Ledger tokenization converts assets into digital tokens recorded on a blockchain ledger, enhancing transparency and traceability in accounting. Smart contracts automate agreements by executing predefined conditions without intermediaries, increasing efficiency and reducing errors. Explore how integrating these technologies can revolutionize financial record-keeping and auditing.
Why it is important
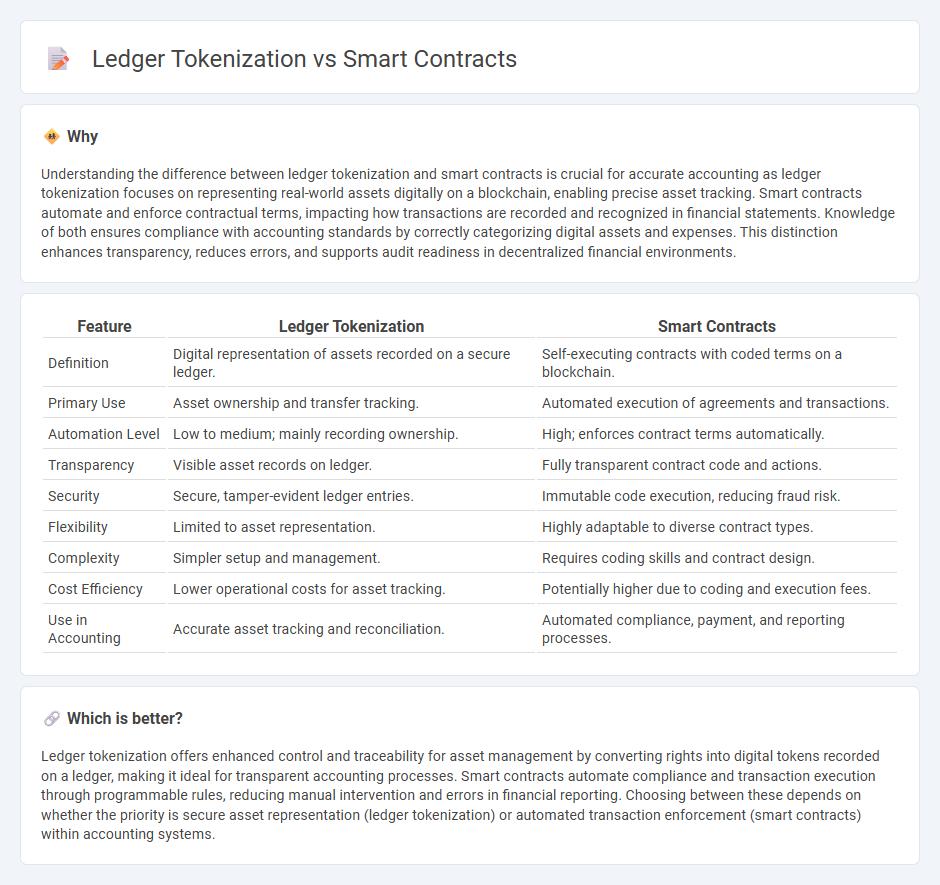
Understanding the difference between ledger tokenization and smart contracts is crucial for accurate accounting as ledger tokenization focuses on representing real-world assets digitally on a blockchain, enabling precise asset tracking. Smart contracts automate and enforce contractual terms, impacting how transactions are recorded and recognized in financial statements. Knowledge of both ensures compliance with accounting standards by correctly categorizing digital assets and expenses. This distinction enhances transparency, reduces errors, and supports audit readiness in decentralized financial environments.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Ledger Tokenization | Smart Contracts |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Digital representation of assets recorded on a secure ledger. | Self-executing contracts with coded terms on a blockchain. |
| Primary Use | Asset ownership and transfer tracking. | Automated execution of agreements and transactions. |
| Automation Level | Low to medium; mainly recording ownership. | High; enforces contract terms automatically. |
| Transparency | Visible asset records on ledger. | Fully transparent contract code and actions. |
| Security | Secure, tamper-evident ledger entries. | Immutable code execution, reducing fraud risk. |
| Flexibility | Limited to asset representation. | Highly adaptable to diverse contract types. |
| Complexity | Simpler setup and management. | Requires coding skills and contract design. |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower operational costs for asset tracking. | Potentially higher due to coding and execution fees. |
| Use in Accounting | Accurate asset tracking and reconciliation. | Automated compliance, payment, and reporting processes. |
Which is better?
Ledger tokenization offers enhanced control and traceability for asset management by converting rights into digital tokens recorded on a ledger, making it ideal for transparent accounting processes. Smart contracts automate compliance and transaction execution through programmable rules, reducing manual intervention and errors in financial reporting. Choosing between these depends on whether the priority is secure asset representation (ledger tokenization) or automated transaction enforcement (smart contracts) within accounting systems.
Connection
Ledger tokenization transforms financial assets into digital tokens recorded on a blockchain ledger, enabling precise and immutable accounting entries. Smart contracts automate the execution of accounting transactions by enforcing predefined rules and conditions, ensuring real-time verification and reducing errors in financial records. This connection streamlines auditing processes and enhances transparency in accounting systems by providing secure, tamper-proof transaction records.
Key Terms
Immutable Records
Immutable records form the core advantage of both smart contracts and ledger tokenization, ensuring data integrity and transparency through cryptographic proof. Smart contracts automate execution and enforce rules on blockchain platforms, while ledger tokenization digitizes assets to represent ownership within an immutable ledger, enhancing security and traceability. Discover how leveraging these technologies can transform your data management and asset handling strategies.
Automation
Smart contracts automate the execution of agreements by embedding code directly onto blockchain networks, ensuring transactions trigger precisely when predefined conditions are met. Ledger tokenization digitally represents assets on a blockchain, streamlining ownership transfers but typically relies on smart contracts to automate those processes. Explore how combining smart contracts with ledger tokenization enhances automation in decentralized finance and asset management.
Asset Representation
Smart contracts enable automated and self-executing agreements that directly encode asset representation and ownership on a blockchain, ensuring transparency and immutability. Ledger tokenization abstracts physical or digital assets into blockchain-based tokens, facilitating liquidity and fractional ownership without altering the underlying asset itself. Explore the nuances of asset representation to understand how each technology transforms asset management.
Source and External Links
What are smart contracts on the blockchain? 4 real-world use cases - Smart contracts are self-executing programs stored on the blockchain that automatically execute transactions when pre-set conditions are met, eliminating intermediaries and enabling transparent, tamper-resistant agreements primarily on platforms like Ethereum.
10 Real-World Smart Contract Use Cases - Hedera - Smart contracts are digital programs on blockchain networks that execute automatically based on predetermined conditions, offering trustless, secure, and fast transactions without middlemen, with applications in property ownership, finance, and multi-party exchanges.
Smart contract - Wikipedia - A smart contract is a computer program designed to automatically execute or document actions according to contractual terms, reducing the need for intermediaries and fraud, and serving as a foundational technology for decentralized finance and NFTs on blockchains like Ethereum.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com