Triple entry accounting integrates blockchain technology to enhance transparency and security by recording transactions in three ledgers, unlike cash basis accounting that recognizes revenue and expenses only when cash is exchanged. This method improves auditability and reduces discrepancies by providing a decentralized and immutable record of financial activities. Explore the advantages and applications of both systems to optimize your accounting practices.
Why it is important
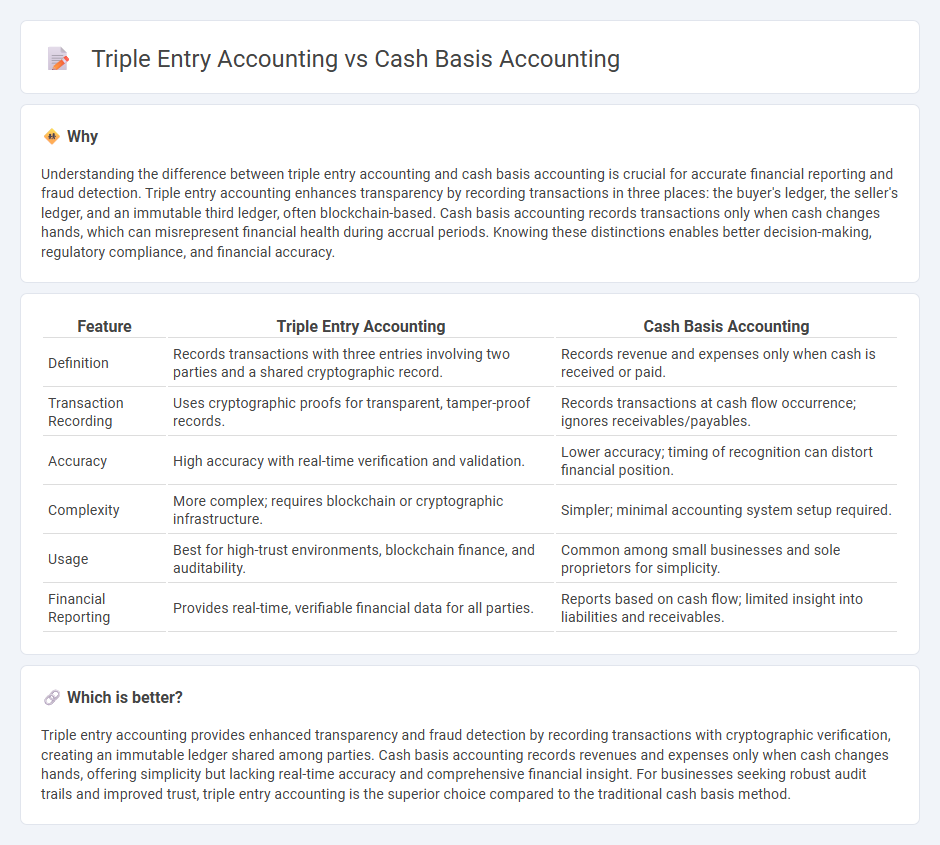
Understanding the difference between triple entry accounting and cash basis accounting is crucial for accurate financial reporting and fraud detection. Triple entry accounting enhances transparency by recording transactions in three places: the buyer's ledger, the seller's ledger, and an immutable third ledger, often blockchain-based. Cash basis accounting records transactions only when cash changes hands, which can misrepresent financial health during accrual periods. Knowing these distinctions enables better decision-making, regulatory compliance, and financial accuracy.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Triple Entry Accounting | Cash Basis Accounting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Records transactions with three entries involving two parties and a shared cryptographic record. | Records revenue and expenses only when cash is received or paid. |
| Transaction Recording | Uses cryptographic proofs for transparent, tamper-proof records. | Records transactions at cash flow occurrence; ignores receivables/payables. |
| Accuracy | High accuracy with real-time verification and validation. | Lower accuracy; timing of recognition can distort financial position. |
| Complexity | More complex; requires blockchain or cryptographic infrastructure. | Simpler; minimal accounting system setup required. |
| Usage | Best for high-trust environments, blockchain finance, and auditability. | Common among small businesses and sole proprietors for simplicity. |
| Financial Reporting | Provides real-time, verifiable financial data for all parties. | Reports based on cash flow; limited insight into liabilities and receivables. |
Which is better?
Triple entry accounting provides enhanced transparency and fraud detection by recording transactions with cryptographic verification, creating an immutable ledger shared among parties. Cash basis accounting records revenues and expenses only when cash changes hands, offering simplicity but lacking real-time accuracy and comprehensive financial insight. For businesses seeking robust audit trails and improved trust, triple entry accounting is the superior choice compared to the traditional cash basis method.
Connection
Triple entry accounting enhances cash basis accounting by recording transactions with cryptographic verification, ensuring transparency and reducing fraud risks. While cash basis accounting recognizes revenue and expenses only when cash changes hands, triple entry accounting adds a secure, immutable record, improving accuracy in financial reporting. This integration supports better audit trails and real-time reconciliation of cash transactions.
Key Terms
Revenue Recognition
Cash basis accounting records revenue only when cash is received, leading to potential timing mismatches with actual performance. Triple entry accounting enhances transparency by documenting each transaction using a cryptographically secured third entry, ensuring accurate and immutable revenue recognition aligned with contractual terms. Explore how triple entry accounting revolutionizes revenue tracking beyond cash basis methods.
Double-entry
Double-entry accounting records financial transactions through equal debits and credits, ensuring balanced books and accurate financial statements, while cash basis accounting recognizes revenues and expenses only when cash changes hands. Triple entry accounting builds upon double-entry by adding a cryptographic third entry, enhancing transparency and fraud prevention in financial reporting. Explore how integrating double-entry principles with emerging technologies can revolutionize accounting accuracy and trust.
Blockchain
Cash basis accounting records revenues and expenses only when cash changes hands, providing a simple and immediate financial snapshot. Triple entry accounting, enhanced by blockchain technology, introduces an immutable third entry verified by the network, increasing transparency and reducing fraud risks. Explore how blockchain-powered triple entry accounting transforms financial accuracy and trust.
Source and External Links
Cash Basis Accounting: Definition, Example, Pros and Cons - Cash basis accounting is a simple method that records income when cash is received and expenses when cash is paid, mainly used by small businesses, but is not acceptable under GAAP or IFRS standards.
Cash-based accounting: A guide to the cash basis - Stripe - Cash basis accounting recognizes revenues and expenses only when cash is received or paid, focusing on cash flow rather than on accounts receivable or payable, making it simpler but less comprehensive than accrual accounting.
What Is Cash Basis Accounting? Definition and Guide - Shopify - Cash basis accounting records sales and expenses only when cash is received or paid, commonly used by small businesses or individuals that deal primarily in cash transactions.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com