Continuous audit utilizes automated tools to provide real-time transaction monitoring, ensuring ongoing compliance and early detection of anomalies. Risk-based audit focuses on identifying and evaluating key risk areas to allocate resources efficiently and enhance audit effectiveness. Explore the distinct advantages and applications of continuous audit and risk-based audit to optimize your organization's financial oversight.
Why it is important
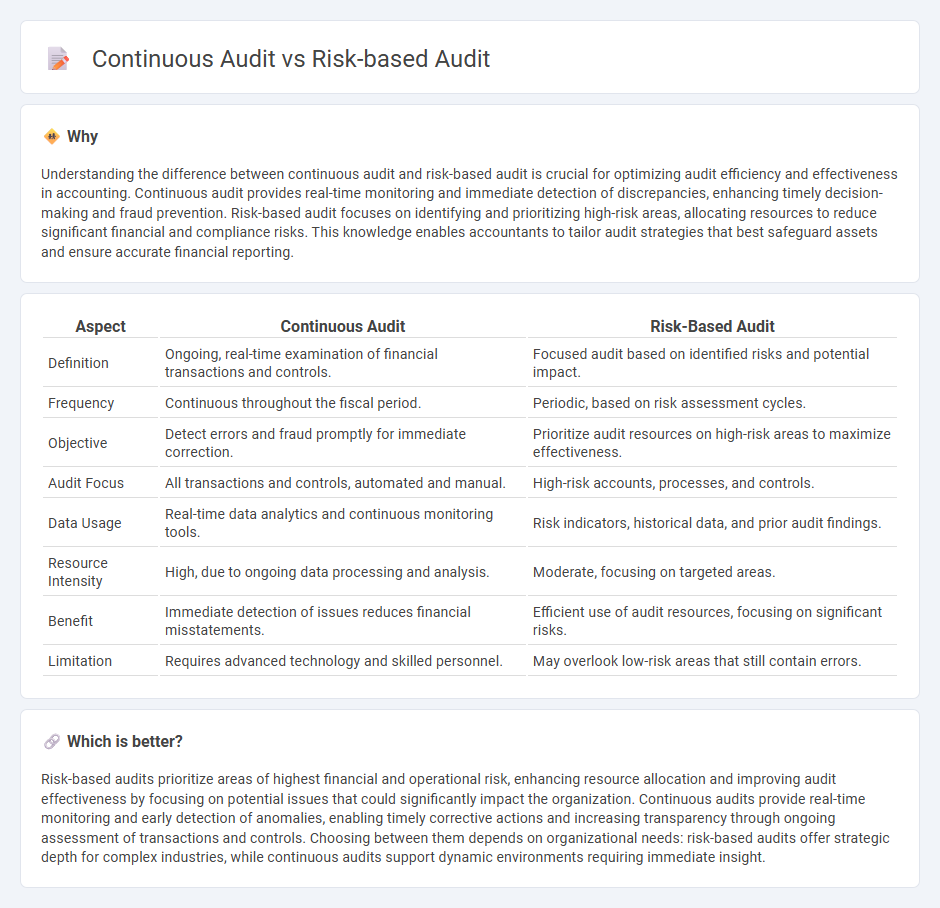
Understanding the difference between continuous audit and risk-based audit is crucial for optimizing audit efficiency and effectiveness in accounting. Continuous audit provides real-time monitoring and immediate detection of discrepancies, enhancing timely decision-making and fraud prevention. Risk-based audit focuses on identifying and prioritizing high-risk areas, allocating resources to reduce significant financial and compliance risks. This knowledge enables accountants to tailor audit strategies that best safeguard assets and ensure accurate financial reporting.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Continuous Audit | Risk-Based Audit |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ongoing, real-time examination of financial transactions and controls. | Focused audit based on identified risks and potential impact. |
| Frequency | Continuous throughout the fiscal period. | Periodic, based on risk assessment cycles. |
| Objective | Detect errors and fraud promptly for immediate correction. | Prioritize audit resources on high-risk areas to maximize effectiveness. |
| Audit Focus | All transactions and controls, automated and manual. | High-risk accounts, processes, and controls. |
| Data Usage | Real-time data analytics and continuous monitoring tools. | Risk indicators, historical data, and prior audit findings. |
| Resource Intensity | High, due to ongoing data processing and analysis. | Moderate, focusing on targeted areas. |
| Benefit | Immediate detection of issues reduces financial misstatements. | Efficient use of audit resources, focusing on significant risks. |
| Limitation | Requires advanced technology and skilled personnel. | May overlook low-risk areas that still contain errors. |
Which is better?
Risk-based audits prioritize areas of highest financial and operational risk, enhancing resource allocation and improving audit effectiveness by focusing on potential issues that could significantly impact the organization. Continuous audits provide real-time monitoring and early detection of anomalies, enabling timely corrective actions and increasing transparency through ongoing assessment of transactions and controls. Choosing between them depends on organizational needs: risk-based audits offer strategic depth for complex industries, while continuous audits support dynamic environments requiring immediate insight.
Connection
Continuous audit integrates real-time data analysis and automated controls, enabling ongoing assessment of financial transactions, which aligns closely with risk-based audit principles by prioritizing areas of highest risk. Risk-based audit focuses on identifying and evaluating significant risks that could affect financial accuracy, while continuous audit uses technology to monitor these risks continuously, ensuring timely detection and mitigation. This synergy enhances audit effectiveness by combining dynamic risk evaluation with persistent scrutiny of financial operations.
Key Terms
Risk Assessment
Risk-based audit prioritizes the evaluation of key risk areas to allocate audit resources efficiently, enhancing the detection of potential threats and control weaknesses. Continuous audit employs ongoing monitoring techniques and real-time data analysis, allowing for immediate identification and mitigation of emerging risks. Explore the distinctions in risk assessment processes between these audit methodologies to optimize your organization's audit strategy.
Real-time Monitoring
Risk-based audit prioritizes high-risk areas by evaluating controls and potential threats periodically, ensuring resources target the most vulnerable parts of an organization. Continuous audit employs real-time monitoring technologies to provide ongoing assurance, detecting anomalies and compliance issues as they occur and enabling immediate corrective actions. Explore how integrating risk-based audits with continuous real-time monitoring enhances audit accuracy and responsiveness.
Control Testing
Risk-based audit prioritizes control testing on high-risk areas identified through risk assessment frameworks like COSO and ISO 31000, ensuring efficient resource allocation. Continuous audit employs automated tools and real-time data monitoring to perform ongoing control testing, enabling early detection of anomalies and compliance issues. Explore detailed methodologies and benefits of each approach to enhance your audit strategy.
Source and External Links
Risk-Based Auditing as a Tool for Strategic Decision-Making - Pirani - Risk-based auditing is a methodology that directs audit efforts toward processes or areas with the highest exposure to risk, optimizing resources and aligning audits with organizational objectives.
Risk-based auditing - Wikipedia - This auditing style emphasizes analyzing and managing risk, prioritizing areas with the greatest potential impact rather than performing routine compliance checks.
Fundamentals of Risk-Based Auditing: A Strategic Framework - Risk-based auditing prioritizes audit activities by assessing the likelihood and impact of risks, typically following steps such as risk identification, assessment, prioritization, audit planning, execution, and reporting.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com