Continuous assurance leverages automated tools and real-time data analytics to enhance accuracy and timeliness in financial reporting, reducing human error inherent in manual audits. Manual audits rely on periodic, in-person verification of records, which can delay the identification of discrepancies and increase risk exposure. Explore how integrating continuous assurance can transform your auditing processes for improved compliance and efficiency.
Why it is important
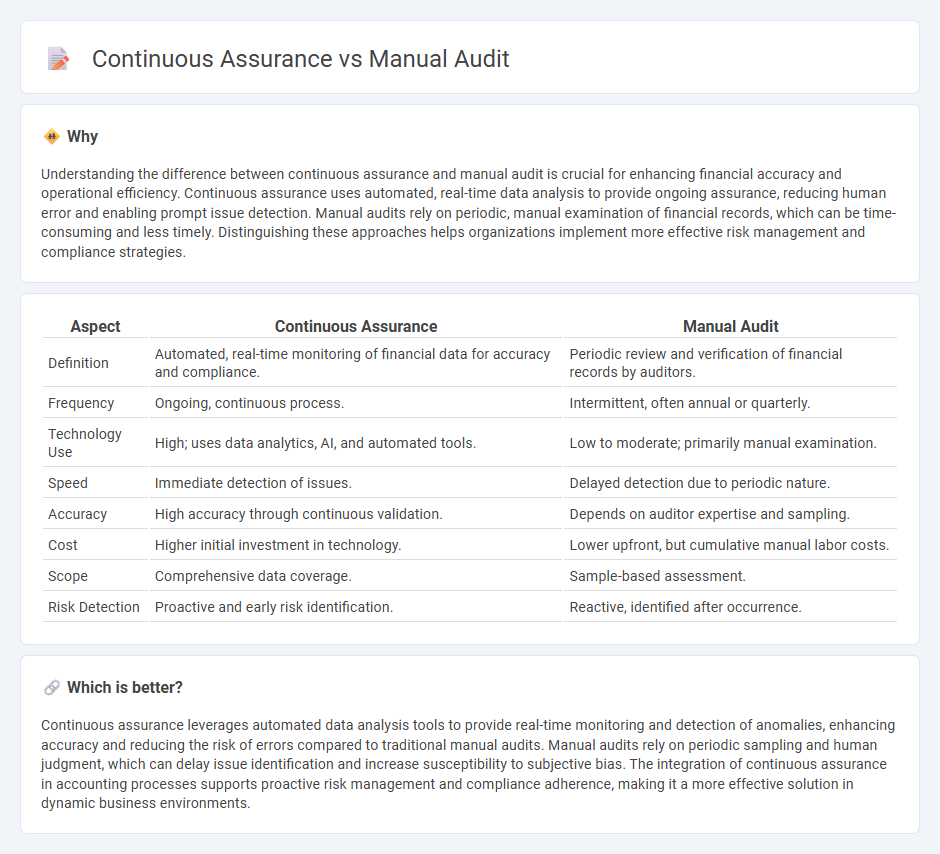
Understanding the difference between continuous assurance and manual audit is crucial for enhancing financial accuracy and operational efficiency. Continuous assurance uses automated, real-time data analysis to provide ongoing assurance, reducing human error and enabling prompt issue detection. Manual audits rely on periodic, manual examination of financial records, which can be time-consuming and less timely. Distinguishing these approaches helps organizations implement more effective risk management and compliance strategies.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Continuous Assurance | Manual Audit |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Automated, real-time monitoring of financial data for accuracy and compliance. | Periodic review and verification of financial records by auditors. |
| Frequency | Ongoing, continuous process. | Intermittent, often annual or quarterly. |
| Technology Use | High; uses data analytics, AI, and automated tools. | Low to moderate; primarily manual examination. |
| Speed | Immediate detection of issues. | Delayed detection due to periodic nature. |
| Accuracy | High accuracy through continuous validation. | Depends on auditor expertise and sampling. |
| Cost | Higher initial investment in technology. | Lower upfront, but cumulative manual labor costs. |
| Scope | Comprehensive data coverage. | Sample-based assessment. |
| Risk Detection | Proactive and early risk identification. | Reactive, identified after occurrence. |
Which is better?
Continuous assurance leverages automated data analysis tools to provide real-time monitoring and detection of anomalies, enhancing accuracy and reducing the risk of errors compared to traditional manual audits. Manual audits rely on periodic sampling and human judgment, which can delay issue identification and increase susceptibility to subjective bias. The integration of continuous assurance in accounting processes supports proactive risk management and compliance adherence, making it a more effective solution in dynamic business environments.
Connection
Continuous assurance leverages real-time data analytics to monitor financial transactions, enhancing the accuracy and timeliness of audit findings. Manual audits complement continuous assurance by providing in-depth, qualitative assessments and judgment-based evaluations that automated systems cannot fully replicate. Integration of both methods strengthens overall audit quality through comprehensive risk assessment and verification processes.
Key Terms
Sample Testing
Manual audit sample testing involves auditors selecting and examining specific transactions or records based on predefined criteria, which may lead to limited data coverage and potential oversight. Continuous assurance leverages automated tools to perform real-time, comprehensive sample testing across entire datasets, enhancing accuracy and timely identification of anomalies. Explore how integrating continuous assurance can revolutionize audit reliability and efficiency.
Real-time Monitoring
Manual audit relies on periodic, retrospective examination of financial records and processes, often leading to delayed detection of discrepancies and increased risk exposure. Continuous assurance, enabled by real-time monitoring technologies, provides ongoing verification of data accuracy and compliance, enhancing transparency and enabling faster corrective actions. Explore how real-time monitoring transforms audit effectiveness and risk management practices in dynamic business environments.
Data Integration
Manual audit processes often rely on periodic data extraction and reconciliation, which can lead to delays and potential inaccuracies in financial reporting. Continuous assurance leverages automated data integration systems that provide real-time access to financial data, enabling timely detection of anomalies and improved audit quality. Explore how implementing advanced data integration tools can enhance audit accuracy and operational efficiency.
Source and External Links
GENERAL AUDIT MANUAL - A detailed manual providing current audit policies, procedures, and guidelines, emphasizing audit documentation, interviews, exit procedures, and the creation of final workpaper files to support assessments.
Audit Manual - Chapter 1 Introduction - CDTFA - A comprehensive guide introducing audit policies and standards, clarifying auditor competencies, confidentiality, taxpayer rights, and procedures for conducting audits within CDTFA.
Audit Manual - University of Illinois - Covers internal audit policies, planning, risk assessment, communication protocols, quality assurance, and internal assessments for continuous improvement of audit processes.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com