Real-time expense recognition records costs immediately as transactions occur, ensuring up-to-date financial statements and accurate cash flow management. Periodic expense recognition aggregates expenses over a set interval, such as monthly or quarterly, which can delay insights but simplify reporting processes. Explore the key differences and benefits of each method to optimize your accounting practices.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between real-time expense recognition and periodic expense recognition is crucial for accurate financial reporting and cash flow management. Real-time expense recognition records expenses immediately when incurred, providing up-to-date financial data that enhances decision-making and budget control. Periodic expense recognition aggregates expenses over a set period, which can simplify accounting but may delay insight into current financial status. Accurate timing in expense recognition ensures compliance with accounting standards such as GAAP and IFRS, preventing misstatements in profit measurement.
Comparison Table
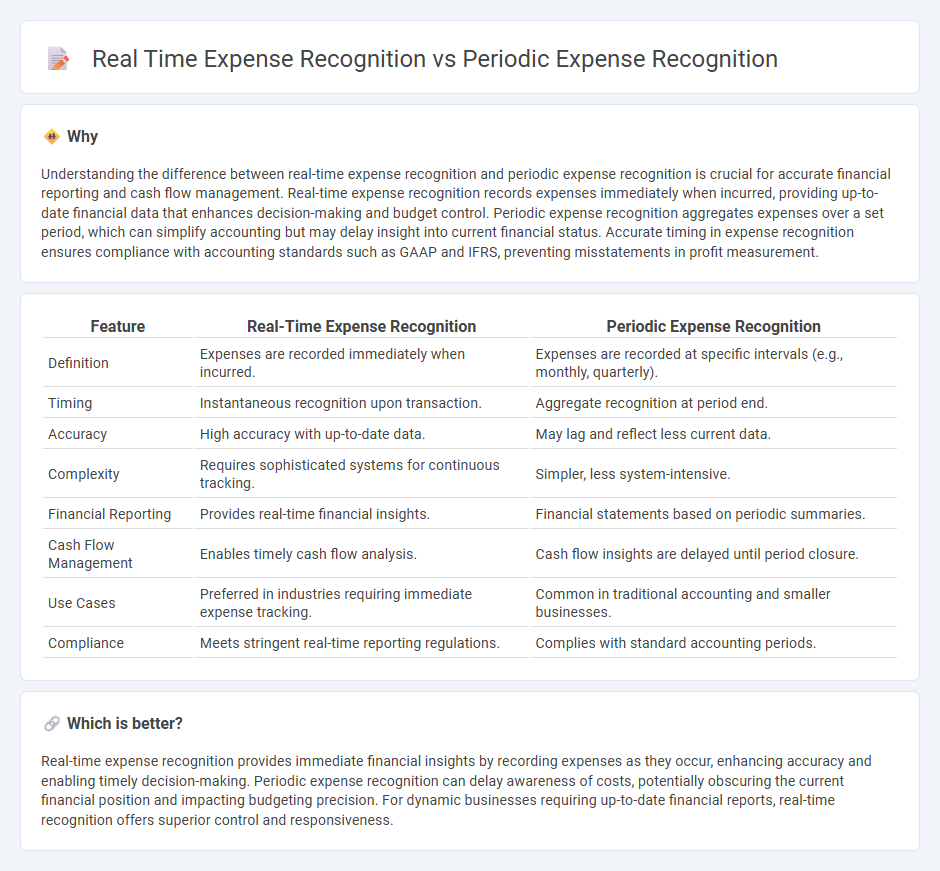
| Feature | Real-Time Expense Recognition | Periodic Expense Recognition |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Expenses are recorded immediately when incurred. | Expenses are recorded at specific intervals (e.g., monthly, quarterly). |
| Timing | Instantaneous recognition upon transaction. | Aggregate recognition at period end. |
| Accuracy | High accuracy with up-to-date data. | May lag and reflect less current data. |
| Complexity | Requires sophisticated systems for continuous tracking. | Simpler, less system-intensive. |
| Financial Reporting | Provides real-time financial insights. | Financial statements based on periodic summaries. |
| Cash Flow Management | Enables timely cash flow analysis. | Cash flow insights are delayed until period closure. |
| Use Cases | Preferred in industries requiring immediate expense tracking. | Common in traditional accounting and smaller businesses. |
| Compliance | Meets stringent real-time reporting regulations. | Complies with standard accounting periods. |
Which is better?
Real-time expense recognition provides immediate financial insights by recording expenses as they occur, enhancing accuracy and enabling timely decision-making. Periodic expense recognition can delay awareness of costs, potentially obscuring the current financial position and impacting budgeting precision. For dynamic businesses requiring up-to-date financial reports, real-time recognition offers superior control and responsiveness.
Connection
Real-time expense recognition records expenditures immediately when they occur, ensuring up-to-date financial statements, while periodic expense recognition consolidates these expenses at regular intervals for comprehensive reporting. Both methods are interconnected as real-time data feeds into periodic reports, enhancing accuracy and timeliness in financial analysis. Implementing a hybrid approach optimizes expense tracking by balancing immediate accountability with structured financial review cycles.
Key Terms
Accrual Accounting
Periodic expense recognition in accrual accounting records expenses at fixed intervals, such as monthly or quarterly, ensuring alignment with revenue within the same period. Real-time expense recognition captures costs immediately when incurred, providing a more accurate and timely financial picture, especially important for dynamic business environments. Explore deeper insights into how these methods impact financial statements and decision-making processes.
Matching Principle
Periodic expense recognition records costs at specific intervals, aligning expenses with revenues recognized during the same period to adhere to the Matching Principle. Real-time expense recognition captures expenses immediately when incurred, ensuring precise matching of costs to the exact timing of related revenues. Explore deeper insights on how these methods impact financial accuracy and reporting standards.
Cash Basis Accounting
In cash basis accounting, periodic expense recognition records expenses at set intervals, matching cash outflows with specific reporting periods, whereas real-time expense recognition logs expenses immediately upon payment, providing up-to-date financial status. Periodic recognition simplifies bookkeeping but may delay accurate expense tracking, while real-time recognition enhances timely financial decision-making and cash flow management. Explore the benefits and challenges of each method to optimize your cash basis accounting approach.
Source and External Links
What's Expense Recognition Principle? - The periodic expense recognition ensures expenses are recorded in the same period as the revenues they help generate, using methods like systematic allocation for expenses benefiting multiple periods (e.g., depreciation) or immediate recognition for costs without future benefits.
Expense recognition principle - Expenses are recognized periodically (typically monthly or annually) to match the revenue generated during each period, which is essential under accrual accounting and required for audited financial statements.
What is The Expense Recognition Principle and How Does It Work - Periodic expense recognition matches expenses with the revenues they generate, involving systematic allocation for long-term benefits and immediate recognition for short-term costs, ensuring financial statements accurately reflect business performance over time.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com