Decentralized ledger accounting leverages blockchain technology to create immutable, transparent financial records accessible to all participants, enhancing accuracy and reducing fraud risks. Traditional auditing relies on manual verification and sampling methods that can be time-consuming and prone to human error. Explore the transformative impact of decentralized ledger accounting on modern auditing practices to understand its benefits fully.
Why it is important
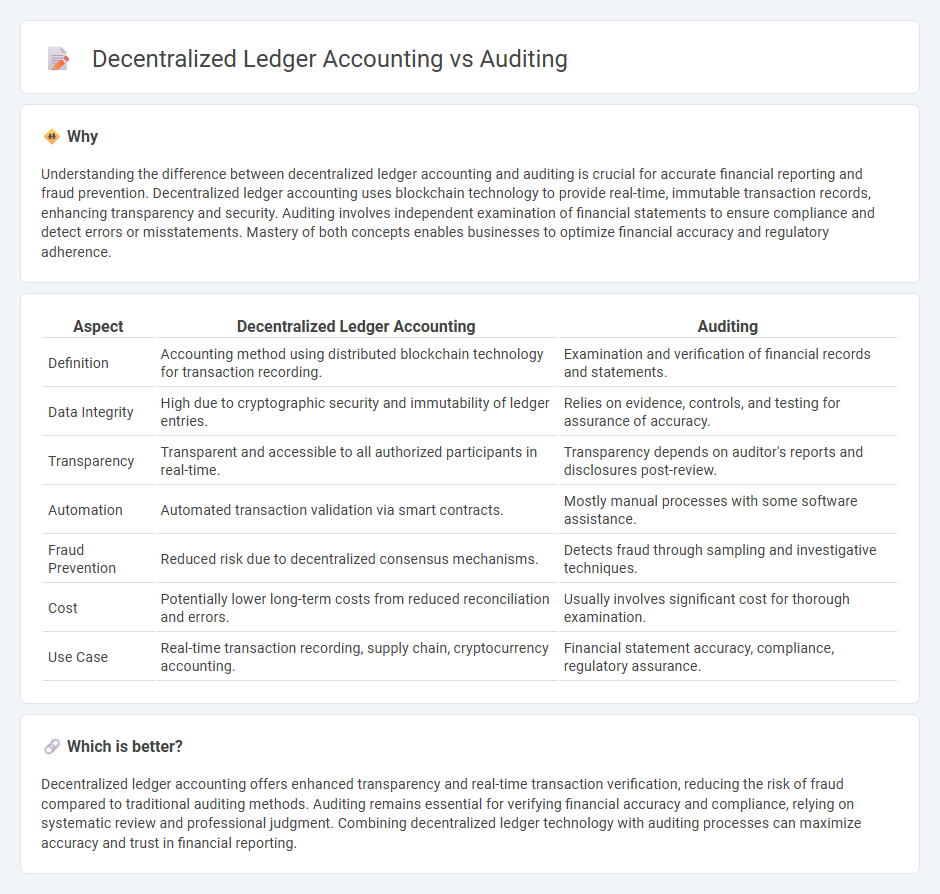
Understanding the difference between decentralized ledger accounting and auditing is crucial for accurate financial reporting and fraud prevention. Decentralized ledger accounting uses blockchain technology to provide real-time, immutable transaction records, enhancing transparency and security. Auditing involves independent examination of financial statements to ensure compliance and detect errors or misstatements. Mastery of both concepts enables businesses to optimize financial accuracy and regulatory adherence.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Decentralized Ledger Accounting | Auditing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Accounting method using distributed blockchain technology for transaction recording. | Examination and verification of financial records and statements. |
| Data Integrity | High due to cryptographic security and immutability of ledger entries. | Relies on evidence, controls, and testing for assurance of accuracy. |
| Transparency | Transparent and accessible to all authorized participants in real-time. | Transparency depends on auditor's reports and disclosures post-review. |
| Automation | Automated transaction validation via smart contracts. | Mostly manual processes with some software assistance. |
| Fraud Prevention | Reduced risk due to decentralized consensus mechanisms. | Detects fraud through sampling and investigative techniques. |
| Cost | Potentially lower long-term costs from reduced reconciliation and errors. | Usually involves significant cost for thorough examination. |
| Use Case | Real-time transaction recording, supply chain, cryptocurrency accounting. | Financial statement accuracy, compliance, regulatory assurance. |
Which is better?
Decentralized ledger accounting offers enhanced transparency and real-time transaction verification, reducing the risk of fraud compared to traditional auditing methods. Auditing remains essential for verifying financial accuracy and compliance, relying on systematic review and professional judgment. Combining decentralized ledger technology with auditing processes can maximize accuracy and trust in financial reporting.
Connection
Decentralized ledger accounting utilizes blockchain technology to create transparent, immutable records that enhance the accuracy and reliability of financial data. Auditing processes leverage these secure ledgers to conduct real-time verification of transactions, reducing fraud risk and improving compliance. This integration streamlines audit trails and facilitates trust in financial reporting through cryptographic validation and distributed consensus mechanisms.
Key Terms
Verification
Verification in auditing involves rigorous examination of financial records, ensuring accuracy and compliance through cross-checking documents and transactions. In decentralized ledger accounting, verification is achieved through consensus mechanisms like proof of work or proof of stake, enabling real-time, transparent validation across multiple nodes without a central authority. Explore how these verification methods impact financial transparency and trust in evolving accounting practices.
Consensus
Consensus mechanisms in decentralized ledger accounting ensure transaction validity through network agreement, enhancing transparency and reducing fraud risk compared to traditional auditing methods reliant on centralized verification. Auditing depends on sampling and expert judgment, while consensus protocols like Proof of Work or Proof of Stake automate trust through cryptographic validation across distributed nodes. Explore our detailed analysis to understand how consensus transforms accounting accuracy and accountability.
Transparency
Auditing ensures transparency by providing an independent verification of financial records, highlighting discrepancies and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards. Decentralized ledger accounting, such as blockchain technology, enhances transparency through immutable, real-time transaction records accessible to all authorized participants. Discover how these mechanisms transform financial transparency and accountability.
Source and External Links
What Is Auditing? Definition, Types & Importance - Deskera - Auditing is a systematic review and verification of financial documents by an independent party to ensure accuracy, compliance with accounting standards, fraud detection, risk management, and stakeholder confidence.
Auditing: Definition, Types, and Importance - FreshBooks - Auditing involves an objective examination of financial records to confirm accuracy, compliance, and to detect errors, covering internal, external, and IRS audits.
Auditing - Overview, Importance, Types, and Accounting Standards - Auditing is an independent evaluation of a company's financial statements to ensure they fairly represent financial position and comply with accounting standards such as GAAP or IFRS.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com