On-demand accruals involve recording expenses and revenues when they are incurred, regardless of cash flow, ensuring accurate financial statements in accordance with the matching principle. Revenue recognition determines the precise point when revenue is recorded, following standards such as ASC 606 or IFRS 15 to reflect economic reality. Explore further to understand how these concepts impact financial reporting and compliance.
Why it is important
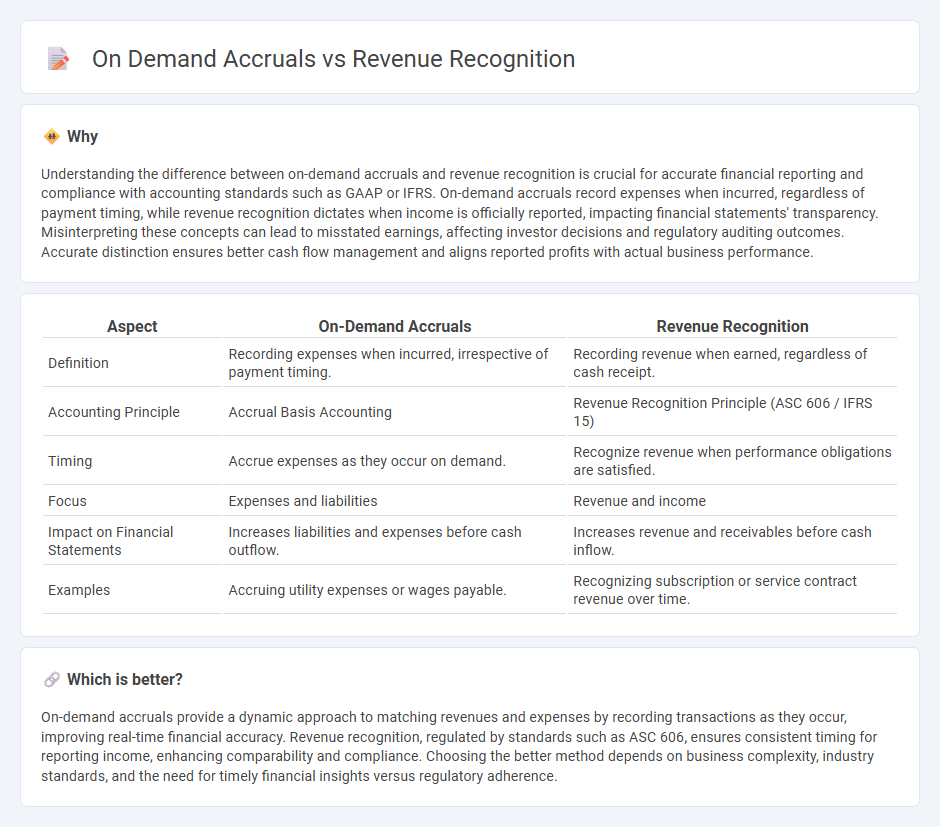
Understanding the difference between on-demand accruals and revenue recognition is crucial for accurate financial reporting and compliance with accounting standards such as GAAP or IFRS. On-demand accruals record expenses when incurred, regardless of payment timing, while revenue recognition dictates when income is officially reported, impacting financial statements' transparency. Misinterpreting these concepts can lead to misstated earnings, affecting investor decisions and regulatory auditing outcomes. Accurate distinction ensures better cash flow management and aligns reported profits with actual business performance.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | On-Demand Accruals | Revenue Recognition |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Recording expenses when incurred, irrespective of payment timing. | Recording revenue when earned, regardless of cash receipt. |
| Accounting Principle | Accrual Basis Accounting | Revenue Recognition Principle (ASC 606 / IFRS 15) |
| Timing | Accrue expenses as they occur on demand. | Recognize revenue when performance obligations are satisfied. |
| Focus | Expenses and liabilities | Revenue and income |
| Impact on Financial Statements | Increases liabilities and expenses before cash outflow. | Increases revenue and receivables before cash inflow. |
| Examples | Accruing utility expenses or wages payable. | Recognizing subscription or service contract revenue over time. |
Which is better?
On-demand accruals provide a dynamic approach to matching revenues and expenses by recording transactions as they occur, improving real-time financial accuracy. Revenue recognition, regulated by standards such as ASC 606, ensures consistent timing for reporting income, enhancing comparability and compliance. Choosing the better method depends on business complexity, industry standards, and the need for timely financial insights versus regulatory adherence.
Connection
On-demand accruals directly impact revenue recognition by ensuring revenues and expenses are recorded in the period they are incurred rather than when cash transactions occur. This alignment helps accurately match revenues with the corresponding costs, providing a realistic representation of financial performance. Effective use of on-demand accruals supports compliance with accounting standards like GAAP and IFRS that mandate timely and precise revenue recognition.
Key Terms
Matching Principle
Revenue recognition and on-demand accruals both adhere to the Matching Principle by ensuring expenses and revenues are recorded in the same period they relate to. Revenue recognition records income when earned, not necessarily when cash is received, while on-demand accruals estimate expenses incurred but not yet paid, matching costs to corresponding revenues. Explore further to understand how precise timing in accounting boosts financial accuracy and compliance.
Performance Obligation
Revenue recognition hinges on satisfying a performance obligation by transferring control of goods or services to the customer, following ASC 606 guidelines. On-demand accruals address timing differences between recognizing revenue and incurring related expenses, ensuring accurate matching when performance obligations are fulfilled. Explore in-depth insights on aligning revenue recognition with on-demand accruals to optimize financial reporting compliance.
Accrual Basis
Revenue recognition under the accrual basis records revenue when earned, regardless of cash receipt, while on-demand accruals focus on matching expenses incurred to the period they relate to, even if invoices or payments have not been finalized. This basis ensures financial statements reflect true economic activity, enhancing accuracy in profit measurement and compliance with accounting standards like GAAP or IFRS. Explore detailed distinctions and applications of these principles to improve your financial reporting accuracy.
Source and External Links
Revenue Recognition: Principles and 5-Step Model - NetSuite - Revenue recognition is an accounting principle that requires revenue to be recognized as it is earned through a five-step model including identifying the contract, performance obligations, transaction price, allocation, and recognizing revenue once obligations are met.
Revenue recognition principles & best practices - Stripe - Revenue recognition follows a five-step model under ASC 606 and IFRS 15 standards, emphasizing the identification of the contract and specific performance obligations before recording revenue.
Revenue Recognition Principle | Definition + Concept Examples - ASC 606 standardizes revenue recognition through a five-step process focusing on contract approval, performance obligations, transaction price, allocation, and formal revenue recognition once contractual obligations are fulfilled.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com