Embedded finance compliance ensures that financial services integrated within non-financial platforms adhere to regulatory standards, reducing risks related to fraud, data privacy, and anti-money laundering (AML) requirements. Internal controls in accounting focus on verifying transactional accuracy, safeguarding assets, and ensuring reliable financial reporting through systematic checks and balances. Explore how aligning embedded finance compliance with robust internal controls strengthens overall financial governance.
Why it is important
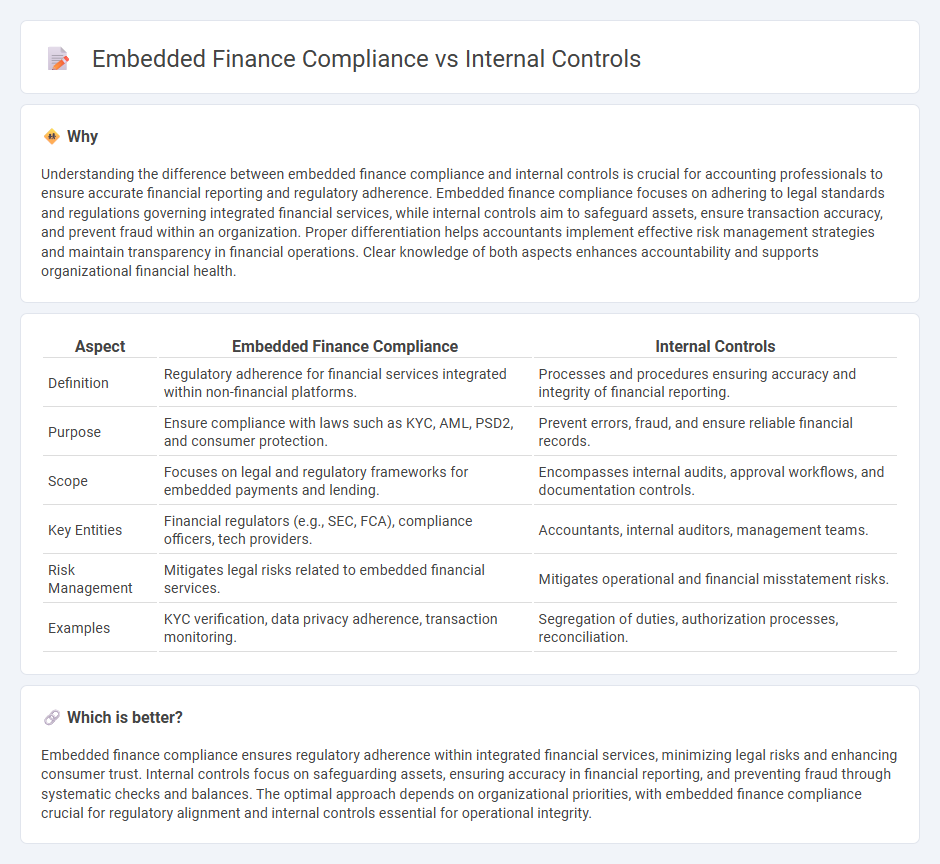
Understanding the difference between embedded finance compliance and internal controls is crucial for accounting professionals to ensure accurate financial reporting and regulatory adherence. Embedded finance compliance focuses on adhering to legal standards and regulations governing integrated financial services, while internal controls aim to safeguard assets, ensure transaction accuracy, and prevent fraud within an organization. Proper differentiation helps accountants implement effective risk management strategies and maintain transparency in financial operations. Clear knowledge of both aspects enhances accountability and supports organizational financial health.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Embedded Finance Compliance | Internal Controls |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Regulatory adherence for financial services integrated within non-financial platforms. | Processes and procedures ensuring accuracy and integrity of financial reporting. |
| Purpose | Ensure compliance with laws such as KYC, AML, PSD2, and consumer protection. | Prevent errors, fraud, and ensure reliable financial records. |
| Scope | Focuses on legal and regulatory frameworks for embedded payments and lending. | Encompasses internal audits, approval workflows, and documentation controls. |
| Key Entities | Financial regulators (e.g., SEC, FCA), compliance officers, tech providers. | Accountants, internal auditors, management teams. |
| Risk Management | Mitigates legal risks related to embedded financial services. | Mitigates operational and financial misstatement risks. |
| Examples | KYC verification, data privacy adherence, transaction monitoring. | Segregation of duties, authorization processes, reconciliation. |
Which is better?
Embedded finance compliance ensures regulatory adherence within integrated financial services, minimizing legal risks and enhancing consumer trust. Internal controls focus on safeguarding assets, ensuring accuracy in financial reporting, and preventing fraud through systematic checks and balances. The optimal approach depends on organizational priorities, with embedded finance compliance crucial for regulatory alignment and internal controls essential for operational integrity.
Connection
Embedded finance compliance ensures adherence to regulatory standards within integrated financial services, directly influencing the design and effectiveness of internal controls in accounting. Robust internal controls are essential to monitor transactions, manage risks, and validate compliance in embedded finance frameworks. This connection safeguards financial data integrity and prevents fraud, thereby enhancing overall accounting accuracy and reliability.
Key Terms
Segregation of Duties
Internal controls emphasize Segregation of Duties (SoD) to prevent fraud and errors by dividing responsibilities among different individuals, ensuring no single person has control over all critical aspects of a transaction. Embedded finance compliance integrates SoD principles within financial technology platforms to safeguard sensitive data and maintain regulatory adherence in real-time operations. Explore further to understand how SoD enhances security and compliance in embedded finance environments.
Transaction Monitoring
Internal controls in transaction monitoring emphasize the systematic review of financial activities to detect and prevent fraud, ensuring adherence to regulatory standards such as AML and KYC. Embedded finance compliance integrates these controls directly into third-party platforms, leveraging real-time data analytics and automated alerts to enhance transaction transparency within digital ecosystems. Explore how advanced transaction monitoring solutions streamline compliance and secure embedded finance operations.
Regulatory Reporting
Internal controls ensure that financial processes adhere to laws and regulations by implementing rigorous checks, reconciliation procedures, and audit trails, crucial for accurate regulatory reporting. Embedded finance compliance integrates financial services within non-financial platforms, requiring stringent monitoring to meet regulatory standards and prevent reporting discrepancies. Discover detailed strategies to optimize regulatory reporting in both internal controls and embedded finance compliance for enhanced financial governance.
Source and External Links
The Essential Guide to Internal Audit and Controls - Provides an overview of internal controls, including the control environment, risk assessment, control activities, information and communication, and monitoring.
Internal Control - Wikipedia - Discusses internal control roles and responsibilities, highlighting the importance of management and the board of directors in maintaining effective internal controls.
Top Ten Things to Strengthen Internal Controls in the Office - Offers practical advice on strengthening internal controls, including duty segregation, physical asset control, and regular reconciliations to prevent fraud and errors.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com