Sustainability reporting focuses on tracking environmental, social, and governance (ESG) performance to meet stakeholder demands for transparency and corporate responsibility, whereas regulatory reporting ensures compliance with legal financial standards set by authorities such as the SEC or IFRS. Companies employ sustainability reports to demonstrate their impact on climate change, resource usage, and social equity, while regulatory reports provide audited financial statements mandated by law. Explore detailed frameworks and best practices to enhance your understanding of both reporting types.
Why it is important
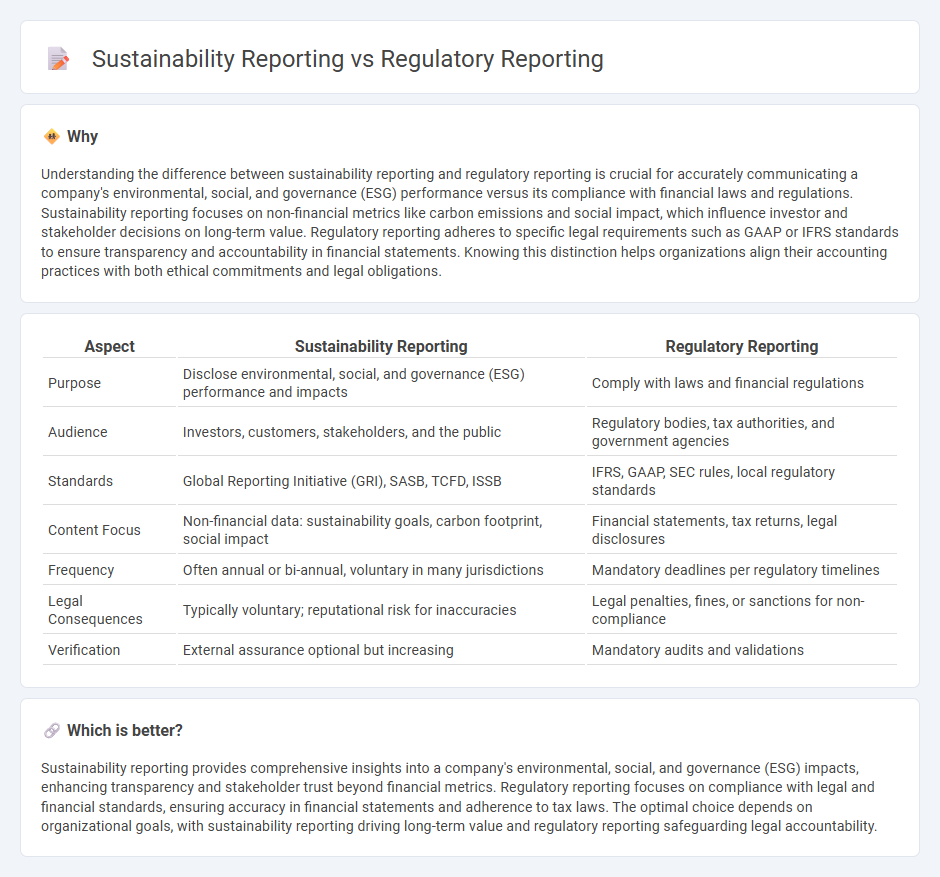
Understanding the difference between sustainability reporting and regulatory reporting is crucial for accurately communicating a company's environmental, social, and governance (ESG) performance versus its compliance with financial laws and regulations. Sustainability reporting focuses on non-financial metrics like carbon emissions and social impact, which influence investor and stakeholder decisions on long-term value. Regulatory reporting adheres to specific legal requirements such as GAAP or IFRS standards to ensure transparency and accountability in financial statements. Knowing this distinction helps organizations align their accounting practices with both ethical commitments and legal obligations.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Sustainability Reporting | Regulatory Reporting |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Disclose environmental, social, and governance (ESG) performance and impacts | Comply with laws and financial regulations |
| Audience | Investors, customers, stakeholders, and the public | Regulatory bodies, tax authorities, and government agencies |
| Standards | Global Reporting Initiative (GRI), SASB, TCFD, ISSB | IFRS, GAAP, SEC rules, local regulatory standards |
| Content Focus | Non-financial data: sustainability goals, carbon footprint, social impact | Financial statements, tax returns, legal disclosures |
| Frequency | Often annual or bi-annual, voluntary in many jurisdictions | Mandatory deadlines per regulatory timelines |
| Legal Consequences | Typically voluntary; reputational risk for inaccuracies | Legal penalties, fines, or sanctions for non-compliance |
| Verification | External assurance optional but increasing | Mandatory audits and validations |
Which is better?
Sustainability reporting provides comprehensive insights into a company's environmental, social, and governance (ESG) impacts, enhancing transparency and stakeholder trust beyond financial metrics. Regulatory reporting focuses on compliance with legal and financial standards, ensuring accuracy in financial statements and adherence to tax laws. The optimal choice depends on organizational goals, with sustainability reporting driving long-term value and regulatory reporting safeguarding legal accountability.
Connection
Sustainability reporting and regulatory reporting are connected through their shared objective of enhancing transparency and accountability in financial disclosures. Both frameworks require organizations to provide standardized and verifiable data on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) metrics, aligning with regulatory mandates such as the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) and the Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB). This integration ensures comprehensive risk management and compliance with evolving legal requirements while supporting sustainable business practices.
Key Terms
Regulatory Reporting:
Regulatory reporting involves the mandatory disclosure of financial and operational data to government agencies to ensure compliance with legal frameworks such as the Sarbanes-Oxley Act or Dodd-Frank Act. This type of reporting focuses on accuracy, timeliness, and adherence to regulatory standards governing industries like banking, healthcare, and energy. Explore more to understand how regulatory reporting safeguards transparency and enforces corporate accountability.
Compliance
Regulatory reporting centers on adhering to legal requirements and standards set by governmental bodies, ensuring accurate and timely submission of financial, operational, and compliance data. Sustainability reporting emphasizes transparent disclosure of environmental, social, and governance (ESG) performance, aiming to demonstrate corporate responsibility and long-term impact. Discover how integrating both frameworks can enhance compliance and corporate accountability by exploring their key distinctions and synergies.
Financial Statements
Regulatory reporting primarily concentrates on the accurate presentation of financial statements to comply with legal requirements and standards such as GAAP or IFRS. Sustainability reporting, meanwhile, extends beyond traditional financial metrics to include environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors, reflecting an organization's long-term impact and responsibility. Explore how integrating sustainability metrics into financial statements enhances transparency and drives informed stakeholder decisions.
Source and External Links
What is Regulatory Reporting? - Regulatory reporting is the process by which financial institutions submit data to regulatory authorities to ensure compliance with statutory requirements.
What is Regulatory Reporting: A Beginner's Guide - This guide explains regulatory reporting as a systematic process of collecting and submitting financial and operational data to regulatory authorities.
What Is Regulatory Reporting? A Complete Guide - This guide provides an overview of regulatory reporting, distinguishing it from financial reporting and highlighting its importance in compliance.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com