Algorithmic compliance leverages automated systems and AI to ensure adherence to regulations by continuously monitoring transactions and flagging anomalies. Risk-based compliance prioritizes resources by assessing and addressing the highest potential risks to the organization's regulatory standing. Explore how these approaches reshape compliance strategies in modern accounting practices.
Why it is important
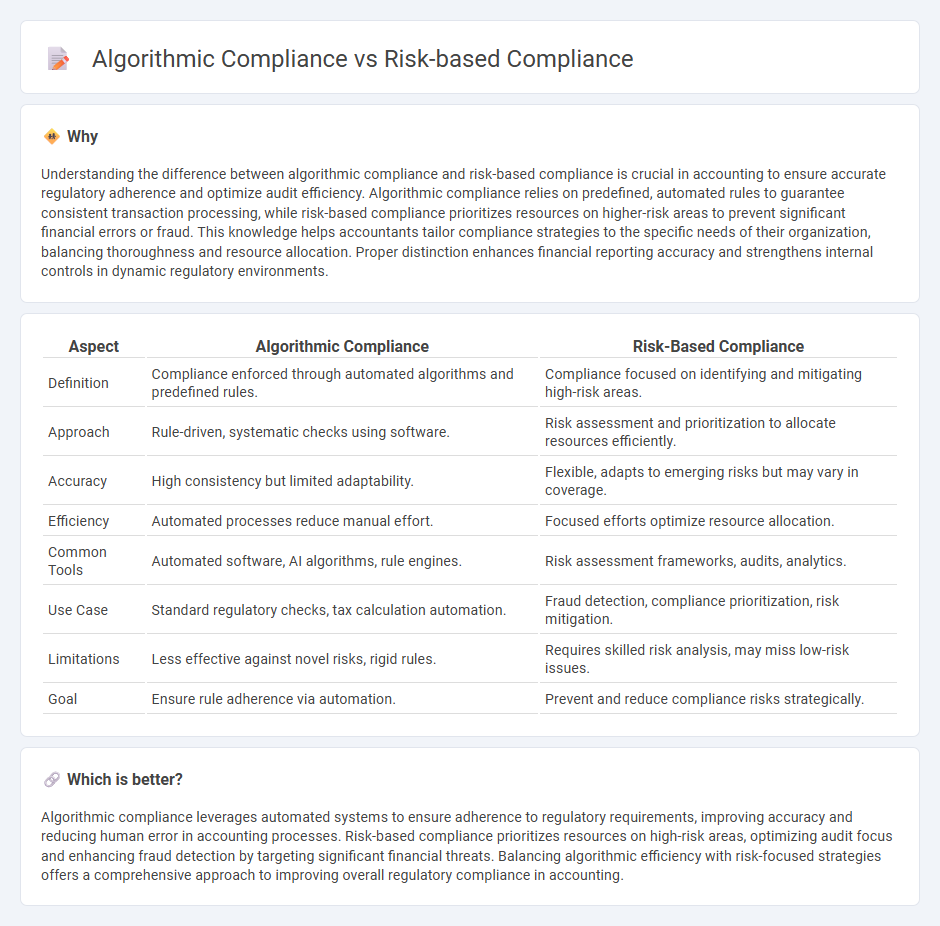
Understanding the difference between algorithmic compliance and risk-based compliance is crucial in accounting to ensure accurate regulatory adherence and optimize audit efficiency. Algorithmic compliance relies on predefined, automated rules to guarantee consistent transaction processing, while risk-based compliance prioritizes resources on higher-risk areas to prevent significant financial errors or fraud. This knowledge helps accountants tailor compliance strategies to the specific needs of their organization, balancing thoroughness and resource allocation. Proper distinction enhances financial reporting accuracy and strengthens internal controls in dynamic regulatory environments.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Algorithmic Compliance | Risk-Based Compliance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Compliance enforced through automated algorithms and predefined rules. | Compliance focused on identifying and mitigating high-risk areas. |
| Approach | Rule-driven, systematic checks using software. | Risk assessment and prioritization to allocate resources efficiently. |
| Accuracy | High consistency but limited adaptability. | Flexible, adapts to emerging risks but may vary in coverage. |
| Efficiency | Automated processes reduce manual effort. | Focused efforts optimize resource allocation. |
| Common Tools | Automated software, AI algorithms, rule engines. | Risk assessment frameworks, audits, analytics. |
| Use Case | Standard regulatory checks, tax calculation automation. | Fraud detection, compliance prioritization, risk mitigation. |
| Limitations | Less effective against novel risks, rigid rules. | Requires skilled risk analysis, may miss low-risk issues. |
| Goal | Ensure rule adherence via automation. | Prevent and reduce compliance risks strategically. |
Which is better?
Algorithmic compliance leverages automated systems to ensure adherence to regulatory requirements, improving accuracy and reducing human error in accounting processes. Risk-based compliance prioritizes resources on high-risk areas, optimizing audit focus and enhancing fraud detection by targeting significant financial threats. Balancing algorithmic efficiency with risk-focused strategies offers a comprehensive approach to improving overall regulatory compliance in accounting.
Connection
Algorithmic compliance leverages automated processes and data analytics to ensure adherence to regulatory standards, while risk-based compliance prioritizes resources based on the assessment of potential risks within financial reporting and operations. Integration of algorithmic approaches enhances risk-based compliance by enabling real-time monitoring and predictive risk identification, significantly reducing the likelihood of non-compliance. This synergy improves accuracy and efficiency in accounting by streamlining audit trails and reinforcing control mechanisms through advanced algorithms.
Key Terms
Risk Assessment
Risk-based compliance prioritizes identifying, evaluating, and mitigating potential risks using qualitative and quantitative assessments to ensure regulatory adherence, emphasizing proactive risk management. Algorithmic compliance leverages machine learning models and automated algorithms to analyze vast datasets for detecting compliance breaches and predicting risk patterns in real time. Explore how risk assessment methodologies differ and complement each approach to optimize compliance strategies.
Control Framework
Risk-based compliance prioritizes control frameworks by identifying and addressing the highest risk areas to optimize resource allocation and enhance organizational resilience. Algorithmic compliance uses automated algorithms to enforce rules within control frameworks, improving consistency, scalability, and real-time monitoring of compliance activities. Explore how integrating both methods can strengthen your control framework for comprehensive compliance management.
Automated Monitoring
Risk-based compliance prioritizes monitoring efforts based on potential impact and likelihood of non-compliance, optimizing resources to address high-risk areas. Algorithmic compliance leverages advanced machine learning models and artificial intelligence to automate detection and response processes, ensuring continuous oversight and real-time corrections. Explore how integrating automated monitoring enhances compliance efficiency and accuracy in complex regulatory environments.
Source and External Links
The necessity of a risk-based approach in modern compliance - A risk-based compliance approach prioritizes regulatory risks by identifying applicable regulations, assessing risk impact and likelihood, targeting risky business processes, implementing risk-proportionate controls, and continuously monitoring and improving these measures to manage compliance effectively.
Risk-Based Approach - Managing AML & KYC Risk - Trulioo - The risk-based approach (RBA) focuses compliance efforts on systematically understanding and mitigating the highest risks an organization faces, rather than applying prescriptive compliance measures, and is central to AML regulatory frameworks such as FATF.
Why a Risk-Based Approach is Essential for Compliance Management - Applying a risk-based approach in compliance not only prevents regulatory failures but also enhances business reputation and cybersecurity by concentrating resources on the most critical risks, enabling proactive detection, response, and workforce awareness.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com