Supply chain finance focuses on optimizing cash flow by enabling suppliers to receive early payments based on approved invoices, improving liquidity across the supply chain. Reverse factoring involves a financial institution paying the supplier on behalf of the buyer, with the buyer repaying the institution at a later date, enhancing payment reliability for suppliers. Explore detailed comparisons to understand which solution best suits your business needs.
Why it is important
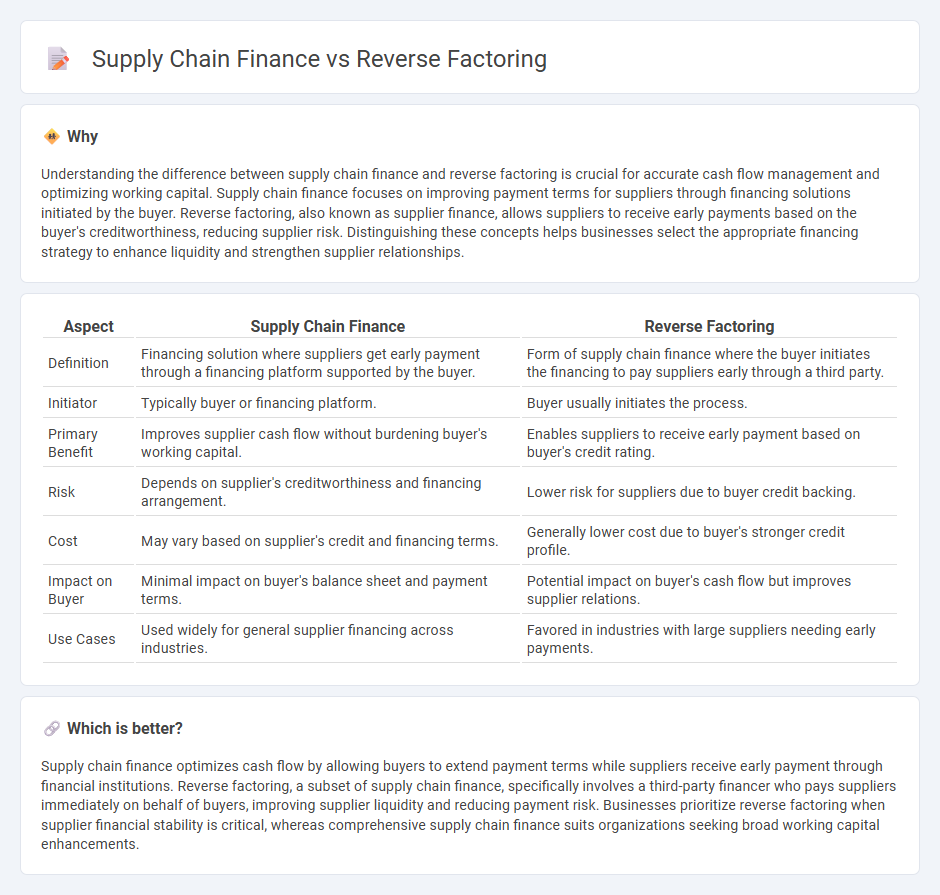
Understanding the difference between supply chain finance and reverse factoring is crucial for accurate cash flow management and optimizing working capital. Supply chain finance focuses on improving payment terms for suppliers through financing solutions initiated by the buyer. Reverse factoring, also known as supplier finance, allows suppliers to receive early payments based on the buyer's creditworthiness, reducing supplier risk. Distinguishing these concepts helps businesses select the appropriate financing strategy to enhance liquidity and strengthen supplier relationships.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Supply Chain Finance | Reverse Factoring |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Financing solution where suppliers get early payment through a financing platform supported by the buyer. | Form of supply chain finance where the buyer initiates the financing to pay suppliers early through a third party. |
| Initiator | Typically buyer or financing platform. | Buyer usually initiates the process. |
| Primary Benefit | Improves supplier cash flow without burdening buyer's working capital. | Enables suppliers to receive early payment based on buyer's credit rating. |
| Risk | Depends on supplier's creditworthiness and financing arrangement. | Lower risk for suppliers due to buyer credit backing. |
| Cost | May vary based on supplier's credit and financing terms. | Generally lower cost due to buyer's stronger credit profile. |
| Impact on Buyer | Minimal impact on buyer's balance sheet and payment terms. | Potential impact on buyer's cash flow but improves supplier relations. |
| Use Cases | Used widely for general supplier financing across industries. | Favored in industries with large suppliers needing early payments. |
Which is better?
Supply chain finance optimizes cash flow by allowing buyers to extend payment terms while suppliers receive early payment through financial institutions. Reverse factoring, a subset of supply chain finance, specifically involves a third-party financer who pays suppliers immediately on behalf of buyers, improving supplier liquidity and reducing payment risk. Businesses prioritize reverse factoring when supplier financial stability is critical, whereas comprehensive supply chain finance suits organizations seeking broad working capital enhancements.
Connection
Supply chain finance enhances liquidity for suppliers by enabling early invoice payments, often facilitated through reverse factoring. In reverse factoring, a buyer approves supplier invoices, allowing a financial institution to pay the supplier promptly while the buyer settles the debt later, optimizing working capital management. This connection streamlines accounting processes by improving cash flow visibility and reducing days payable outstanding (DPO) across the supply chain.
Key Terms
Accounts Payable
Reverse factoring is a subset of supply chain finance focused specifically on optimizing Accounts Payable processes by allowing suppliers to receive early payments backed by a buyer's creditworthiness. Supply chain finance encompasses a broader set of financial solutions designed to improve working capital across the entire supply chain, including both payables and receivables. Explore detailed differences and benefits of reverse factoring versus supply chain finance to enhance your company's financial efficiency.
Early Payment
Reverse factoring is a financing solution where suppliers receive early payment on invoices through a third-party financier, improving cash flow without impacting the buyer's credit. Supply chain finance broadly encompasses various payment solutions, including reverse factoring, to optimize working capital and strengthen supplier relationships. Explore how early payment strategies within these frameworks can transform your supply chain resilience and efficiency.
Third-party Financer
Reverse factoring involves a buyer-initiated process where a third-party financier pays suppliers early, improving supplier cash flow while securing favorable payment terms for the buyer. In supply chain finance, the third-party financer extends credit to suppliers based on the buyer's creditworthiness, optimizing working capital for both parties within the supply chain network. Discover more about how third-party financiers revolutionize cash flow and risk management in supply chain finance solutions.
Source and External Links
What Is Reverse Factoring? - Reverse factoring is a financing method where a third-party financier pays the supplier early and the buyer pays the financier later, improving cash flow for both buyer and supplier through a short-term loan arrangement.
Reverse factoring definition - Reverse factoring allows a bank or financier to pay a company's suppliers earlier than the original terms in exchange for a discount, benefiting suppliers by improving cash flow and buyers by strengthening supplier relations and preserving payment terms.
What is reverse factoring? | Definition & Meaning - Reverse factoring is a supplier finance solution where suppliers get early payment on approved invoices from a financer based on the buyer's credit rating, which enhances working capital and supplier relationships while reducing supply chain risk.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com