Continuous assurance leverages real-time data monitoring and automated controls to provide ongoing verification of financial transactions, enhancing accuracy and timeliness in accounting processes. Post-facto analysis involves retrospective examination of financial records to identify discrepancies and ensure compliance after transactions have occurred. Explore the advantages and implementation strategies of both approaches to optimize your financial auditing practices.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between continuous assurance and post-facto analysis is vital for improving the accuracy and timeliness of financial reporting. Continuous assurance provides real-time monitoring and risk detection, enabling proactive decision-making and fraud prevention. Post-facto analysis, performed after transactions occur, helps identify and correct errors but may delay response times. Mastery of both enhances audit quality and regulatory compliance in accounting practices.
Comparison Table
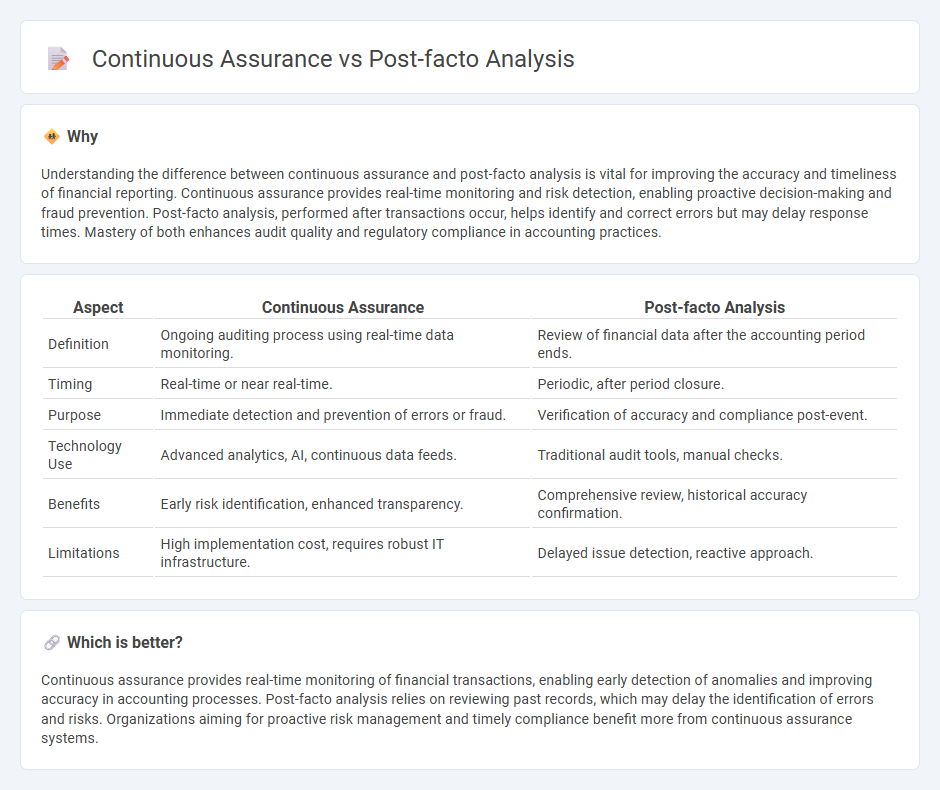
| Aspect | Continuous Assurance | Post-facto Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ongoing auditing process using real-time data monitoring. | Review of financial data after the accounting period ends. |
| Timing | Real-time or near real-time. | Periodic, after period closure. |
| Purpose | Immediate detection and prevention of errors or fraud. | Verification of accuracy and compliance post-event. |
| Technology Use | Advanced analytics, AI, continuous data feeds. | Traditional audit tools, manual checks. |
| Benefits | Early risk identification, enhanced transparency. | Comprehensive review, historical accuracy confirmation. |
| Limitations | High implementation cost, requires robust IT infrastructure. | Delayed issue detection, reactive approach. |
Which is better?
Continuous assurance provides real-time monitoring of financial transactions, enabling early detection of anomalies and improving accuracy in accounting processes. Post-facto analysis relies on reviewing past records, which may delay the identification of errors and risks. Organizations aiming for proactive risk management and timely compliance benefit more from continuous assurance systems.
Connection
Continuous assurance provides real-time monitoring and verification of financial data, enabling immediate detection of discrepancies and enhancing data accuracy. Post-facto analysis reviews historical financial records to identify patterns and anomalies that may have been missed during initial assessments. Together, they form a comprehensive framework for ensuring ongoing accuracy and reliability in accounting processes.
Key Terms
Audit Trail
Post-facto analysis examines historical audit trails to identify discrepancies and compliance issues after transactions have occurred, providing a retrospective view critical for forensic audits. Continuous assurance utilizes real-time monitoring of audit trails, enabling immediate detection of anomalies and ongoing validation of financial data accuracy. Explore how integrating both methods enhances audit trail reliability and improves overall audit quality.
Real-time Monitoring
Post-facto analysis evaluates data after transactions occur, identifying discrepancies and trends to improve future controls and reporting accuracy. Continuous assurance involves real-time monitoring using automated systems that provide immediate insights into financial processes, enhancing fraud detection and compliance adherence. Explore how integrating real-time monitoring elevates audit quality and operational efficiency.
Variance Analysis
Variance analysis in post-facto analysis provides insights by examining deviations between actual and budgeted performance after transactions occur. Continuous assurance enhances this by integrating real-time data monitoring, enabling immediate detection and correction of variances. Explore how combining these approaches improves financial accuracy and decision-making.
Source and External Links
Ex Post Facto Research Design Examples - Provides an overview of ex post facto research, focusing on analyzing existing phenomena to identify causal relationships without manipulating variables.
Understanding Effects After the Fact with Ex-Post Facto Research - Explains how ex post facto research works, identifying independent and dependent variables after an event has occurred.
Ex Post Facto Analysis at the European Patent Office - Discusses the importance of avoiding *ex post facto* analysis in patent examination to ensure fair assessment of inventions.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com