Decentralized ledger accounting leverages blockchain technology to provide transparent, immutable transaction records that enhance security and reduce the risk of fraud in financial reporting. ERP accounting systems integrate multiple business processes into a centralized platform, enabling streamlined data management and real-time financial analytics for improved decision-making. Explore the differences and benefits of these accounting methods to determine the best fit for your organization.
Why it is important
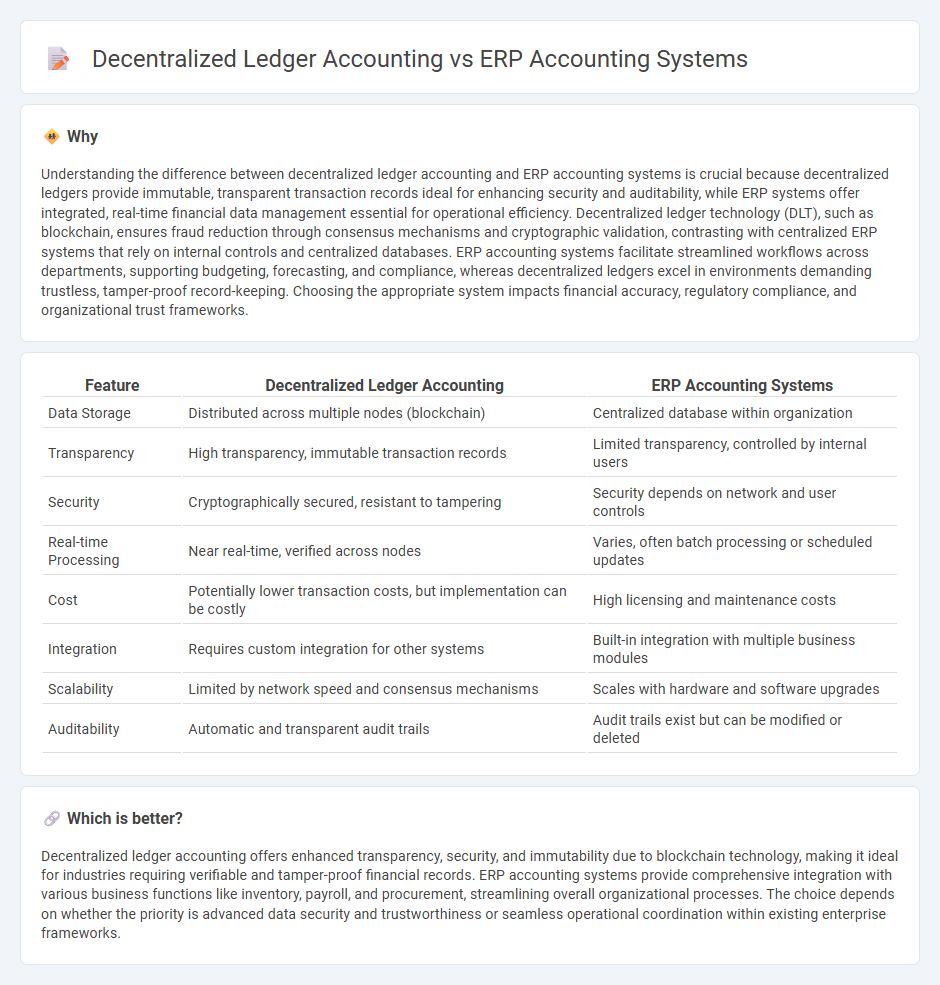
Understanding the difference between decentralized ledger accounting and ERP accounting systems is crucial because decentralized ledgers provide immutable, transparent transaction records ideal for enhancing security and auditability, while ERP systems offer integrated, real-time financial data management essential for operational efficiency. Decentralized ledger technology (DLT), such as blockchain, ensures fraud reduction through consensus mechanisms and cryptographic validation, contrasting with centralized ERP systems that rely on internal controls and centralized databases. ERP accounting systems facilitate streamlined workflows across departments, supporting budgeting, forecasting, and compliance, whereas decentralized ledgers excel in environments demanding trustless, tamper-proof record-keeping. Choosing the appropriate system impacts financial accuracy, regulatory compliance, and organizational trust frameworks.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Decentralized Ledger Accounting | ERP Accounting Systems |
|---|---|---|
| Data Storage | Distributed across multiple nodes (blockchain) | Centralized database within organization |
| Transparency | High transparency, immutable transaction records | Limited transparency, controlled by internal users |
| Security | Cryptographically secured, resistant to tampering | Security depends on network and user controls |
| Real-time Processing | Near real-time, verified across nodes | Varies, often batch processing or scheduled updates |
| Cost | Potentially lower transaction costs, but implementation can be costly | High licensing and maintenance costs |
| Integration | Requires custom integration for other systems | Built-in integration with multiple business modules |
| Scalability | Limited by network speed and consensus mechanisms | Scales with hardware and software upgrades |
| Auditability | Automatic and transparent audit trails | Audit trails exist but can be modified or deleted |
Which is better?
