Zero trust accounting emphasizes stringent verification measures and continuous monitoring to protect financial data from unauthorized access, aligning with cybersecurity frameworks in modern enterprises. Managerial accounting focuses on internal financial analysis and decision-making support, providing detailed reports for budgeting, forecasting, and performance evaluation. Explore the key differences and applications of zero trust versus managerial accounting to enhance your financial strategy.
Why it is important
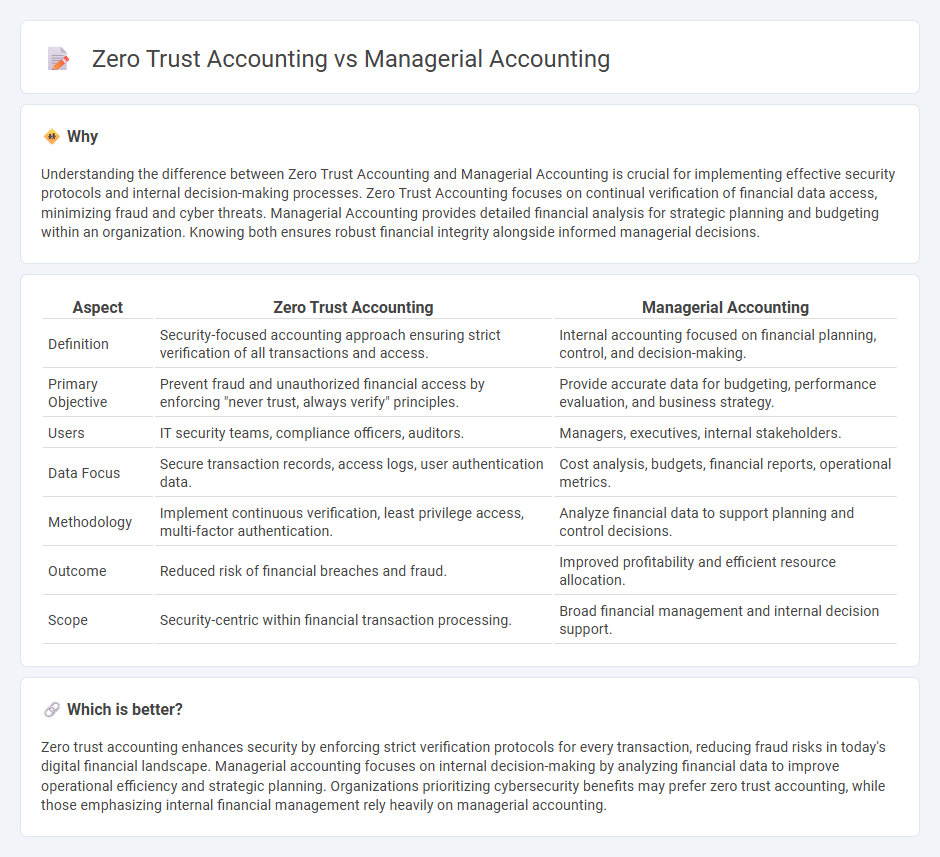
Understanding the difference between Zero Trust Accounting and Managerial Accounting is crucial for implementing effective security protocols and internal decision-making processes. Zero Trust Accounting focuses on continual verification of financial data access, minimizing fraud and cyber threats. Managerial Accounting provides detailed financial analysis for strategic planning and budgeting within an organization. Knowing both ensures robust financial integrity alongside informed managerial decisions.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Zero Trust Accounting | Managerial Accounting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Security-focused accounting approach ensuring strict verification of all transactions and access. | Internal accounting focused on financial planning, control, and decision-making. |
| Primary Objective | Prevent fraud and unauthorized financial access by enforcing "never trust, always verify" principles. | Provide accurate data for budgeting, performance evaluation, and business strategy. |
| Users | IT security teams, compliance officers, auditors. | Managers, executives, internal stakeholders. |
| Data Focus | Secure transaction records, access logs, user authentication data. | Cost analysis, budgets, financial reports, operational metrics. |
| Methodology | Implement continuous verification, least privilege access, multi-factor authentication. | Analyze financial data to support planning and control decisions. |
| Outcome | Reduced risk of financial breaches and fraud. | Improved profitability and efficient resource allocation. |
| Scope | Security-centric within financial transaction processing. | Broad financial management and internal decision support. |
Which is better?
Zero trust accounting enhances security by enforcing strict verification protocols for every transaction, reducing fraud risks in today's digital financial landscape. Managerial accounting focuses on internal decision-making by analyzing financial data to improve operational efficiency and strategic planning. Organizations prioritizing cybersecurity benefits may prefer zero trust accounting, while those emphasizing internal financial management rely heavily on managerial accounting.
Connection
Zero trust accounting enhances managerial accounting by enforcing strict access controls and real-time monitoring of financial data, reducing the risk of fraud and errors in budgeting, forecasting, and performance analysis. Managerial accounting benefits from zero trust principles through improved data integrity and transparency, enabling more accurate decision-making and resource allocation. Integrating zero trust frameworks supports managerial accountants in safeguarding sensitive financial information while optimizing operational efficiency.
Key Terms
Managerial accounting:
Managerial accounting provides crucial financial insights through detailed cost analysis, budgeting, and performance evaluation to enhance internal decision-making and operational efficiency. It emphasizes the use of internal reports tailored for managers, supporting strategic planning and resource allocation within organizations. Explore further to understand how managerial accounting drives business success through data-driven management.
Budgeting
Managerial accounting emphasizes budgeting by providing detailed financial forecasts, cost control, and performance analysis to support strategic decision-making and efficient resource allocation within organizations. Zero trust accounting applies stringent access controls and verification processes to financial data, enhancing security and minimizing risks associated with budget manipulation or unauthorized financial activities. Explore how combining managerial accounting principles with zero trust frameworks can optimize budgeting accuracy and data integrity.
Cost analysis
Managerial accounting emphasizes detailed cost analysis to aid internal decision-making by tracking, allocating, and controlling expenses related to production and operations. Zero trust accounting integrates cost analysis with cybersecurity principles, continuously verifying resource usage and expenses to prevent fraudulent activities and ensure financial integrity in decentralized environments. Explore how these distinct approaches redefine cost management in their respective domains.
Source and External Links
Managerial Accounting: Everything You Need To Know - Managerial accounting focuses on using financial data and analysis to support business decision-making, planning, budgeting, performance tracking, and internal reporting to management, rather than reporting to external parties.
Managerial Accounting Made Easy - Managerial accounting provides decision support through detailed reports, cost analysis, and financial segmentation, helping companies with planning, performance control, business problem-solving, and strategy development, while using principles like causality and analogy.
Your Guide to Managerial Accounting: Types, Careers, and ... - Managerial accounting involves analyzing, interpreting, and measuring an organization's financial processes to guide internal strategic decisions, unlike financial accounting which deals with external compliance and reporting.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com