Zero trust accounting emphasizes strict verification and minimal trust in financial transactions to enhance security and prevent fraud, a critical approach in modern digital environments. Governmental accounting follows standardized protocols to ensure transparency, accountability, and legal compliance in public sector financial reporting. Explore the differences and benefits of these accounting frameworks to optimize your financial management practices.
Why it is important
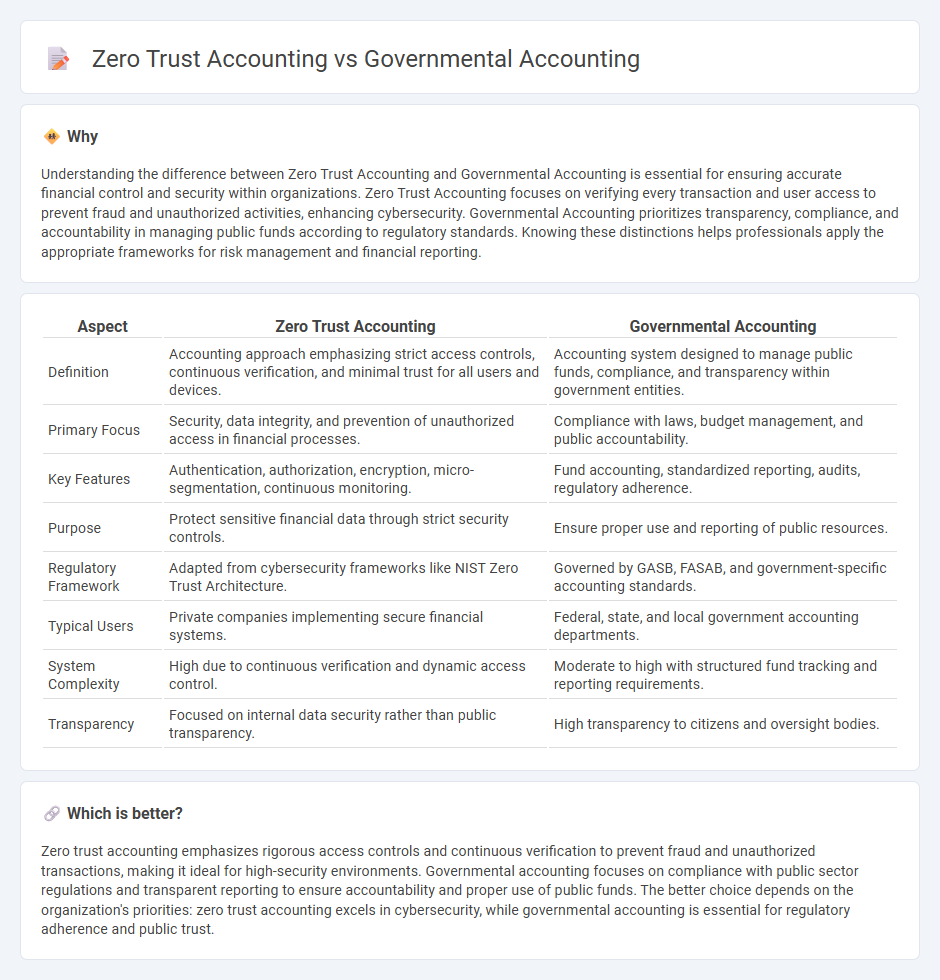
Understanding the difference between Zero Trust Accounting and Governmental Accounting is essential for ensuring accurate financial control and security within organizations. Zero Trust Accounting focuses on verifying every transaction and user access to prevent fraud and unauthorized activities, enhancing cybersecurity. Governmental Accounting prioritizes transparency, compliance, and accountability in managing public funds according to regulatory standards. Knowing these distinctions helps professionals apply the appropriate frameworks for risk management and financial reporting.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Zero Trust Accounting | Governmental Accounting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Accounting approach emphasizing strict access controls, continuous verification, and minimal trust for all users and devices. | Accounting system designed to manage public funds, compliance, and transparency within government entities. |
| Primary Focus | Security, data integrity, and prevention of unauthorized access in financial processes. | Compliance with laws, budget management, and public accountability. |
| Key Features | Authentication, authorization, encryption, micro-segmentation, continuous monitoring. | Fund accounting, standardized reporting, audits, regulatory adherence. |
| Purpose | Protect sensitive financial data through strict security controls. | Ensure proper use and reporting of public resources. |
| Regulatory Framework | Adapted from cybersecurity frameworks like NIST Zero Trust Architecture. | Governed by GASB, FASAB, and government-specific accounting standards. |
| Typical Users | Private companies implementing secure financial systems. | Federal, state, and local government accounting departments. |
| System Complexity | High due to continuous verification and dynamic access control. | Moderate to high with structured fund tracking and reporting requirements. |
| Transparency | Focused on internal data security rather than public transparency. | High transparency to citizens and oversight bodies. |
Which is better?
Zero trust accounting emphasizes rigorous access controls and continuous verification to prevent fraud and unauthorized transactions, making it ideal for high-security environments. Governmental accounting focuses on compliance with public sector regulations and transparent reporting to ensure accountability and proper use of public funds. The better choice depends on the organization's priorities: zero trust accounting excels in cybersecurity, while governmental accounting is essential for regulatory adherence and public trust.
Connection
Zero trust accounting enhances Governmental accounting by enforcing strict verification protocols for all financial transactions, reducing the risk of fraud and unauthorized access. Governmental accounting benefits from zero trust principles through increased transparency, data integrity, and compliance with regulatory standards. Implementing zero trust frameworks ensures that government financial records are securely monitored and audited in real-time.
Key Terms
**Governmental accounting:**
Governmental accounting centers on recording, analyzing, and reporting financial transactions for public sector entities, ensuring transparency, accountability, and compliance with regulations such as the Governmental Accounting Standards Board (GASB) guidelines. This accounting framework emphasizes fund accounting and budgetary control to manage public resources effectively and support decision-making processes within government bodies. Explore in-depth differences and specific use cases between governmental accounting and Zero Trust accounting methodologies.
Fund Accounting
Governmental accounting centers on fund accounting to ensure legal compliance and accountability by separating resources into specific funds with distinct purposes, facilitating transparent financial reporting. Zero trust accounting, evolving from cybersecurity principles, emphasizes continuous verification and strict access controls for financial data integrity, although it does not alter the fundamental principles of fund accounting. Explore how zero trust models can revolutionize governmental accounting fund management and enhance financial security.
Budgetary Control
Governmental accounting emphasizes strict budgetary control by monitoring appropriations, expenditures, and fund balances to ensure compliance with legislative mandates. Zero trust accounting integrates continuous verification and granular access controls to enhance budget security and prevent unauthorized financial transactions. Explore more to understand how these methodologies reshape fiscal oversight and budget integrity.
Source and External Links
Governmental accounting - Governmental accounting refers to the process of recording and managing all financial transactions incurred by the government, focusing on financial rather than economic resources.
Governmental Accounting Standards Board: What is GASB? - GASB is an independent organization that develops and issues accounting and financial reporting standards for U.S. state and local governments to ensure transparency and accountability.
What Is Government Accounting? - Government accounting involves tracking public finances to ensure proper use and efficiency, with a focus on accountability, transparency, and compliance with legal standards.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com