Decentralized ledger accounting offers enhanced transparency, security, and immutability due to blockchain technology, making it ideal for industries requiring verifiable and tamper-proof financial records. ERP accounting systems provide comprehensive integration with various business functions like inventory, payroll, and procurement, streamlining overall organizational processes. The choice depends on whether the priority is advanced data security and trustworthiness or seamless operational coordination within existing enterprise frameworks.
Connection
Decentralized ledger accounting leverages blockchain technology to provide secure, transparent, and immutable financial records, enhancing the accuracy and trustworthiness of data. ERP accounting systems integrate this decentralized ledger data to streamline financial processes, improve real-time reporting, and ensure regulatory compliance. This connection enables organizations to synchronize transactional data across departments while maintaining a verified audit trail.
Key Terms
Centralization vs. Decentralization
ERP accounting systems centralize financial data within a singular platform, enabling streamlined reporting, data consistency, and controlled user access, enhancing organizational oversight. Decentralized ledger accounting distributes financial records across multiple, interconnected nodes, promoting transparency, immutability, and reduced risk of single-point failures commonly associated with centralized databases. Explore the transformative impact of centralized versus decentralized accounting models to optimize financial management strategies.
Real-time Data Synchronization
ERP accounting systems provide centralized data management, ensuring consistent and accurate financial records through integrated modules and real-time updates across departments. Decentralized ledger accounting leverages blockchain technology to enable transparent, tamper-proof transactions with instantaneous synchronization across distributed nodes, enhancing security and auditability. Explore the differences in real-time data synchronization to optimize your financial workflows effectively.
Immutable Audit Trail
ERP accounting systems maintain audit trails within centralized databases, which can be vulnerable to tampering or unauthorized alterations, potentially compromising data integrity. Decentralized ledger accounting, such as blockchain technology, offers an immutable audit trail by recording transactions across multiple nodes, ensuring transparency and resistance to fraud. Explore how immutable audit trails transform financial record-keeping and enhance trust by diving deeper into decentralized ledger solutions.
Source and External Links
ERP for Accounting and Financial Management - ERP accounting systems integrate core finance functions like general ledger, cash flow, accounts receivable/payable, and expense management, centralizing data to improve efficiency, accuracy, visibility, and enable strategic financial planning and regulatory compliance within organizations.
What Is an ERP System in Accounting? - ERP systems eliminate data duplication by centralizing sales, transaction, and inventory data, streamlining payment processing and cash flow, and are particularly valuable for growing mid-market businesses through integration with accounting and payment automation tools.
Top 10 ERP Systems for Finance and Accounting - Some ERP systems excel in finance and accounting features such as financial planning, general ledger, tax, and treasury management, with options ranging from full ERP suites to popular finance-focused platforms like QuickBooks for smaller organizations.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com