Cryptocurrency taxation involves tracking digital asset transactions and applying specific tax rules distinct from traditional income tax, which is based on wages and salaries. Tax authorities often classify cryptocurrencies as property, requiring capital gains reporting when they are sold or exchanged, unlike regular income tax that taxes earned income directly. Explore how these tax regimes differ to ensure compliance and optimize your financial strategy.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between cryptocurrency taxation and income tax is crucial for accurate financial reporting and compliance with IRS regulations, preventing costly penalties. Cryptocurrency transactions often require specific record-keeping for gains, losses, and fair market value, unlike traditional income tax reporting. Knowing these distinctions helps individuals and businesses optimize tax strategies and avoid audits. Proper tax treatment ensures legal adherence and maximizes financial efficiency in the evolving digital economy.
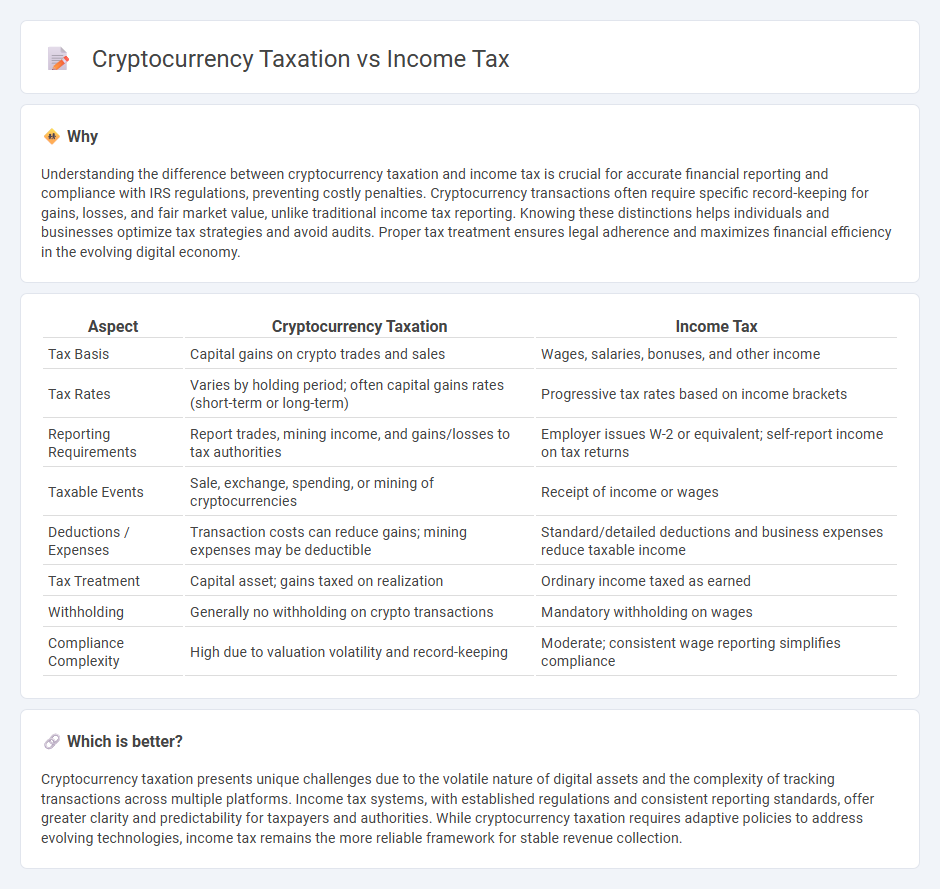
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Cryptocurrency Taxation | Income Tax |
|---|---|---|
| Tax Basis | Capital gains on crypto trades and sales | Wages, salaries, bonuses, and other income |
| Tax Rates | Varies by holding period; often capital gains rates (short-term or long-term) | Progressive tax rates based on income brackets |
| Reporting Requirements | Report trades, mining income, and gains/losses to tax authorities | Employer issues W-2 or equivalent; self-report income on tax returns |
| Taxable Events | Sale, exchange, spending, or mining of cryptocurrencies | Receipt of income or wages |
| Deductions / Expenses | Transaction costs can reduce gains; mining expenses may be deductible | Standard/detailed deductions and business expenses reduce taxable income |
| Tax Treatment | Capital asset; gains taxed on realization | Ordinary income taxed as earned |
| Withholding | Generally no withholding on crypto transactions | Mandatory withholding on wages |
| Compliance Complexity | High due to valuation volatility and record-keeping | Moderate; consistent wage reporting simplifies compliance |
Which is better?
Cryptocurrency taxation presents unique challenges due to the volatile nature of digital assets and the complexity of tracking transactions across multiple platforms. Income tax systems, with established regulations and consistent reporting standards, offer greater clarity and predictability for taxpayers and authorities. While cryptocurrency taxation requires adaptive policies to address evolving technologies, income tax remains the more reliable framework for stable revenue collection.
Connection
Cryptocurrency taxation and income tax are interconnected as cryptocurrencies are considered taxable assets by tax authorities such as the IRS, requiring individuals to report gains and losses on their income tax returns. Transactions involving cryptocurrency, including mining, trading, and payments, generate taxable events that must be accurately recorded to comply with income tax regulations. Failure to report cryptocurrency income properly can result in penalties, making understanding tax compliance essential for digital asset holders.
Key Terms
Taxable Income
Income tax regulations classify cryptocurrency transactions as taxable events, requiring accurate reporting of gains and losses to determine taxable income. The IRS treats cryptocurrencies as property, making capital gains and income from mining or staking subject to income tax. Explore detailed guidelines to ensure compliance and optimize tax reporting for cryptocurrency assets.
Capital Gains
Capital gains from cryptocurrency transactions are subject to income tax regulations, often treated as property rather than currency by tax authorities like the IRS. Accurate record-keeping of purchase prices and sale proceeds is essential for calculating taxable gains or losses on digital asset trades. Explore detailed guidelines on cryptocurrency capital gains taxation to ensure compliance and optimize your tax strategy.
Reporting Requirements
Income tax regulations require individuals to report all sources of taxable income, including earnings from wages, investments, and self-employment, under specified forms such as the IRS Form 1040. Cryptocurrency taxation mandates detailed reporting of digital asset transactions, including sales, exchanges, and mining activities, often using Form 8949 and Schedule D to accurately calculate capital gains or losses. Explore comprehensive guidelines to ensure full compliance with evolving tax reporting obligations for both traditional income and cryptocurrency holdings.
Source and External Links
Federal Income Tax Calculator (2024-2025) - The U.S. federal income tax has brackets ranging from 10% to 37% depending on taxable income and filing status, with marginal rates applied only to income within each bracket.
United States - Individual - Taxes on personal income - The top federal income tax rate in 2024 is 37%, with additional taxes like the 3.8% Medicare contribution tax on unearned income, and most states have their own income tax with some exceptions.
Federal income tax rates and brackets - Taxpayers pay federal income tax according to graduated brackets where higher rates apply only to income within each bracket, with 2024 rates for singles starting at 10% and topping out at 37% above $609,350.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com