breaking down revenues, expenses, and profits across distinct operating segments, aiding regulatory compliance and investor transparency. Transfer pricing analytics focuses on setting and analyzing intra-company transaction prices between operating segments to comply with tax regulations and optimize profit allocation. Explore how these approaches impact financial strategy and regulatory adherence in greater detail.
Intersegment Revenue
Intersegment revenue is a critical metric in segment reporting, reflecting transactions between different business units within the same organization, providing transparency on internal sales and profitability. Transfer pricing analytics evaluates these intersegment transactions to ensure compliance with tax regulations and fairness in pricing, minimizing risks of tax adjustments and penalties. Explore how mastering intersegment revenue management can enhance financial accuracy and regulatory compliance.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com